Abstract
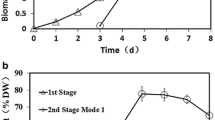
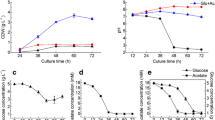
Though less attention has been paid to microalgae as a feedstock for bioethanol production, many microalgae seem to have this potential since they contain no lignin, minor hemicellulose, and abundant carbohydrate. The objective of this study was to investigate the effect of nitrogen starvation on carbohydrate and starch accumulation in green microalga Chlorella zofingiensis and assess the feasibility of using this microalga as a bioethanol feedstock. The results showed that the specific growth rate under nitrogen starvation (0.48 day−1) was much lower than that under nitrogen repletion (1.02 day−1). However, nitrogen starvation quickly induced the accumulation of carbohydrate, especially starch. After merely 1 day of nitrogen starvation, carbohydrate and starch increased 37 % and 4.7-fold, respectively. The highest carbohydrate content reached 66.9 % of dry weight (DW), and 66.7 % of this was starch. In order to obtain enough carbohydrate productivities for bioethanol production, two-stage cultivation strategy was implemented and found to be effective for enhancing biomass, carbohydrate, and starch simultaneously. The optimal biomass, carbohydrate, and starch productivities of C. zofingiensis were obtained after 5 days of cultivation, and their values were 699, 407, and 268 mg L−1 day−1, respectively.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dragone, G., Fernandes, B. D., Abreu, A. P., Vicente, A. A., & Teixeira, J. A. (2011). Nutrient limitation as a strategy for increasing starch accumulation in microalgae. Applied Energy, 88(10), 3331–3335.
Doan, Q. C., Moheimani, N. R., Mastrangelo, A. J., & Lewis, D. M. (2012). Microalgal biomass for bioethanol fermentation: implications for hypersaline systems with an industrial focus. Biomass and Bioenergy, 46, 79–88.
Sun, Y., & Cheng, J. Y. (2002). Hydrolysis of lignocellulosic materials for ethanol production: a review. Bioresource Technology, 83, 1–11.
Chen, C. Y., Zhao, X. Q., Yen, H. W., Ho, S. H., Cheng, C. L., Lee, D. J., Bai, F. W., & Chang, J. S. (2013). Microalgae-based carbohydrates for biofuel production. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 78, 1–10.
Hu, Q., Sommerfeld, M., Jarvis, E., Ghirardi, M., Posewitz, M., Seibert, M., & Darzins, A. (2008). Microalgal triacylglycerols as feedstocks for biofuel production: perspectives and advances. Plant Journal, 54(4), 621–639.
Wijffels, R. H., & Barbosa, M. J. (2010). An outlook on microalgal biofuels. Science, 329(5993), 796–799.
Ho, S. H., Huang, S. W., Chen, C. Y., Hasunuma, T., Kondo, A., & Chang, J. S. (2013). Characterization and optimization of carbohydrate production from an indigenous microalga Chlorella vulgaris FSP-E. Bioresource Technology, 135, 157–165.
Markou, G., Angelidaki, I., & Georgakakis, D. (2012). Microalgal carbohydrates: an overview of the factors influencing carbohydrates production, and of main bioconversion technologies for production of biofuels. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 96(3), 631–645.
Choix, F. J., de Bashan, L. E., & Bashan, Y. (2012). Enhanced accumulation of starch and total carbohydrates in alginate-immobilized Chlorella spp. induced by Azospirillum brasilense: I. Autotrophic conditions. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 51(5), 294–299.
Dubois, M., Gilles, K. A., Hamilton, J. K., Rebers, P., & Smith, F. (1956). Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Analytical Chemistry, 28(3), 350–356.
Branyikova, I., Marsalkova, B., Doucha, J., Branyik, T., Bisova, K., Zachleder, V., & Vitova, M. (2011). Microalgae-novel highly efficient starch producers. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 108(4), 766–776.
Recht, L., Zarka, A., & Boussiba, S. (2012). Patterns of carbohydrate and fatty acid changes under nitrogen starvation in the microalgae Haematococcus pluvialis and Nannochloropsis sp. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 94(6), 1495–1503.
Lv, J. M., Cheng, L. H., Xu, X. H., Zhang, L., & Chen, H. L. (2010). Enhanced lipid production of Chlorella vulgaris by adjustment of cultivation conditions. Bioresource Technology, 101, 6797–6804.
Wang, L., Li, Y. G., Sommerfeld, M., & Hu, Q. (2013). A flexible culture process for production of the green microalga Scenedesmus dimorphus rich in protein, carbohydrate or lipid. Bioresource Technology, 129, 289–295.
González-Fernández, C., & Ballesteros, M. (2012). Linking microalgae and cyanobacteria culture conditions and key-enzymes for carbohydrate accumulation. Biotechnology Advances, 30(6), 1655–1661.
Roessler, P. G. (1987). Udpglucose pyrophosphorylase activity in the diatom Cyclotella cryptica—pathway of chrysolaminarin biosynthesis. Journal of Phycology, 23(3), 494–498.
Yao, C., Ai, J., Cao, X., Xue, S., & Zhang, W. (2012). Enhancing starch production of a marine green microalga Tetraselmis subcordiformis through nutrient limitation. Bioresource Technology, 118, 438–444.
Fan, J. L., Yan, C. S., Andre, C., Shanklin, J., Schwender, J., & Xu, C. C. (2012). Oil accumulation is controlled by carbon precursor supply for fatty acid synthesis in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant and Cell Physiology, 53(8), 1380–1390.
Zhu, S., Huang, W., Xu, J., Wang, Z., Xu, J., & Yuan, Z. (2014). Metabolic changes of starch and lipid triggered by nitrogen starvation in the microalga Chlorella zofingiensis. Bioresource Technology, 152, 292–298.
Li, Y. T., Han, D. X., Sommerfeld, M., & Hu, Q. (2011). Photosynthetic carbon partitioning and lipid production in the oleaginous microalga Pseudochlorococcum sp. (Chlorophyceae) under nitrogen-limited conditions. Bioresource Technology, 102, 123–129.
Wan, L. L., Han, J., Sang, M., Li, A. F., Wu, H., Yin, S. J., & Zhang, C. W. (2012). De novo transcriptomic analysis of an oleaginous microalga: pathway description and gene discovery for production of next-generation biofuels. Plos One, 7, e35142.
Foy, R. H., & Smith, R. V. (1980). The role of carbohydrate accumulation in the growth of planktonic Oscillatoria species. British Phycological Journal, 15(2), 139–150.
Ballicora, M., Iglesias, A., & Preiss, J. (2004). ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase: a regulatory enzyme for plant starch synthesis. Photosynthesis Research, 79(1), 1–24.
Rodolfi, L., Zittelli, G. C., Bassi, N., Padovani, G., Biondi, N., Bonini, G., & Tredici, M. R. (2009). Microalgae for oil: strain selection, induction of lipid synthesis and outdoor mass cultivation in a low-cost photobioreactor. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 102(1), 100–112.
Ho, S. H., Chen, W. M., & Chang, J. S. (2010). Scenedesmus obliquus CNW-N as a potential candidate for CO2 mitigation and biodiesel production. Bioresource Technology, 101, 8725–8730.
Han, D. X., Li, Y. T., & Hu, Q. (2013). Astaxanthin in microalgae: pathways, functions and biotechnological implications. Algae, 28(2), 131–147.
Ho, S. H., Li, P. J., Liu, C. C., & Chang, J. S. (2013). Bioprocess development on microalgae-based CO2 fixation and bioethanol production using Scenedesmus obliquus CNW-N. Bioresource Technology, 145, 142–149.
Griffiths, M. J., & Harrison, S. T. L. (2009). Lipid productivity as a key characteristic for choosing algal species for biodiesel production. Journal of Applied Phycology, 21(5), 493–507.
Ho, S. H., Chen, C. Y., & Chang, J. S. (2012). Effect of light intensity and nitrogen starvation on CO2 fixation and lipid/carbohydrate production of an indigenous microalga Scenedesmus obliquus CNW-N. Bioresource Technology, 113, 244–252.
Yao, C. H., Ai, J. N., Cao, X. P., & Xue, S. (2013). Characterization of cell growth and starch production in the marine green microalga Tetraselmis subcordiformis under extracellular phosphorus-deprived and sequentially phosphorus-replete conditions. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 97(13), 6099–6110.
Sassano, C. E. N., Gioielli, L. A., Ferreira, L. S., Rodrigues, M. S., Sato, S., Converti, A., & Carvalho, J. C. M. (2010). Evaluation of the composition of continuously-cultivated Arthrospira (Spirulina) platensis using ammonium chloride as nitrogen source. Biomass and Bioenergy, 34(12), 1732–1738.
De Philippis, R., Sili, C., & Vincenzini, M. (1992). Glycogen and poly-β-hydroxybutyrate synthesis in Spirulina maxima. Journal of General Microbiology, 138(8), 1623–1628.
Acknowledgments
This research was financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31100189), the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program) (2011CB200905), the 12th Five Year Support Plan of the Ministry of Science and Technology, China (2011BAD14B03), National High-tech R&D Program (2013AA065803), and the Scientific Research Foundation for the Returned Overseas Chinese Scholars, State Education Ministry.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, S., Wang, Y., Huang, W. et al. Enhanced Accumulation of Carbohydrate and Starch in Chlorella zofingiensis Induced by Nitrogen Starvation. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 174, 2435–2445 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-014-1183-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-014-1183-9