Abstract
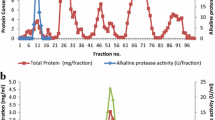
A novel alkaline protease was purified from Pseudomonas aeruginosa HY1215 using ammonium sulfate, DEAE-Sepharose and Sephacryl S-200 gel filtration chromatographic techniques. The protease had a relative molecular weight of 32.8 KDa by SDS-PAGE, and the optimal temperature and pH for excellent stability and activity were determined as 25 °C and 10.0, respectively. Within the pH range of 7.0–11.0, the protease had a good stability, which could retain more than 80 % of its original activity; in the temperature range of 15–35 °C, the protease had a higher activity, and its activity at 20 °C could amount to 85 % of the maximum activity at 25 °C. Besides, the enzyme activity showed a valuable stability towards several commercially available surfactants (Tween-80, Tween-40, and Triton X-100) and bleaches (H2O2) even when their concentrations ranged up to 2.0 and 1.6 %.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ponnambalam, S., Neelamegam, A., Ayyappan, S., & Thangavel, B. (2012). Biologia, 67(4), 629–635.
Anwar, A., & Mohammed, S. (1998). Bioresource Technology, 64, 139–144.
Erikson, N. (1996). Industrial enzymology. 2nd. The Macmillan Press Ltd. London.
Gupta, R., Beg, Q. K., & Lorenz, P. (2002). Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 59, 15–32.
Zhu, H. Y., Tian, Y., Hou, Y. H., & Wang, T. H. (2009). Molecular Biology Reports, 36(8), 2169–2174.
Wang, F., Hao, J. H., Yang, C. Y., & Sun, M. (2010). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 162(5), 1497–1505.
Iram, S., Parvaiz, H. Q., & Shabir, A. R. (2012). India. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 28(3), 1071–1079.
Lowry, O. H., Rosebrough, N. J., Farr, A. L., & Randall, R. J. (1951). Journal of Biological Chemistry, 193, 265–275.
Fogarty, W. M., Griffin, P. J., & Joyce, A. M. (1974). Process Biochemistry, 9, 27–29.
Stephane, D., Georges, F., Emmanuel, N., & Charles, G. (1994). Journal of Biological Chemistry, 26, 17448–17453.
Samal, B. B., Karan, B., Parker, C., & Stabinsky, Y. (1991). Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 13, 66–70.
Kasana, R. C., & Yadav, S. K. (2007). Current Microbiology, 54, 224–229.
Kumar, C. G., Tiwari, M. P., & Jany, K. D. (1999). Process Biochemistry, 34, 441–449.
Steel, D. B., Fiske, M. J., Steele, B. P., & Kelley, V. C. (1992). Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 14, 358–360.
Banerje, U. C., Sani, R. K., & Azmi, W. (1999). Process Biochemistry, 35, 213–219.
Beg, K. B., Sahai, V., & Gupta, R. (2003). Process Biochemistry, 39, 2003–2209.
Kumar, D., & Bhalla, T. C. (2004). Indian Journal of Experimental Biology, 42, 515–521.
Miyaji, T., Otta, Y., & Shibata, T. (2005). Letters in Applied Microbiology, 41, 253–257.
Takami, H., Akiba, T., & Horikoshi, K. (1989). Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 30, 120–124.
Papagianni, M., & Sergelidis, D. (2014). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 172, 3926–3938.
Niyonzima, F. N., & More, S. (2014). Preparative Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 44(7), 738–759.
Ghareib, M., Fawzi, E. M., & Aldossary, N. A. (2014). Annals of Microbiology, 64(2), 859–867.
Raval, V. H., Pillai, S., Rawal, C. M., & Singh, S. P. (2014). Process Biochemistry, 49(6), 955–962.
Oberoi, R., Beg, Q. K., & Puri, S. (2001). World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 17, 493–497.
Saeki, K., Hitomi, J., Okuda, M., & Hatada, Y. (2002). Extremophiles, 6, 65–72.
Rao, M. B., Tanksale, A. M., Ghatge, M. S., & Deshpande, V. V. (1998). Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews, 62, 597–635.
Kulakova, L., Galkin, A., Nakayama, T., Nishino, T., & Esaki, N. (2003). Journal of Molecular Catalysis B-Enzyme, 22, 113–117.
Acknowledgments
This research work has been supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41376175) and Qingdao Municipal Science and Technology Plan Project (14-2-4-11-jch).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hao, JH., Sun, M. Purification and Characterization of a Cold Alkaline Protease from a Psychrophilic Pseudomonas aeruginosa HY1215. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 175, 715–722 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-014-1315-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-014-1315-2