Abstract
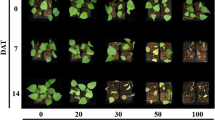
Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) is a fast-growing and high biomass producing plant species, which has been traditionally grown as multiple-use crop and recently considered as an energy crop. In order to screen accessions that can be cultivated in cadmium (Cd)-contaminated soils for biodiesel production, the ability of Cd tolerance and bioaccumulation of 18 hemp cultivars or ecotypes were evaluated in pot experiment under 25 mg Cd kg−1 (dry weight, DW) soil condition, in terms of plant growth, pigment contents, chlorophyll fluorescence, and Cd accumulation at 45 days after seedling emergence. Results showed that seedlings of all cultivars, except USO-31, Shenyang and Shengmu, could grow quite well under 25 mg Cd kg−1 (DW) soil condition. Among them, Yunma 1, Yunma 2, Yunma 3, Yunma 4, Qujing, Longxi, Lu'an, Xingtai, and Shuyang showed great biomass (>0.5 g plant−1), high tolerance factors (68.6–92.3%), and little reduction of pigment content and chlorophyll fluorescence under 25 mg Cd kg−1 (DW) soil stress, indicating these cultivars had a strong tolerance to Cd stress and could be cultivated in Cd-contaminated soils. Cultivars Longxi, Lu'an, Xingtai, Yunma 2, Yunma 3, Yunma 4, and Qujing exhibited higher Cd concentrations and total Cd in shoots. These cultivars, therefore, are good candidates for the implementation of the new strategy of cultivating biodiesel crops for phytoremediation of Cd-contaminated soils.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yang, X. E., Long, X. X., Ye, H. B., He, Z. L., Calvert, D. V., & Stoffella, P. J. (2004). Cadmium tolerance and hyperaccumulation in a new Zn-hyperaccumulating plant species (Sedum alfredii Hance). Plant and Soil, 259, 181–189.
Shi, G., Cai, Q., Liu, C., & Wu, L. (2010). Silicon alleviates cadmium toxicity in peanut plants in relation to cadmium distribution and stimulation of antioxidative enzymes. Plant Growth Regulation, 61, 45–52.
Pinto, A. P., Mota, A. M., De Varennes, A., & Pinto, F. C. (2004). Influence of organic matter on the uptake of cadmium, zinc, copper and iron by sorghum plants. Science of the Total Environment, 326, 239–247.
Liu, W., Zhou, Q., An, J., Sun, Y., & Liu, R. (2010). Variations in cadmium accumulation among Chinese cabbage cultivars and screening for Cd-safe cultivars. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 173, 737–743.
Pulford, I. D., & Watson, C. (2003). Phytoremediation of heavy metal-contaminated land by trees-a review. Environment International, 29, 529–540.
Linger, P., Müssig, J., Fischer, H., & Kobert, J. (2002). Industrial hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) growing on heavy metal contaminated soil: fibre quality and phytoremediation potential. Industrial Crops and Products, 16, 33–42.
McGrath, S. P., & Zhao, F. J. (2003). Phytoextraction of metals and metalloids from contaminated soils. Current Opinion In Biotechnology, 14, 277–282.
Peuke, A. D., & Rennenberg, H. (2005). Phytoremediation. EMBO Reports, 6, 497.
Shi, G., & Cai, Q. (2009). Cadmium tolerance and accumulation in eight potential energy crops. Biotechnology Advances, 27, 555–561.
Shi, G., & Cai, Q. (2010). Zinc tolerance and accumulation in eight oil crops. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 33, 982–997.
Ranalli, P. (2004). Current status and future scenarios of hemp breeding. Euphytica, 140, 121–131.
Elisa, B., Marsano, F., Cavaletto, M., & Berta, G. (2007). Copper stress in Cannabis sativa roots: morphological and proteomic analysis. Caryologia, 60, 96–101.
Citterio, S., Santagostino, A., Fumagalli, P., Prato, N., Ranalli, P., & Sgorbati, S. (2003). Heavy metal tolerance and accumulation of Cd, Cr and Ni by Cannabis sativa L. Plant and Soil, 256, 243–252.
Shi, G., Cai, Q., Liu, Q., & Wu, L. (2009). Salicylic acid-mediated alleviation of cadmium toxicity in hemp plants in relation to cadmium uptake, photosynthesis, and antioxidant enzymes. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum, 31, 969–977.
Linger, P., Ostwald, A., & Haensler, J. (2005). Cannabis sativa L. growing on heavy metal contaminated soil: growth, cadmium uptake and photosynthesis. Biologia Plantarum, 49, 567–576.
Casas, X. A., & Pons, J. R. I. (2005). Environmental analysis of the energy use of hemp–analysis of the comparative life cycle: diesel oil vs. hemp–diesel. International Journal of Agricultural Resources Governance and Ecology, 4, 133–139.
Grispen, V. M. J., Nelissen, H. J. M., & Verkleij, J. A. C. (2006). Phytoextraction with Brassica napus L.: a tool for sustainable management of heavy metal contaminated soils. Environmental Pollution, 144, 77–83.
Lichtenthaler, H. K. (1987). Chlorophylls and carotenoids: pigments of photosynthetic biomembranes. In S. P. Colowick & N. O. Kaplan (Eds.), Methods in enzymology (pp. 350–382). San Diego: Academic.
Ait Ali, N., Bernal, M. P., & Ater, M. (2002). Tolerance and bioaccumulation of copper in Phragmites australis and Zea mays. Plant and Soil, 239, 103–111.
Lima, A. I. G., Pereira, S. I. A., Figueira, E. M. A. P., Caldeira, G. C. N., & Caldeira, H. D. Q. M. (2006). Cadmium detoxification in roots of Pisum sativum seedlings: relationship between toxicity levels, thiol pool alterations and growth. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 55, 149–162.
Li, P., Wang, X., Allinson, G., Li, X., & Xiong, X. (2009). Risk assessment of heavy metals in soil previously irrigated with industrial wastewater in Shenyang, China. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 161, 516–521.
Zhou, W., & Qiu, B. (2005). Effects of cadmium hyperaccumulation on physiological characteristics of Sedum alfredii Hance (Crassulaceae). Plant Science, 169, 737–745.
Baryla, A., Carrier, P., Franck, F., Coulomb, C., Sahut, C., & Havaux, M. (2001). Leaf chlorosis in oilseed rape plants (Brassica napus) grown on cadmium-polluted soil: causes and consequences for photosynthesis and growth. Planta, 212, 696–709.
Küpper, H., Küpper, F., & Spiller, M. (1998). In situ detection of heavy metal substituted chlorophylls in water plants. Photosynthesis Research, 58, 123–133.
Küpper, H., Šetlik, I., Spiller, M., Küpper, F., & Prášil, O. (2002). Heavy metal-induced inhibition of photosynthesis: targets of in vivo heavy metal chlorophyll formation. Journal of Phycology, 38, 429–441.
Padmaja, K., Prasad, D. D. K., & Prasad, A. R. K. (1990). Inhibition of chlorophyll synthesis in Phaseolus vulgaris L. seedlings by cadmium acetate. Photosynthetica, 24, 399–405.
Böddi, B., Oravecz, A. R., & Lehoczki, E. (1995). Effect of cadmium on organization and photoreduction of protochlorphyllide in dark-grown leaves and etioplast inner membrane preparations of wheat. Photosynthetica, 31, 411–420.
Ouzounidou, G., Moustakas, M., & Eleftheriou, E. P. (1997). Physiological and ultrastructural effects of cadmium on wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) leaves. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 32, 154–160.
Maxwell, K., & Johnson, G. N. (2000). Chlorophyll fluorescence—a practical guide. Journal of Experimental Botany, 51, 659–668.
Mallick, N., & Mohn, F. H. (2003). Use of chlorophyll fluorescence in metal-stress research: a case study with the green microalga Scenedesmus. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 55, 64–69.
Shi, G., Liu, C., Cai, Q., Liu, Q., & Hou, C. (2010). Cadmium accumulation and tolerance of two safflower cultivars in relation to photosynthesis and antioxidantive enzymes. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 85, 256–263.
Baker, A. J. M. (1981). Accumulators and excluders-strategies in the response of plants to heavy metals. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 3, 643–654.
Baker, A. J. M., & Whiting, S. N. (2002). In search of the holy grail: a further step in understanding metal hyperaccumulation? The New Phytologist, 155, 1–4.
Grant, C. A., Clarke, J. M., Duguid, S., & Chaney, R. L. (2008). Selection and breeding of plant cultivars to minimize cadmium accumulation. Science of the Total Environment, 390, 301–310.
Zhu, Y., Yu, H., Wang, J., Fang, W., Yuan, J., & Yang, Z. (2007). Heavy metal accumulations of 24 asparagus bean cultivars grown in soil contaminated with Cd alone and with multiple metals (Cd, Pb, and Zn). Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 55, 1045–1052.
Yu, H., Wang, J., Fang, W., Yuan, J., & Yang, Z. (2006). Cadmium accumulation in different rice cultivars and screening for pollution-safe cultivars of rice. Science of the Total Environment, 370, 302–309.
Acknowledgments
Financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 40971296) and the Anhui Provincial Natural Science Foundation (No. 11040606M87) is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, G., Liu, C., Cui, M. et al. Cadmium Tolerance and Bioaccumulation of 18 Hemp Accessions. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 168, 163–173 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-011-9382-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-011-9382-0