Abstract
Background
Although the Ponseti method is accepted as the best choice for treatment of clubfoot, the treatment protocol is labor intensive and requires strict attention to details. Deviations in strict use of this method are likely responsible for the variations among centers in reported success rates.
Questions/purposes
We wished to determine (1) to what degree the Ponseti method was followed in terms of manipulation, casting, and percutaneous Achilles tenotomy, (2) whether there was variation in the bracing type and protocol used for relapse prevention, and (3) if the same criteria were used to diagnose and manage clubfoot relapse.
Methods
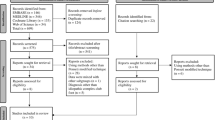
We conducted a systematic review of MEDLINE, EMBASETM, and the Cochrane Library. Studies were summarized according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses Statement. Five hundred ninety-one records were identified with 409 remaining after deduplication, in which 278 irrelevant studies and 22 review articles were excluded. Of the remaining 109 papers, 19 met our inclusion criteria. All 19 articles were therapeutic studies of the Ponseti method.
Results
The details of manipulation, casting, or percutaneous Achilles tenotomy of the Ponseti method were poorly described in 11 studies, whereas the main principles were not followed in three studies. In three studies, the brace type deviated significantly from that recommended, whereas in another three studies the bracing protocol in terms of hours of recommended use was not followed. Furthermore no unified criteria were used for judgment of compliance with brace use. The indication for recognition and management of relapse varied among studies and was different from the original description of the Ponseti method.
Conclusions
We found that the observed clinically important variation may have been the result of deviations from the details regarding manipulation, casting, percutaneous Achilles tenotomy, use of the bar-connected brace, and indication for relapse recognition and management recommended for the classic Ponseti approach to clubfoot management. We strongly recommend that clinicians follow the Ponseti method as it initially was described without deviation to optimize treatment outcomes.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelgawad AA, Lehman WB, van Bosse HJ, Scher DM, Sala DA. Treatment of idiopathic clubfoot using the Ponseti method: minimum 2-year follow-up. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2007;16:98–105.
Avilucea FR, Szalay EA, Bosch PP, Sweet KR, Schwend RM. Effect of cultural factors on outcome of Ponseti treatment of clubfeet in rural America. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91:530–540.
Balshem H, Helfand M, Schünemann HJ, Oxman AD, Kunz R, Brozek J, Vist GE, Falck-Ytter Y, Meerpohl J, Norris S, Guyatt GH. GRADE guidelines: 3. Rating the quality of evidence. J Clin Epidemiol. 2011;64:401–406.
Boehm S, Limpaphayom N, Alaee F, Sinclair MF, Dobbs MB. Early results of the Ponseti method for the treatment of clubfoot in distal arthrogryposis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008;90:1501–1507.
Bor N, Coplan JA, Herzenberg JE. Ponseti treatment for idiopathic clubfoot: minimum 5-year followup. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009;467:1263–1270.
Changulani M, Garg NK, Rajagopal TS, Bass A, Nayagam SN, Sampath J, Bruce CE. Treatment of idiopathic club foot using the Ponseti method: initial experience. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2006;88:1385–1387.
Clarke NM, Uglow MG, Valentine KM. Comparison of Ponseti versus surgical treatment in congenital talipes equinovarus. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2011;50:529–534.
Colburn M, Williams M. Evaluation of the treatment of idiopathic clubfoot by using the Ponseti method. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2003;42:259–267.
Cooper DM, Dietz FR. Treatment of idiopathic clubfoot: a thirty-year follow-up note. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1995;77:1477–1489.
Dobbs MB, Rudzki JR, Purcell DB, Walton T, Porter KR, Gurnett CA. Factors predictive of outcome after use of the Ponseti method for the treatment of idiopathic clubfeet. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004;86:22–27.
Diméglio A, Bensahel H, Souchet P, Mazeau P, Bonnet F. Classification of clubfoot. J Pediatr Orthop B. 1995;4:129–136.
Dyer PJ, Davis N. The role of the Pirani scoring system in the management of club foot by the Ponseti method. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2006;88:1082–1084.
Garg S, Dobbs MB. Use of the Ponseti method for recurrent clubfoot following posteromedial release. Indian J Orthop. 2008;42:68–72.
Gerlach DJ, Gurnett CA, Limpaphayom N, Alaee F, Zhang Z, Porter K, Kirchhofer M, Smyth MD, Dobbs MB. Early results of the Ponseti method for the treatment of clubfoot associated with myelomeningocele. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91:1350–1359.
Gray K, Pacey V, Gibbons P, Little D, Frost C, Burns J. Interventions for congenital talipes equinovarus (clubfoot). Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012;4:CD008602.
Gurnett CA, Boehm S, Connolly A, Reimschisel T, Dobbs MB. Impact of congenital talipes equinovarus etiology on treatment outcomes. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2008;50:498–502.
Haft GF, Walker CG, Crawford HA. Early clubfoot recurrence after use of the Ponseti method in a New Zealand population. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89:487–493.
Hemo Y, Segev E, Yavor A, Ovadia D, Wientroub S, Hayek S. The influence of brace type on the success rate of the Ponseti treatment protocol for idiopathic clubfoot. J Child Orthop. 2011;5:115–119.
Herzenberg JE, Radler C, Bor N. Ponseti versus traditional methods of casting for idiopathic clubfoot. J Pediatr Orthop. 2002;22:517–521.
Ippolito E, Farsetti P, Caterini R, Tudisco C. Long-term comparative results in patients with congenital clubfoot treated with two different protocols. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003;85:1286–1294.
Janicki JA, Wright JG, Weir S, Narayanan UG. A comparison of ankle foot orthoses with foot abduction orthoses to prevent recurrence following correction of idiopathic clubfoot by the Ponseti method. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2011;93:700–704.
Jowett CR, Morcuende JA, Ramachandran M. Management of congenital talipes equinovarus using the Ponseti method: a systematic review. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2011;93:1160–1164.
Khan SA, Kumar A. Ponseti’s manipulation in neglected clubfoot in children more than 7 years of age: a prospective evaluation of 25 feet with long-term follow-up. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2010;19:385–389.
Laaveg SJ, Ponseti IV. Long-term results of treatment of congenital club foot. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1980;62:23–31.
Lehman WB, Mohaideen A, Madan S, Scher DM, Van Bosse HJ, Iannacone M, Bazzi JS, Feldman DS. A method for the early evaluation of the Ponseti (Iowa) technique for the treatment of idiopathic clubfoot. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2003;12:133–140.
Lourenço AF, Morcuende JA. Correction of neglected idiopathic club foot by the Ponseti method. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2007;89:378–381.
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG; PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. BMJ. 2009;339:b2535
Morcuende JA, Dobbs MB, Frick SL. Results of the Ponseti method in patients with clubfoot associated with arthrogryposis. Iowa Orthop J. 2008;28:22–26.
Morcuende JA, Dolan LA, Dietz FR, Ponseti IV. Radical reduction in the rate of extensive corrective surgery for clubfoot using the Ponseti method. Pediatrics. 2004;113:376–380.
Niki H, Nakajima H, Hirano T, Okada H, Beppu M. Effect of Achilles tenotomy on congenital clubfoot-associated calf-muscle atrophy: an ultrasonographic study. J Orthop Sci. 2013;18:552–556.
Niki H, Nakajima H, Hirano T, Okada H, Beppu M. Ultrasonographic observation of the healing process in the gap after a Ponseti-type Achilles tenotomy for idiopathic congenital clubfoot at two-year follow-up. J Orthop Sci. 2013;18:70–75.
Nogueira MP, Ey Batlle AM, Alves CG. (2009) Is it possible to treat recurrent clubfoot with the Ponseti technique after posteromedial release?: a preliminary study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 467:1298–1305.
Nogueira MP, Farcetta M, Fox MH, Miller KK, Pereira TS, Morcuende JA. Treatment of congenital clubfoot with the Ponseti method: the parents’ perspective. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2013;22:583–588.
Panjavi B, Sharafatvaziri A, Zargarbashi RH, Mehrpour S. Use of the Ponseti method in the Iranian population. J Pediatr Orthop. 2012;32:e11–14.
Park SS, Kim SW, Jung BS, Lee HS, Kim JS. Selective soft-tissue release for recurrent or residual deformity after conservative treatment of idiopathic clubfoot. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2009;91:1526–1530.
Park SS, Lee HS, Han SH, Park JW, de Peralta MJ. Gastrocsoleus fascial release for correction of equinus deformity in residual or relapsed clubfoot. Foot Ankle Int. 2012;33:1075–1078.
Ponseti IV. Congenital Clubfoot: Fundamentals of Treatment. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press; 1996.
Ponseti IV. Relapsing clubfoot: causes, prevention, and treatment. Iowa Orthop J. 2002;22:55–56.
Ponseti IV, Smoley EN. The classic: congenital club foot: the results of treatment. 1963. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009;467:1133–1145.
Ponseti IV, Zhivkov M, Davis N, Sinclair M, Dobbs MB, Morcuende JA. Treatment of the complex idiopathic clubfoot. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006;451:171–176.
Porecha MM, Parmar DS, Chavda HR. Mid-term results of Ponseti method for the treatment of congenital idiopathic clubfoot: a study of 67 clubfeet with mean five year follow-up. J Orthop Surg Res. 2011;6:3.
Ramírez N, Flynn JM, Fernández S, Seda W, Macchiavelli RE. Orthosis noncompliance after the Ponseti method for the treatment of idiopathic clubfeet: a relevant problem that needs reevaluation. J Pediatr Orthop. 2011;31:710–715.
Richards BS, Faulks S, Rathjen KE, Karol LA, Johnston CE, Jones SA. A comparison of two nonoperative methods of idiopathic clubfoot correction: the Ponseti method and the French functional (physiotherapy) method. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008;90:2313–2321.
Sætersdal C, Fevang JM, Fosse L, Engesæter LB. Good results with the Ponseti method: a multicenter study of 162 clubfeet followed for 2–5 years. Acta Orthop. 2012;83:288–293.
Segev E, Keret D, Lokiec F, Yavor A, Wientroub S, Ezra E, Hayek S. Early experience with the Ponseti method for the treatment of congenital idiopathic clubfoot. Isr Med Assoc J. 2005;7:307–310.
Selmani E. Is Ponseti’s method superior to Kite’s for clubfoot treatment? Eur Orthop Traumatol. 2012;3:183–187.
Spiegel DA, Shrestha OP, Sitoula P, Rajbhandary T, Bijukachhe B, Banskota AK. Ponseti method for untreated idiopathic clubfeet in Nepalese patients from 1 to 6 years of age. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009;467:1164–1170.
Staheli L, ed. Clubfoot: Ponseti Management. 3rd ed. Global-HELP Publications. Available at: http://www.global-help.org/publications/books/help_cfponseti.pdf. Accessed July 22, 2013.
Steinman S, Richards BS, Faulks S, Kaipus K. A comparison of two nonoperative methods of idiopathic clubfoot correction: the Ponseti method and the French functional (physiotherapy) method. Surgical technique. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91 suppl 2):299–312.
Sud A, Tiwari A, Sharma D, Kapoor S. Ponseti’s vs Kite’s method in the treatment of clubfoot: a prospective randomised study. Int Orthop. 2008;32:409–413.
Thacker MM, Scher DM, Sala DA, van Bosse HJ, Feldman DS, Lehman WB. Use of the foot abduction orthosis following Ponseti casts: is it essential? J Pediatr Orthop. 2005;25:225–228.
Verma A, Mehtani A, Sural S, Maini L, Gautam VK, Basran SS, Arora S. Management of idiopathic clubfoot in toddlers by Ponseti’s method. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2012;21:79–84.
Zionts LE, Dietz FR. Bracing following correction of idiopathic clubfoot using the Ponseti method. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2010;18:486–493.
Zionts LE, Zhao G, Hitchcock K, Maewal J, Ebramzadeh E. Has the rate of extensive surgery to treat idiopathic clubfoot declined in the United States? J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010;92:882–889.
Acknowledgments
We thank David A. Spiegel MD and Monica P. Nogueira MD for their input in the discussion and communications which encouraged us to do this investigation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The institution of all the six authors has received, during the study period, funding from the Science Foundation of Shanghai Science and Technology Commission (11ZR1423900).
All ICMJE Conflict of Interest Forms for authors and Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research editors and board members are on file with the publication and can be viewed on request.
Each author certifies that his or her institution has approved the human protocol for this investigation, that all investigations were conducted in conformity with ethical principles of research, and that informed consent for participation in the study was obtained.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, D., Li, H., Zhao, L. et al. Results of Clubfoot Management Using the Ponseti Method: Do the Details Matter? A Systematic Review. Clin Orthop Relat Res 472, 1329–1336 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-014-3463-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-014-3463-7