Abstract
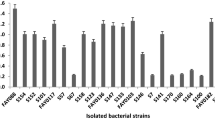
Seventeen bacterial isolates were screened for their cellulase activity by carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) plate assay. The bacterial strain K1 showed the largest depolymerized region in CMC plate assay and was further studied for quantitative cellulase activity. On the basis of 16S rDNA sequence analysis, the strain K1 was found to be Bacillus sp. This strain produced the maximum CMCase at pH 6 and 50 °C in the presence of peptone (1 %) as a source of nitrogen. The CMCase activity was stimulated by Ca2+ (2 mM) by 20 % over the control. The CMCase activity of this Bacillus sp. K1 was highly induced when lactose was used as a source of carbon during fermentation.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mussatto, S. I., Dragone, G., Guimaraes, P. M., Silva, J. P., Carneiro, L. M., Roberto, I. C., Vicente, A., Domingues, L., & Teixeira, J. A. (2010). Technological trends, global market, and challenges of bio-ethanol production. Biotechnology Advances, 28, 817–830.
Perlack, R. D., Wright, L. L., Turhollow, A. F., Graham, R. L., Stokes, B. J., and Erbach, D. C. (2005). Biomass as feedstock for a bioenergy and bioproducts industry: the technical feasibility of a billion-ton annual supply. DTIC Document
Zambare, V. P., Bhalla, A., Muthukumarappan, K., Sani, R. K., & Christopher, L. P. (2011). Bioprocessing of agricultural residues to ethanol utilizing a cellulolytic extremophile. Extremophiles, 15, 611–618.
Lynd, L. R., Wyman, C. E., & Gerngross, T. U. (1999). Biocommodity engineering. Biotechnol Prog, 15, 777–793.
Demirbas, A. (2007). Progress and recent trends in biofuels. Progress in Energy and Combustion Science, 33, 1–18.
Kim, J., Yun, S., & Ounaies, Z. (2006). Discovery of cellulose as a smart material. Macromolecules, 39, 4202–4206.
Immanuel, G., Dhanusha, R., Prema, P., & Palavesam, A. (2006). Effect of different growth parameters on endoglucanase enzyme activity by bacteria isolated from coir retting effluents of estuarine environment. Int J Environ Sci Technol, 3, 25–34.
Saha, S., Roy, R. N., Sen, S. K., & Ray, A. K. (2006). Characterization of cellulase producing bacteria from the digestive tract of tilapia, Oreochromis mossambica (Peters) and grass carp, Ctenopharyngodon idella (Valenciennes). Aquaculture Research, 37, 380–388.
Perez, J., Munoz-Dorado, J., de la Rubia, T. D. L. R., & Martinez, J. (2002). Biodegradation and biological treatments of cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin: an overview. International Microbiology, 5, 53–63.
Nagendran, S., & Hallen-Adams, H. E. (2009). Reduced genomic potential for secreted plant cell-wall-degrading enzymes in the ectomycorrhizal fungus Amanita bisporigera, based on the secretome of Trichoderma reesei. Fungal Genetics and Biology, 46, 427–435.
Cherry, J. R., & Fidantsef, A. L. (2003). Directed evolution of industrial enzymes: an update. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 14, 438–443.
Vyas, S., & Lachke, A. (2003). Biodeinking of mixed office waste paper by alkaline active cellulases from alkalotolerant Fusarium sp. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 32, 236–245.
Doi, R. (2008). Cellulases of mesophilic microorganisms. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1125, 267.
Miller, G. L. (1959). Use of DNS reagent for the measurement of reducing sugar. Analytical Chemistry, 31, 426–428.
Laemmli, U. K. (1970). Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature, 227, 680–685.
Maki, M. L., Broere, M., Leung, K. T., & Qin, W. (2011). Characterization of some efficient cellulase producing bacteria isolated from paper mill sludges and organic fertilizers. Int J Biochem Mol Biol, 2, 146.
Gautam, S. P., Bundela, P. S., Pandey, A. K., Khan, J., Awasthi, M. K., & Sarsaiya, S. (2011). Optimization for the production of cellulase enzyme from municipal solid waste residue by two novel cellulolytic fungi. Biotechnology Research International, 1–8.
Shankar, T., & Isaiarasu, L. (2011). Cellulase production by Bacillus pumilus EWBCM1 under varying cultural conditions. Middle-East Journal of Scientific Research, 8, 40–45.
Amritkar, N., Kamat, M., & Lali, A. (2004). Expanded bed affinity purification of bacterial a-amylase and cellulase on composite substrate analogue-cellulose matrices. Process Biochemistry, 39, 565–570.
Sheng, P., Huang, S., Wang, Q., Wang, A., & Zhang, H. (2012). Isolation, screening, and optimization of the fermentation conditions of highly cellulolytic bacteria from the hindgut of Holotrichia parallela larvae (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 167, 270–284.
Dees, C., Ringleberg, D., Scott, T. C., & Phelps, T. (1994). Taxonomic characterization of the cellulose-degrading bacterium NCIB 10462. TN: Oak Ridge National Lab.
Guedon, E., Desvaux, M., & Petitdemange, H. (2002). Improvement of cellulolytic properties of Clostridium cellulolyticum by metabolic engineering. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 68, 53–58.
Priest, F. G. (1977). Extracellular enzyme synthesis in the genus Bacillus. Bacteriological Reviews, 41, 711.
Kang, S. W., Park, Y. S., Lee, J. S., Hong, S. I., & Kim, S. W. (2004). Production of cellulases and hemicellulases by Aspergillus niger KK2 from lignocellulosic biomass. Bioresource Technology, 91, 153–156.
Kotchoni, S. O., & Shonukan, O. O. (2002). Regulatory mutations affecting the synthesis of cellulase in Bacillus pumilus. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 18, 487–491.
Ariffin, H., Hassan, M. A., Shah, U. K. M., Abdullah, N., Ghazali, F. M., & Shirai, Y. (2008). Production of bacterial endoglucanase from pretreated oil palm empty fruit bunch by Bacillus pumilus EB3. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 106, 231–236.
Narasimha, G., Sridevi, A., Viswanath, B., & Reddy, R. (2006). Nutrient effects on production of cellulolytic enzymes by Aspergillus niger. African Journal of Biotechnology, 5, 472–476.
Kocher, G. S., Kalra, K. L., & Banta, G. (2008). Optimization of cellulase production by submerged fermentation of rice straw by Trichoderma harzianum Rut-C 8230. Internet J Microbiol, 5, 2.
Rastogi, G., Bhalla, A., Adhikari, A., Bischoff, K. M., Hughes, S. R., Christopher, L. P., & Sani, R. K. (2010). Characterization of thermostable cellulases produced by Bacillus and Geobacillus strains. Bioresource Technology, 101, 8798–8806.
Abdel-Fattah, Y. R., El-Helow, E. R., Ghanem, K. M., & Lotfy, W. A. (2007). Application of factorial designs for optimization of avicelase production by a thermophilic Geobacillus isolate. Research Journal of Microbiology, 2, 13–23.
Kim, B. K., Lee, B. H., Lee, Y. J., Jin, I. H., Chung, C. H., & Lee, J. W. (2009). Purification and characterization of carboxymethylcellulase isolated from a marine bacterium, Bacillus subtilis subsp. subtilis A-53. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 44, 411–416.
Ray, A. K., Bairagi, A., Ghosh, K. S., & Sen, S. K. (2007). Optimization of fermentation conditions for cellulase production by Bacillus subtilis CY5 and Bacillus circulans TP3 isolated from fish gut. Acta Ichthyologica et Piscatoria, 1, 47–53.
Robson, L. M., & Chambliss, G. H. (1989). Cellulases of bacterial origin. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 11, 626–644.
Mawadza, C., Hatti-Kaul, R., Zvauya, R., & Mattiasson, B. (2000). Purification and characterization of cellulases produced by two Bacillus strains. Journal of Biotechnology, 83, 177–187.
Sadhu, S., Ghosh, P. K., De, T. K., & Maiti, T. K. (2013). Optimization of cultural condition and synergistic effect of lactose with carboxymethyl cellulose on cellulase production by Bacillus sp. isolated from fecal matter of elephant (Elephas maximus). Adv Microbiol, 3, 280.
Sadhu, S., Ghosh, P. K., Aditya, G., & Maiti, T. K. (2014). Optimization and strain improvement by mutation for enhanced cellulase production by Bacillus sp. (MTCC10046) isolated from cow dung. J King Saud Univ Sci, 26, 323–332.
Lee, Y. J., Kim, B. K., Lee, B. H., Jo, K. I., Lee, N. K., Chung, C. H., Lee, Y. C., & Lee, J. W. (2008). Purification and characterization of cellulase produced by Bacillus amyoliquefaciens DL-3 utilizing rice hull. Bioresource Technology, 99, 378–386.
Fu, X., Liu, P., Lin, L., Hong, Y., Huang, X., Meng, X., & Liu, Z. (2010). A novel endoglucanase (Cel9P) from a marine bacterium Paenibacillus sp. BME-14. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 160, 1627–1636.
Mansfield, S. D., Saddler, J. N., & Gubitz, G. M. (1998). Characterization of endoglucanases from the brown rot fungi Gloeophyllum sepiarium and Gloeophyllum trabeum. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 23, 133–140.
Aygan, A. S. H. A., & Arikan, B. U. R. H. (2008). A new halo-alkaliphilic, thermostable endoglucanase from moderately halophilic Bacillus sp. C14 isolated from Van soda lake. Int J Agric Biol, 10, 369–374.
Yang, W., Meng, F., Peng, J., Han, P., Fang, F., Ma, L., & Cao, B. (2014). Isolation and identification of a cellulolytic bacterium from the Tibetan pig’s intestine and investigation of its cellulase production. Electronic Journal of Biotechnology, 17, 262–267.
Bairagi, A., Ray, A. K., Sarkar, G. K., & Sen, S. K. (2007). Optimization of fermentation conditions for cellulase production by Bacillus subtilis CY5 and Bacillus circulans TP3 isolated from fish gut. Acta Ichthyologica et Piscatoria, 37, 47–53.
Acharya, S., & Chaudhary, A. (2011). Effect of nutritional and environmental factors on cellulases activity by thermophilic bacteria isolated from hot spring. J Sci Ind Res, 70, 142–148.
Miyamoto, Y., Ooi, T., & Kinoshita, S. (2000). Production of lactobionic acid from whey by Pseudomonas sp. LS13-1. Biotechnology Letters, 22, 427–430.
Sadhu, S., Saha, P., Mayilraj, S., & Maiti, T. K. (2011). Lactose-enhanced cellulase production by Microbacterium sp. isolated from fecal matter of zebra (Equus zebra). Current Microbiology, 62, 1050–1055.
El-Hadi, A. A., El-Nour, S. A., Hammad, A., Kamel, Z., & Anwar, M. (2014). Optimization of cultural and nutritional conditions for carboxymethylcellulase production by Aspergillus hortai. J Radiat Res Appl Sci, 7, 23–28.
Karaffa, L., Fekete, E., Gamauf, C., Szentirmai, A., Kubicek, C. P., & Seiboth, B. (2006). d-Galactose induces cellulase gene expression in Hypocrea jecorina at low growth rates. Microbiology, 152, 1507–1514.
Bischoff, K. M., Rooney, A. P., Li, X. L., Liu, S., & Hughes, S. R. (2006). Purification and characterization of a family 5 endoglucanase from a moderately thermophilic strain of Bacillus licheniformis. Biotechnology Letters, 28, 1761–1765.
Hakamada, Y., Endo, K., Takizawa, S., Kobayashi, T., Shirai, T., Yamane, T., & Ito, S. (2002). Enzymatic properties, crystallization, and deduced amino acid sequence of an alkaline endoglucanase from Bacillus circulans. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj, 1570, 174–180.
Ozaki, K., & Ito, S. (1991). Purification and properties of an acid endo-1, 4- β -glucanase from Bacillus sp. KSM-330. Journal of General Microbiology, 137, 41–48.
Li, Y. H., Ding, M., Wang, J., Xu, G. J., & Zhao, F. (2006). A novel thermoacidophilic endoglucanase, Ba-EGA, from a new cellulose-degrading bacterium, Bacillus sp. AC-1. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 70, 430–436.
Christakopoulos, P., Hatzinikolaou, D. G., Fountoukidis, G., Kekos, D., Claeyssens, M., & Macris, B. J. (1999). Purification and mode of action of an alkali-resistant endo-1, 4- β-glucanase from Bacillus pumilus. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 364, 61–66.
Okoshi, H., Ozaki, K., Shikata, S., Oshino, K., Kawai, S., & Ito, S. (1990). Purification and characterization of multiple carboxymethyl cellulases from Bacillus sp. KSM-522. Agricultural and Biological Chemistry, 54, 83–89.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paudel, Y.P., Qin, W. Characterization of Novel Cellulase-producing Bacteria Isolated From Rotting Wood Samples. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 177, 1186–1198 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-015-1806-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-015-1806-9