Abstract
Our shared moral framework is negotiated as part of the social contract. Some elements of that framework are established (tell the truth under oath), but other elements lack an overlapping consensus (just when can an individual lie to protect his or her privacy?). The tidy bits of our accepted moral framework have been codified, becoming the subject of legal rather than ethical consideration. Those elements remaining in the realm of ethics seem fragmented and inconsistent.
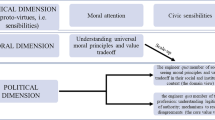
Yet, our engineering students will need to navigate the broken ground of this complex moral landscape. A minimalist approach would leave our students with formulated dogma—principles of right and wrong such as the National Society for Professional Engineers (NSPE) Code of Ethics for Engineers—but without any insight into the genesis of these principles. A slightly deeper, micro-ethics approach would teach our students to solve ethical problems by applying heuristics—giving our students a rational process to manipulate ethical dilemmas using the same principles simply referenced a priori by dogma. A macro-ethics approach—helping students to inductively construct a posteriori principles from case studies—goes beyond the simple statement or manipulation of principles, but falls short of linking personal moral principles to the larger, social context. Ultimately, it is this social context that requires both the application of ethical principles, and the negotiation of moral values—from an understanding of meta-ethics.
The approaches to engineering ethics instruction (dogma, heuristics, case studies, and meta-ethics) can be associated with stages of moral development. If we leave our students with only a dogmatic reaction to ethical dilemmas, they will be dependent on the ethical decisions of others (a denial of their fundamental potential for moral autonomy). Heuristics offers a tool to deal independently with moral questions, but a tool that too frequently reduces to casuistry when rigidly applied to “simplified” dilemmas. Case studies, while providing a context for engineering ethics, can encourage the premature analysis of specific moral conduct rather than the development of broad moral principles—stifling our students’ facility with meta-ethics. Clearly, if a moral sense is developmental, ethics instruction should lead our students from lower to higher stages of moral development.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
James, William (1907/1987), Pragmatism: A New Name for Some Old Ways of Thinking, In: William James: Writings 1902–1910, pp. 576.
Clement, John (1982). Students’ Preconceptions in Introductory Mechanics, American Journal of Physics 50 (1): 66–71.
diSessa, Andrea (1983). Phenomenology and the Evolution of Intuition, in: (eds.) Gentner, D., & A. L. Stevens, Mental Models, Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Publishers, Hillsdale, New Jersey.
diSessa, Andrea (1982). Unlearning Aristotelian Physics: A Study of Knowledge-Based learning, Cognitive Science 6 (1): 37–75.
Weil, Vivian (2002) A Seven-Step Procedure for Ethical Decision Making, Proceedings, National Conference on Ethics and Social Responsibility in Engineering and Technology, Coeur d’Alene, Idaho.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haws, D.R. The importance of meta-ethics in engineering education. SCI ENG ETHICS 10, 204–210 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11948-004-0015-7
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11948-004-0015-7