Abstract
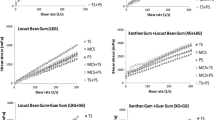
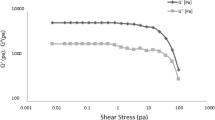
Mixture design was used to investigate the effects of four different gums (xanthan gum, guar gum, alginate and locust bean gum) and their combinations on the rheological properties of a prebiotic model instant hot chocolate beverage (including 3.5% inulin) and to determine their interactions in the model beverage. Simplex centroid mixture design was applied to predict the physicochemical (soluble solids, pH, colour properties) and rheological parameters (consistency index (K), flow behaviour index (n) and apparent viscosity (η 50)) of the samples. In the model, the optimum gum combination was found by simplex centroid mixture design as 59% xanthan gum and 41% locust bean gum, and the highest K value was 33.56 Pa sn. The increase of guar gum and alginate in the gum mixture caused a decrease in the K value of the sample.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- K :
-
Consistency index (Pa sn)
- n :
-
Flow behaviour index
- η 50 :
-
Apparent viscosity at 50 s−1 (Pa s)
- L*:
-
Brightness
- a*:
-
Redness
- b*:
-
Yellowness
- SCMD:
-
Simplex centroid mixture design
- X 1 :
-
Alginate concentration
- X 2 :
-
Xanthan gum concentration
- X 3 :
-
Locust bean gum concentration
- X 4 :
-
Guar gum concentration
- Alg.:
-
Alginate
- GG:
-
Guar gum
- XG:
-
Xanthan gum
- LBG:
-
Locust bean gum
- σ :
-
Shear stress (Pa)
- γ :
-
Shear rate (s−1)
- PHCB:
-
Prebiotic hot chocolate beverage
- β 1 β 2 :
-
Linear and non-linear constants
- BD:
-
Bulk density (g/l)
- °C:
-
Degree centigrade
References
Antonelli, A., Cocchi, M., Fava, P., Foca, G., Franchini, G. C., Manzini, D., & Ulrici, A. (2004). Automated evaluation of food colour by means of multivariate image analysis coupled to wavelet-based classification algorithm. Analytica Chimica Acta, 515, 3–13.
Arteaga, G. E., Li-Chan, E., Nakai, S., Confrades, S., & Jimenez-Colmenero, F. (1993). Ingredient interaction effects on protein functionality: Mixture design approach. Journal of Food Science, 58(3), 656–662.
Bourne, M. C. (2002). Physics and texture. Chapter 3 Food texture and viscosity. 558 concept and measurement (pp. 59–106). London: Academic.
Brennan, C. S., & Tudorica, C. M. (2007). Fresh pasta quality as affected by enrichment of nonstarch polysaccharides. Journal of Food Science, 72, 659–665.
Brown, F., & Diller, R. K. (2008). Calculating the optimum temperature for serving hot beverages. Burns, 34(5), 648–654.
Cairns, P., Miles, M. J., & Morris, V. J. (1986). Intermolecular bonding of xanthan gum and carob gum. Nature, 322, 89–90.
Cairns, P., Miles, M. J., Morris, V. J., & Brownsey, G. J. (1987). X-ray fibre-diffraction studies of synergistic, binary polysaccharide gels. Carbohydrate Research, 160, 411–423.
Cardarelli, H. R., Buriti, F. C. A., Castro, I. A., & Saad, S. M. I. (2008). Inulin and oligofructose improve sensory quality and increase the probiotic viable count in potentially symbiotic petit-suisse cheese. LWT—Food Science and Technology, 41(6), 1037–1046.
Carman, K. (1996). Physical properties of lentil seeds. Journal of Agricultural Engineering Research, 63, 87–92.
Da Silva Lannes, S. C., & Medeiros, M. L. (2008). Rheological properties of chocolate drink from cupuassu. International Journal of food engineering, 4(1), 1–11.
Dea, I. C. M., Morris, E. D., Rees, D. A., & Welsh, E. J. (1977). Associations of like and unlike polysaccharides: mechanism and specificity in galactomannans, interacting bacterial polysaccharides, and related systems. Carbohydrate Research, 57, 249–272.
Dello Staffolo, M., Bertola, N., Martino, M., & Bevilacqua, A. (2004). Influence of dietary fiber addition on sensory and rheological properties of yogurt. International Dairy Journal, 14, 783–789.
Dogan, M., Kayacier, A., & Ic, E. (2007). Rheological characteristics of some food hydrocolloids processed with gamma irradiation. Food Hydrocolloids, 21(3), 392–396.
Dogan, M., Toker, O. S., & Goksel, M. (2011). Rheological behaviour of instant hot chocolate beverage: Part 1. Optimization of the effect of different starches and gums. Food Biophysics, 6, 512–518
Dutcosky, S. D., Grossmann, V. M. E., Silva, R. S. S. F., & Welsch, A. K. (2006). Combined sensory optimization of a prebiotic cereal product using multicomponent mixture experiments. Food Chemistry, 98(4), 630–638.
El-Nagar, G., Clowes, G., Tudorica, C. M., Kuri, V., & Brennan, C. (2002). Rheological quality and stability of yog-ice cream with added inulin. International Journal of Dairy Technology, 55(2), 89–93.
Fagan, C. C., O’Donnel, C. P., Cullen, P. J., & Brennan, C. S. (2006). The effect of dietary fibre inclusion on milk coagulation kinetics. Journal of Food Engineering, 77, 261–268.
Flores, S. K., Costa, D., Yamashita, F., Gerschenson, L. N., & Grossmann, M. V. (2010). Mixture design for evaluation of potassium sorbate and xanthan gum effect on properties of tapioca starch films obtained by extrusion. Materials Science and Engineering: C, 30, 196–202.
Franck, A. (2002). Technological functionality of inulin and oligofructose. British Journal of Nutrition, 87, 287–291.
Guven, M., Yasar, K., Karaca, O. B., & Hayaloglu, A. A. (2005). The effect of inulin as a fat replacer on the quality of set-type low-fat yogurt manufacture. International Journal of Dairy Technology, 58(3), 180–184.
Hassan, B. H., & Hobani, A. I. (1998). Flow properties of Roselle (Hibiscus sabdariffa L.) extract. Journal of Food Engineering, 35, 459–470.
Henelly, P. J., Dunne, P. G., O’Sullivan, M., & O’Riordan, E. D. (2006). Textural, rheological and microstructural properties of imitation cheese containing inulin. Journal of Food Engineering, 75, 388–395.
Henika, R. G. (1982). Use of response surface methodology in sensory evaluation. Food Technology-Chic, 36, 96–101.
Higiro, J., Herald, T. J., & Alavi, S. (2006). Rheological study of xanthan and locust bean interaction in dilute solution. Food Research International, 39, 165–175.
Karaman, S., Yilmaz, M. T., & Kayacier, A. (2011). Simplex lattice design approach on the rheological behaviour of glucomannan based salep–honey drink mixtures: An optimization study based on the sensory properties. Food Hydrocolloids, 25(5), 1319–1326.
Kayacier, A., & Dogan, M. (2006). Rheological properties of some gums-salep mixed solutions. Journal of Food Engineering, 72, 261–265.
Khouryieh, H. A., Herald, T. J., Aramouni, F., & Alavi, S. (2006). Influence of mixing temperature on xanthan conformation and interaction xanthan-guar gum in dilute aqueous solutions. Food Research International, 39, 964–973.
Koca, N., & Metin, M. (2004). Textural, melting and sensory properties of low-fat fresh kashar cheeses produced by using fat replacers. International Dairy Journal, 14, 365–373.
Lop, S. C. F., Silva, R. S. F., & Beleia, A. P. (1999). Formulation and evaluation of dry dessert mix containing sweetener combinations using mixture response methodology. Food Chemistry, 66(2), 167–171.
Marcotte, M., Hoshahili, A. R. T., & Ramaswamy, H. S. (2001). Rheological properties of selected hydrocolloids as a function of concentration and temperature. Food Research International, 34, 695–703.
Nardi, J. V., Acchar, W., & Hotza, D. (2004). Enhancing the properties of ceramic products through mixture design and response surface analysis. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 24, 375.
Oje, K. (1994). Moisture dependence of some physical properties of cowpea. Ife Journal of Technology, 4, 23–27.
Okaka, J. E., & Potter, N. N. (1979). Physicochemical and functional properties of soybean powders processed to reduce flavor. Journal of Food Science, 44, 1235–1240.
Rameshbabu, M., Jayas, D. S., Muir, W. E., White, N. D. G., & Mills, J. T. (1996). Bulk and handling properties of hull-less barley. Canadian Agricultural Engineering, 38, 31–35.
Rao, M. A. (1999). Rheology of fluid and semisolid foods (pp. 371–372). Gaithersburg: Aspen.
Rodriguez Furlán LT, Pérez Padilla A, Campderros M (2011). Development of a functional beverage formulation with high protein content, inulin and Stevia. International Journal of Food Engineering, 7(3), Art. No. 1.
Schaller-Povolny, L. A., & Smith, D. E. (1999). Sensory attributes and storage life of reduced fat ice cream as related to inulin content. Journal of Food Science, 64(3), 555–559.
Schaller-Povolny, L. A., & Smith, D. E. (2001). Viscosity and freezing point of a reduced fat ice cream mix as related to inulin content. Milchwissenschaft-Milk Science International, 56(1), 25–29.
Schubert, H. (1987a). Process and properties of instant powdered foods. In P. Link, Y. Milky, J. Lockup, & J. Laminar (Eds.), Food processing engineering (pp. 657–684). London: Elsevier Applied Science.
Schubert, H. (1987b). Food particle technology. Part I: Properties of particles and particulate food systems. Journal of Food Engineering, 6, 1–32.
Shittu, T. A., & Lawal, M. O. (2007). Factors affecting instant properties of powdered cocoa beverages. Food Chemistry, 100, 91–98.
Sopade, P. A., & Filibus, T. E. (1995). The influence of solid and sugar contents on rheological characteristics of akamu, a semi-liquid maize food. Journal of Food Engineering, 24(2), 197–211.
Suthar, S. H., & Das, S. K. (1996). Some physical properties of Karingda [Citrus lanatus (thumb) mansf] grains. Journal of Agricultural Engineering Research, 65, 15–22.
Sutinium, D., Haruthaithasan, V., & Chompreeda, P. (2008). Development of instant nutritious beverage from germinated jasmine brown rice for elderly consumers. Kasetsart Journal—Natural Science, 42(1), 88–98.
Takashi, S., & Seibi, P. A. (1988). Paste and gel properties of prime corn and wheat starches with and without nitric liquids. Cereal Chemistry, 65, 474.
Tako, M., Asato, A., & Nakamura, S. (1984). Rheological aspects of the intermolecular interaction between xanthan and locust bean gum in aqueous media. Agricultural and Biological Chemistry, 48(12), 2995–3000.
Tárrega, A., & Costell, E. (2006). Effect of inulin addition on rheological and sensory properties of fat-free starch-based dairy desserts. International Dairy Journal, 16(9), 1104–1112.
Togrul, H., & Arslan, N. (2004). Mathematical model for prediction of apparent viscosity of molasses. Journal of Food Engineering, 62, 281–289.
Toker, Ö. S., Doğan, M., & Göksel, M. (2011). Prediction of rheological parameters of model instant hot chocolate beverage by adaptive neuro fuzzy inference system. Milchwissenchaft-Milk Science International, In press.
Tungland, B. C., & Meyer, D. (2002). Non digestible oligo-and polysaccharides (dietary fiber): Their physiology and role in human health and food. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety, 1, 73–92.
Walkenström, P., Kidman, S., Hermansson, A., Rasmussen, P. B., & Hoegh, L. (2003). Microstructure and rheological behaviour of xanthan/pectin mixed gels. Food Hydrocolloids, 17, 593–603.
Wang, F., Wang, Y. J., & Sun, Z. (2002). Conformational role of xanthan in its interaction with locust bean gum. Journal of Food Science, 67(7), 2609–2614.
Williams, P. A., Clegg, S. M., Day, D. H., Phillips, G. O., & Nishinari, K. (1991). Mixed gels formed with konjac mannan and xanthan gum. In E. Dickinson (Ed.), Food polymers, gels and colloids (pp. 339–348). Cambridge: Royal Society of Chemistry.
Wielinga, W. C. (2000). Galactomannans. In G. O. Philips & P. A. Williams (Eds.), Handbook of hydrocolloids. Cambridge: Woodhead.
Yanes, M., Durán, L., & Costell, E. (2002a). Effect of hydrocolloid type and concentration on flow behaviour and sensory properties of milk beverages model systems. Food Hydrocolloids, 16, 605–611.
Yanes, M., Durán, L., & Costell, E. (2002b). Rheological and optical properties of commercial chocolate milk beverages. Journal of Food Engineering, 51, 229–234.
Yılmaz, M. T., Karaman, S., Cankurt, H., Kayacier, A., & Sagdic, O. (2011). Steady and dynamic oscillatory shear rheological properties of ketchup-processed cheese mixtures: Effect of temperature and concentration. Journal of Food Engineering, 103, 197–210.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dogan, M., Toker, O.S., Aktar, T. et al. Optimization of Gum Combination in Prebiotic Instant Hot Chocolate Beverage Model System in Terms of Rheological Aspect: Mixture Design Approach. Food Bioprocess Technol 6, 783–794 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-011-0736-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-011-0736-y