Abstract
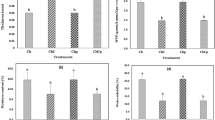
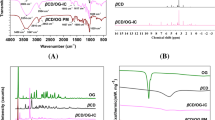
In this work, cinnamaldehyde was reversibly anchored to chitosan films via imino-covalent bonding. The Schiff base was synthesized in solid phase employing neutralized chitosan films immersed in acidified 95 % (v/v) ethanolic solution in which the aldehyde was dissolved. The substitution degree (%) of cinnamaldehyde to the amine group was close to 70 %. Attenuated total reflectance–Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (ATR-FTIR) analysis revealed the formation of the chitosan-cinnamaldehyde Schiff base. The hydrolysis of the imino bond and subsequent release of cinnamaldehyde were studied after the films had been subjected to different combinations of temperature/time treatments simulating food preservation methods. The amount of aldehyde that remained covalently attached to the films was monitored by ATR-FTIR, and the substitution degree was determined by elemental analysis. Surface contact angle and colour parameters of cinnamaldehyde-imine-chitosan films and these films subjected to different treatments were also evaluated. The antimicrobial properties of chitosan-Schiff base films were tested in vitro against Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli and in milk inoculated with Listeria monocytogenes. The antimicrobial activity varied depending on the treatment applied and consequently the degree of imino bond hydrolysis achieved and cinnamaldehyde released. Films of Schiff base-chitosan derivative subjected to different time/temperature treatments inhibited the growth of L. monocytogenes for 12 days under refrigeration conditions, which may extend the microbiological shelf life of such products. Sensory analysis of milk in contact with the films showed that a cinnamon smell does not cause any rejection among potential consumers. These novel films could be used in the design of antimicrobial food packaging and in various other technological areas where sustained-release systems are required.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abreu, F. O., Oliveira, E. F., Paula, H. C., & de Paula, R. (2012). Chitosan/cashew gum nanogels for essential oil encapsulation. Carbohydrate Polymers, 89(4), 1277–1282.
Balaguer, M. P., Gómez-Estaca, J., Gavara, R., & Hernández-Muñoz, P. (2011a). Biochemical properties of bioplastics made from wheat gliadins cross-linked with cinnamaldehyde. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 59(24), 13212–13220.
Balaguer, M. P., Gómez-Estaca, J., Gavara, R., & Hernández-Muñoz, P. (2011b). Functional properties of bioplastics made from wheat gliadins modified with cinnamaldehyde. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 59(12), 6689–6695.
Belletti, N., Lanciotti, R., Patrignani, F., & Gardini, F. (2008). Antimicrobial efficacy of citron essential oil on spoilage and pathogenic microorganisms in fruit-based salads. Journal of Food Science, 73(7), M331–M338.
Burt, S. (2004). Essential oils: their antibacterial properties and potential applications in foods—a review. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 94(3), 223–253.
Cocchiara, J., Lalko, J., Lapczynski, A., Letizia, C. S., & Api, A. M. (2005). Fragrance material review on cinnamaldehyde. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 43(6), 867–923.
Coma, V., Martial-Gros, A., Garreau, S., Copinet, A., Salin, F., & Deschamps, A. (2002). Edible antimicrobial films based on chitosan matrix. Journal of Food Science, 67(3), 1162–1169.
Damodaran, S., & Kinsella, J. E. (1980). Flavor protein interactions. Binding of carbonyls to bovine serum-albumin: thermodynamic and conformational effects. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 28(3), 567–571.
dos Santos, J. E., Dockal, E. R., & Cavalheiro, E. T. G. (2005). Synthesis and characterization of Schiff bases from chitosan and salicylaldehyde derivatives. Carbohydrate Polymers, 60(3), 277–282.
Doyle, M. P., & Beuchat, L. R. (2007). Food microbiology: fundamentals and frontiers. Washington: ASM Press.
Fleming, D. W., Cochi, S. L., MacDonald, K. L., Brondum, J., Hayes, P. S., Plikaytis, B. D., Holmes, M. B., Audurier, A., Broome, C. V., & Reingold, A. L. (1985). Pasteurized milk as a vehicle of infection in an outbreak of listeriosis. New England Journal of Medicine, 312(7), 404–407.
Foster, L. J. R., & Butt, J. (2011). Chitosan films are not antimicrobial. Biotechnology Letters, 33(2), 417–421.
Gallstedt, M., & Hedenqvist, M. S. (2006). Packaging-related mechanical and barrier properties of pulp-fiber-chitosan sheets. Carbohydrate Polymers, 63(1), 46–53.
Gill, A., & Holley, R. (2004). Mechanisms of bactericidal action of cinnamaldehyde against Listeria monocytogenes and of eugenol against L. monocytogenes and Lactobacillus sakei. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 70(10), 5750–5755.
Guinesi, L. S., & Cavalheiro, E. T. G. (2006). Influence of some reactional parameters on the substitution degree of biopolymeric Schiff bases prepared from chitosan and salicylaldehyde. Carbohydrate Polymers, 65(4), 557–561.
Guo, Z. Y., Xing, R. E., Liu, S., Zhong, Z. M., Ji, X., Wang, L., & Li, P. C. (2007). Antifungal properties of Schiff bases of chitosan, N-substituted chitosan and quaternized chitosan. Carbohydrate Research, 342(10), 1329–1332.
Gutierrez, J., Barry-Ryan, C., & Bourke, R. (2008). The antimicrobial efficacy of plant essential oil combinations and interactions with food ingredients. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 124(1), 91–97.
Higueras, L., López-Carballo, G., Cerisuelo, J. P., Gavara, R., & Hernández-Muñoz, P. (2013). Preparation and characterization of chitosan/HP-beta-cyclodextrins composites with high sorption capacity for carvacrol. Carbohydrate Polymers, 97(2), 262–268.
Holley, R. A., & Patel, D. (2005). Improvement in shelf-life and safety of perishable foods by plant essential oils and smoke antimicrobials. Food Microbiology, 22(4), 273–292.
Hosseini, S., Zandi, M., Rezaei, M., & Farahmandghavi, F. (2013). Two-step method for encapsulation of oregano essential oil in chitosan nanoparticles: preparation, characterization and in vitro release study. Carbohydrate Polymers, 95(1), 50–56.
Huang, Z.H., Wan, D.C. & Huang, J.L. (2001). Hydrolysis of Schiff bases promoted by UV light. Chemistry Letters, (7), 708–709.
Inukai, Y., Chinen, T., Matsuda, T., Kaida, Y., & Yasuda, S. J. (1998). Selective separation of germanium (IV) by 2,3-dihydroxypropylchitosan resin. Analytica Chimica Acta, 371(2–3), 187–193.
Ji, C., & Shi, J. (2013). Thermal-crosslinked porous chitosan scaffolds for soft tissue engineering applications. Materials Science and Engineering: C, 33(7), 3780–3785.
Jin, X., Wang, J., & Bai, J. (2009). Synthesis and antimicrobial activity of the Schiff base from chitosan and citral. Carbohydrate Research, 344(6), 825–829.
Junttila, J. R., Niemela, S. I., & Hirn, J. (1988). Minimum growth temperatures of Listeria monocytogenes and non-haemolytic Listeria. Journal of Applied Bacteriology, 65(4), 321–327.
Kasaai, M. R., Arul, J., Chin, S. L., & Charlet, G. (1999). The use of intense femtosecond laser pulses for the fragmentation of chitosan. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology, A: Chemistry, 120(3), 201–205.
Kirdant, A. S., Shelke, V. A., Shankarwar, S. G., Shankarwar, A. G., & Chondhekar, T. K. (2011). Kinetic study of hydrolysis of N-salicylidene-m-methyl aniline spectrophotomerically. Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 3(4), 790–796.
Kuhn, J., Considine, T., & Singh, H. (2006). Interactions of milk proteins and volatile flavor compounds: implications in the development of protein foods. Journal of Food Science, 71(5), R72–R82.
Li, X., Shao, T., Shi, Q., & Hu, M. (2013). A diaryl Schiff base as a photo- and pH-responsive bifunctional molecule. RSC Advances, 3(45), 22877–22881.
Lovett, J., Francis, D. W., & Hunt, J. M. (1987). Listeria monocytogenes in raw milk: detection, incidence, and pathogenicity. Journal of Food Protection, 50(3), 188–192.
Mohamad, A. (2013). Reactivity of base catalysed hydrolysis of 2-pyridinylmethylene-8-quinolinyl-Schiff base iron(II) iodide complexes: solvent effects. Chemické zvesti, 67(4), 464–476.
Muhamad, S. G. (2011). First photolysis of benzidine Schiff base in non aqueous solvents. International Journal of Chemistry, 1(3), 142–145.
Muriel-Galet, V., López-Carballo, G., Gavara, R., & Hernández-Muñoz, P. (2012). Antimicrobial food packaging film based on the release of LAE from EVOH. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 157(2), 239–244.
Nazzaro, F., Fratianni, F., De Martino, L., Coppola, R., & De Feo, V. (2013). Effect of essential oils on pathogenic bacteria. Pharmaceuticals, 6(12), 1451–1474.
Renault, F., Sancey, B., & Crini, G. (2009). Chitosan for coagulation/flocculation processes—an eco-friendly approach. European Polymer Journal, 45(5), 1337–1348.
Sashiwa, H., & Aiba, S. I. (2004). Chemically modified chitin and chitosan as biomaterials. Progress in Polymer Science, 29(9), 887–908.
Shahidi, F., Arachchi, J. K. V., & Jeon, Y. J. (1999). Food applications of chitin and chitosans. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 10(2), 37–51.
Vallapa, N., Wiarachai, O., Thongchul, N., Pan, J. S., Tangpasuthadol, V., Kiatkamjornwong, S., & Hoven, V. P. (2011). Enhancing antibacterial activity of chitosan surface by heterogeneous quaternization. Carbohydrate Polymers, 83(2), 868–875.
Wang, J. T., Lian, Z. R., Wang, H. D., Jin, X. X., & Liu, Y. J. (2012). Synthesis and antimicrobial activity of Schiff base of chitosan and acylated chitosan. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 123(6), 3242–3247.
Zivanovic, S., Chi, S., & Draughon, A. F. (2005). Antimicrobial activity of chitosan films enriched with essential oils. Journal of Food Science, 70(1), M45–M51.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank the financial support provided by the Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation (project AGL2012-39920-C03-01) and Spanish Research Council (CSIC, JAE-Predoc L.H. fellowship).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Higueras, L., López-Carballo, G., Gavara, R. et al. Reversible Covalent Immobilization of Cinnamaldehyde on Chitosan Films via Schiff Base Formation and Their Application in Active Food Packaging. Food Bioprocess Technol 8, 526–538 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-014-1421-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-014-1421-8