Abstract
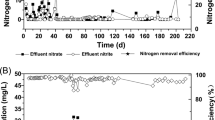
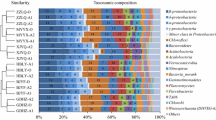
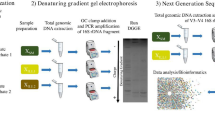
Denitrifying phosphorus removal is an attractive wastewater treatment process due to its reduced carbon source demand and sludge minimization potential. In the present study, the metagenome of denitrifying phosphorus removal sludge from a lab-scale anaerobic–anoxic SBR was generated by Illumina sequencing to study the microbial community. Compared with the aerobic phosphorus removal sludge, the denitrifying phosphorus removal sludge demonstrated quite similar microbial community profile and microbial diversity with sludge from Aalborg East EBPR WWTP. Proteobacteria was the most dominant phylum; within Proteobacteria, β-Proteobacteria was the most dominant class, followed by α-, γ-, δ-, and ε-Proteobacteria. The genes involved in phosphate metabolism and biofilm formation reflected the selective pressure of the phosphorus removal process. Moreover, ppk sequence from DPAO was outside the Accumulibacter clusters, which suggested different core phosphorus removal bacteria in denitrifying and aerobic phosphorus removal systems. In a summary, putative DPAO might be a novel genus that is closely related between Accumulibacter and Dechloromonas within Rhodocyclus. The microbial community and metabolic profiles achieved in this study will eventually help to improve the understanding of key microorganisms and the entire community in order to improve the phosphorus removal efficiency of EBPR processes.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Broughton, A., Pratt, S., & Shilton, A. (2008). Enhanced biological phosphorus removal for high-strength wastewater with a low rbCOD:P ratio. Bioresource Technology, 99, 1236–1241.
Oehmen, A., Lemos, P. C., Carvalho, G., Yuan, Z. G., Keller, J., Blackall, L. L., & Reis, M. (2007). Advances in enhanced biological phosphorus removal: from micro to macro scale. Water Research, 41, 2271–2300.
Painting, S. J., Devlin, M. J., Malcolm, S. J., et al. (2007). Assessing the impact of nutrient enrichment in estuaries: susceptibility to eutrophication. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 55, 74–90.
Seviour, R. J., Mino, T., & Onuki, M. (2003). The microbiology of biological phosphorus removal in activated sludge systems. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 27, 99–127.
Ahn, J., Daidou, T., Tsuneda, S., & Hirata, A. (2002). Characterization of denitrifying phosphate-accumulating organisms cultivated under different electron acceptor conditions using polymerase chain reaction-denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis assay. Water Research, 36, 403–412.
Vargas, M., Guisasola, A., Artigues, A., Casas, C., & Baeza, J. A. (2011). Comparison of a nitrite-based anaerobic–anoxic EBPR system with propionate or acetate as electron donors. Process Biochemistry, 46, 714–720.
Zhou, S. Q., Zhang, X. J., & Feng, L. Y. (2010). Effect of different types of electron acceptors on the anoxic phosphorus uptake activity of denitrifying phosphorus removing bacteria. Bioresource Technology, 101, 1603–1610.
Kapagiannidis, A. G., Zafiriadis, I., & Aivasidis, A. (2009). Comparison between UCT type and DPAO biomass phosphorus removal efficiency under aerobic and anoxic conditions. Water Science Technology, 60, 2695–2703.
Kuba, T., Smolders, G., Van Loosdrecht, M., & Heijnen, J. J. (1993). Biological phosphorus removal from waste-water by anaerobic–anoxic sequencing batch reactor. Water Science Technology, 27, 241–252.
Guerrero, J., Taya, C., Guisasola, A., & Baeza, J. A. (2012). Understanding the detrimental effect of nitrate presence on EBPR systems: effect of the plant configuration. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, 87, 1508–1511.
Hongbo, L., Liping, S., & Siqing, X. (2008). An efficient DPB utilization process: the modified A(2)N process. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 38, 158–163.
Ostgaard, K., Christensson, M., Lie, E., Jonsson, K., & Welander, T. (1997). Anoxic biological phosphorus removal in a full-scale UCT process. Water Research, 31, 2719–2726.
Sunagawa, S., Mende, D. R., Zeller, G., et al. (2013). Metagenomic species profiling using universal phylogenetic marker genes. Nature Methods, 10, 1196–1199.
Faust, K., & Raes, J. (2012). Microbial interactions: from networks to models. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 10, 538–550.
Shendure, J., & Ji, H. L. (2008). Next-generation DNA sequencing. Nature Biotechnology, 26, 1135–1145.
Qin, J. J., Li, R. Q., Raes, J., et al. (2010). A human gut microbial gene catalogue established by metagenomic sequencing. Nature, 464, 59–70.
Hess, M., Sczyrba, A., Egan, R., et al. (2011). Metagenomic discovery of biomass-degrading genes and genomes from cow rumen. Science, 331, 463–467.
Gilbert, J. A., Field, D., Huang, Y., Edwards, R., Li, W. Z., Gilna, P., & Joint, I. (2008). Detection of large numbers of novel sequences in the metatranscriptomes of complex marine microbial communities. PLoS One, 3, e3042.
Urich, T., Lanzen, A., Qi, J., Huson, D. H., Schleper, C., & Schuster, S. C. (2008). Simultaneous assessment of soil microbial community structure and function through analysis of the meta-transcriptome. PLoS One, 3, e2527.
Martin, H. G., Ivanova, N., Kunin, V., et al. (2006). Metagenomic analysis of two enhanced biological phosphorus removal (EBPR) sludge communities. Nature Biotechnology, 24, 1263–1269.
Albertsen, M., Hansen, L., Saunders, A. M., Nielsen, P. H., & Nielsen, K. L. (2012). A metagenome of a full-scale microbial community carrying out enhanced biological phosphorus removal. ISME Journal, 6, 1094–1106.
Patel, P. V., Gianoulis, T. A., Bjornson, R. D., Yip, K. Y., Engelman, D. M., & Gerstein, M. B. (2010). Analysis of membrane proteins in metagenomics: networks of correlated environmental features and protein families. Genome Research, 20, 960–971.
Sanapareddy, N., Hamp, T. J., Gonzalez, L. C., Hilger, H. A., Fodor, A. A., & Clinton, S. M. (2009). Molecular diversity of a North Carolina wastewater treatment plant as revealed by pyrosequencing. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 75, 1688–1696.
Lv, X. M., Shao, M. F., Li, C. L., Li, J., Gao, X. L., & Sun, F. Y. (2014). A comparative study of bacterial community in denitrifying and traditional enhanced biological phosphorous removal processes. Microbes and Environments, 29, 261–268.
Meyer, F., Paarmann, D., D'Souza, M., et al. (2008). The metagenomics RAST server—a public resource for the automatic phylogenetic and functional analysis of metagenomes. BMC Bioinformatics, 9, 386.
Dinsdale, E. A., Edwards, R. A., Hall, D., et al. (2008). Functional metagenomic profiling of nine biomes. Nature, 455, 830.
Xia, S. Q., Duan, L., Song, Y. H., et al. (2010). Bacterial community structure in geographically distributed biological wastewater treatment reactors. Environmental Science and Technology, 44, 7391–7396.
Yu, K., & Zhang, T. (2012). Metagenomic and metatranscriptomic analysis of microbial community structure and gene expression of activated sludge. PLoS One, 7, e38183.
Pope, P. B., Totsika, M., de Carcer, D. A., Schembri, M. A., & Morrison, M. (2011). Muramidases found in the foregut microbiome of the Tammar wallaby can direct cell aggregation and biofilm formation. ISME Journal, 5, 341–350.
Barr, J. J., Slater, F. R., Fukushima, T., & Bond, P. L. (2010). Evidence for bacteriophage activity causing community and performance changes in a phosphorus-removal activated sludge. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 74, 631–642.
Kunin, V., He, S., Warnecke, F., et al. (2008). A bacterial metapopulation adapts locally to phage predation despite global dispersal. Genome Research, 18, 293–297.
McMahon, K. D., Dojka, M. A., Pace, N. R., Jenkins, D., & Keasling, J. D. (2002). Polyphosphate kinase from activated sludge performing enhanced biological phosphorus removal. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 68, 4971–4978.
He, S., Gall, D. L., & McMahon, K. D. (2007). “Candidatus Accumulibacter” population structure in enhanced biological phosphorus removal sludges as revealed by polyphosphate kinase genes. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 73, 5865–5874.
McMahon, K. D., Yilmaz, S., He, S. M., Gall, D. L., Jenkins, D., & Keasling, J. D. (2007). Polyphosphate kinase genes from full-scale activated sludge plants. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 77, 167–173.
Peterson, S. B., Warnecke, F., Madejska, J., McMahon, K. D., & Hugenholtz, P. (2008). Environmental distribution and population biology of Candidatus Accumulibacter., a primary agent of biological phosphorus removal. Environmental Microbiology, 10, 2692–2703.
Kim, J. M., Lee, H. J., Lee, D. S., & Jeon, C. O. (2013). Characterization of the denitrification-associated phosphorus uptake properties of “Candidatus Accumulibacter phosphatis” clades in sludge subjected to enhanced biological phosphorus removal. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 79, 969–1979.
Kong, Y. H., Xia, Y., Nielsen, J. L., & Nielsen, P. H. (2007). Structure and function of the microbial community in a full-scale enhanced biological phosphorus removal plant. Microbiology-SGM, 153, 4061–4073.
Zilles, J. L., Peccia, J., Kim, M. W., Hung, C. H., & Noguera, D. R. (2002). Involvement of Rhodocyclus-related organisms in phosphorus removal in full-scale wastewater treatment plants. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 68, 2763–2769.
Acknowledgments
The author would like to acknowledge the financial support of the China Major Science and Technology Program for Water Pollution Control and Treatment (2012ZX07313001), Shenzhen Basic Research Project (JC201105160582A) and Natural Science Foundation of China (31200104).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Table S1
Metagenomes of wastewater treatment unrelated sludge samples (DOCX 16 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lv, XM., Shao, MF., Li, J. et al. Metagenomic Analysis of the Sludge Microbial Community in a Lab-Scale Denitrifying Phosphorus Removal Reactor. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 175, 3258–3270 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-015-1491-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-015-1491-8