Abstract
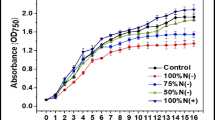
This study investigated the feasibility of lipid production of Chlorella sp. from waste materials. Lipid-extracted microalgal biomass residues (LMBRs) and molasses were hydrolyzed, and their hydrolysates were analyzed. Five different hydrolysate mixture ratios (w/w) of LMBRs/molasses (1/0, 1/1, 1/4, 1/9, and 0/1) were used to cultivate Chlorella sp. The results showed that carbohydrate and protein were the two main compounds in the LMBRs, and carbohydrate was the main compound in the molasses. The highest biomass concentration of 5.58 g/L, Y biomass/sugars of 0.59 g/g, lipid productivity of 335 mg/L/day, and Y lipids/sugars of 0.25 g/g were obtained at the hydrolysate mixture ratio of LMBRs/molasses of 1/4. High C/N ratio promoted the conversion of sugars into lipids. The lipids extracted from Chlorella sp. shared similar lipid profile of soybean oil and is therefore a potential viable biodiesel feedstock. These results showed that Chlorella sp. can utilize mixed sugars and amino acids from LMBRs and molasses to accumulate lipids efficiently, thus reducing the cost of microalgal biodiesel production and improving its economic viability.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rios, L. F., Klein, B. C., Luz, J. L. F., Fiho, R. M., & Wolf Maciel, M. R. (2015). Nitrogen starvation for lipid accumulation in the microalga species Desmodesmus sp. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 175, 469–476.
Jonker, J. G. G., & Faaij, A. P. C. (2013). Techno-economic assessment of micro-algae as feedstock for renewable bio-energy production. Applied Energy, 102, 461–475.
Sun, A., Davis, R., Starbuck, M., Ben-Amotz, A., Pate, R., & Pienkos, P. T. (2011). Comparative cost analysis of algal oil production for biofuels. Energy, 36, 5169–5179.
Quinn, J. C., & Davis, R. (2015). The potentials and challenges of algae based biofuels: a review of the techno-economic, life cycle, and resource assessment modeling. Bioresource Technology, 184, 444–452.
Liang, Y. N. (2013). Producing liquid transportation fuels from heterotrophic microalgae. Applied Energy, 104, 860–868.
Andrade, M. R., & Costa, J. A. V. (2007). Mixotrophic cultivation of microalga Spirulina platensis using molasses as organic substrate. Aquaculture, 264, 130–134.
Zhou, W. G., Chen, P., Min, M., Ma, X. C., Wang, J. H., Griffith, R., et al. (2014). Environment-enhancing algal biofuel production using wastewaters. Renewable & Sustainable Energy Reviews, 36, 256–269.
Ehimen, E. A., Connaughton, S., Sun, Z. F., & Carrington, G. C. (2009). Energy recovery from lipid extracted, transesterified and glycerol codigested microalgae biomass. GCB Bioenergy, 1, 371–381.
Ma, X. C., Zheng, H. L., Huang, H., Liu, Y. H., & Ruan, R. (2014). Effects of temperature and substrate concentration on lipid production by Chlorella vulgaris from enzymatic hydrolysates of lipid-extracted microalgal biomass residues (LMBRs). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 174, 1631–1650.
Zheng, H. L., Gao, Z., Yin, F. W., Ji, X. J., & Huang, H. (2012). Lipid production of Chlorella vulgaris from lipid-extracted microalgal biomass residues through two-step enzymatic hydrolysis. Bioresource Technology, 117, 1–6.
Ben-Amotz, A., Tornabene, T. G., & Thomas, W. H. (1985). Chemical profiles of selected species of microalgae with emphasis on lipids. Journal of Phycology, 21, 72–81.
Zor, T., & Selinger, Z. (1996). Linearization of the Bradford protein assay increases its sensitivity: theoretical and experimental studies. Analytical Chemistry, 236, 302–308.
Yan, L. S., Zhang, H. M., Chen, J. W., Lin, Z. X., Jin, Q., Jia, H. H., et al. (2009). Dilute sulfuric acid cycle spray flow-through pretreatment of corn stover for enhancement of sugar recovery. Bioresource Technology, 100(5), 1803–1808.
Spellmana, D., McEvoya, E., O’Cuinnb, G., & FitzGeralda, R. J. (2003). Proteinase and exopeptidase hydrolysis of whey protein: comparison of the TNBS, OPA and pH stat methods for quantification of degree of hydrolysis. International Dairy Journal, 13, 447–453.
Zheng, H. L., Yin, J. L., Gao, Z., Huang, H., Ji, X. J., & Dou, C. (2011). Disruption of Chlorella vulgaris cells for the release of biodiesel-producing lipids: a comparison of grinding, ultrasonication, bead milling, enzymatic lysis, and microwaves. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 164, 1215–1224.
Metchalfe, L. D., & Schmitz, A. A. (1961). The rapid preparation of fatty acid esters for gas chromatographic analysis. Analytical Chemistry, 33, 363–372.
Ren, L. J., Ji, X. J., Huang, H., Qu, L., Feng, Y., Tong, Q. Q., et al. (2010). Development of a stepwise aeration control strategy for efficient docosahexaenoic acid production by Schizochytrium sp. Applied Microbiology Biotechnology, 87, 1649–1656.
Duncan, D. B. (1955). Multiple range and multiple F tests. Biometrics, 11, 1–42.
Grima, E. M., Belarbi, E. H., Acién Fernández, F. G., Medinaa, A. R., & Chisti, Y. (2003). Recovery of microalgal biomass and metabolites: process options and economics. Biotechnology Advance, 20, 491–515.
Brown, M. R. (1991). The amino-acid and sugar composition of 16 species of microalgae used in mariculture. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 145, 79–99.
Harun, R., & Danquah, M. K. (2011). Enzymatic hydrolysis of microalgal biomass for bioethanol production. Chemical Engineering Journal, 168, 1079–1084.
Daroch, M., Geng, S., & Wang, G. Y. (2013). Recent advances in liquid biofuel production from algal feedstocks. Applied Energy, 102, 1371–1381.
Ye, Q., Li, X. M., Yan, M., Cao, H., Xu, L., Zhang, Y. Y., et al. (2010). High-level production of heterologous proteins using untreated cane molasses and corn steep liquor in Escherichia coli medium. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 87, 517–525.
Yeh, K. L., Chen, C. Y., & Chang, J. S. (2012). pH-stat photoheterotrophic cultivation of indigenous Chlorella vulgaris ESP-31 for biomass and lipid production using acetic acid as the carbon source. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 64, 1–7.
Jia, Z. C., Liu, Y., Daroch, M., Geng, S., & Cheng, G. J. (2014). Screening, growth medium optimization and heterotrophic cultivation of microalgae for biodiesel production. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 173, 1667–1679.
Silaban, A., Bai, R., Gutierrez-Wing, M. T., Negulescu, I. I., & Rusch, K. A. (2014). Effect of organic carbon, C:N ratio and light on the growth and lipid productivity of microalgae/cyanobacteria coculture. Engineering Life Science, 14, 47–56.
Zheng, Y. B., Yu, X. C., Li, T. T., Xiong, X. C., & Chen, S. L. (2014). Induction of D-xylose uptake and expression of NAD(P)H-linked xylose reductase and NADP+-linked xylitol dehydrogenase in the oleaginous microalga Chlorella sorokiniana. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 7, 125–132.
Hawkins, R. L. (1999). Utilization of xylose for growth by the eukaryotic alga, Chlorella. Current Microbiology, 38, 360–363.
Wang, W. R., Zhou, W. W., Liu, J., Li, Y. H., & Zhang, Y. K. (2013). Biodiesel production from hydrolyzate of Cyperus esculentus waste by Chlorella vulgaris. Bioresource Technology, 136, 24–29.
Hu, Q., Sommerfeld, M., Jarvis, E., Ghirardi, M., Posewitz, M., Seibert, M., et al. (2008). Microalgal triacylglycerols as feedstocks for biofuel production: perspectives and advances. Plant Journal, 54, 621–639.
Praveenkumar, R., Shameera, K., Mahalakshmi, G., Akbarsha, M. A., & Thajuddin, N. (2012). Influence of nutrient deprivations on lipid accumulation in a dominant indigenous microalga Chlorella sp., BUM11008: evaluation for biodiesel production. Biomass & Bioenergy, 37, 60–66.
Morales-Sánchez, D., Tinoco-Valencia, R., Kyndt, J., & Martinez, A. (2013). Heterotrophic growth of Neochloris oleoabundans using glucose as a carbon source. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 6, 100–111.
Serio, M. D., Ledda, M., Cozzolino, M., Minutillo, G., Tesser, R., & Santacesaria, E. (2006). Transesterification of soybean oil to biodiesel by using heterogeneous basic catalysts. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 45, 3009–3014.
Avinash, A., Subramaniam, D., & Murugesan, A. (2014). Bio-diesel—A global scenario. Renewable & Sustainable Energy Reviews, 29, 517–527.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Research Program of Sate Key Laboratory of Food Science and Technology, Nanchang University, China (Grant No. SKLF-ZZB-201312), the Major State Basic Research Development Program of China (973 Project) (Grant No. 2011CB200906), the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (863 Project) (Grant Nos. 2012AA021704, 2012AA021205, and 2014AA022004), China International Cooperation Projects (Grant No. 2014DFA61040), the Science and Technology Project of Jiangxi Provincial Department of Science and Technology (Grant Nos. 20142BBF60007 and 2013AFC30044), and National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 21266022).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Hongli Zheng and Xiaochen Ma contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, H., Ma, X., Gao, Z. et al. Lipid Production of Heterotrophic Chlorella sp. from Hydrolysate Mixtures of Lipid-Extracted Microalgal Biomass Residues and Molasses. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 177, 662–674 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-015-1770-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-015-1770-4