Abstract
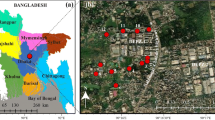
The ambient air quality in Raipur city, Chhattisgarh state, India is poor during the winter season due to the lowest wind speed and temperature inversion. The whole buildings in the city are covered by the black fugitive dust. In this work, characterization and sources of contaminants, i.e. carbons, Al, As, Cr, Mn, Fe, Ni, Cu, Zn, Pb, Cd, F−, Cl−, SO4 2−, NO3 −, NH4 +, Na+, K+, Mg2+ and Ca2+, in the building roof dust of Raipur area, central India are described. Significant concentration of black carbon (BC), SO4 2−, Ca2+, Al, Fe and Mn in the dusts was observed, ranging from 8.7 to 21.9, 0.5 to 2.1, 1.8 to 2.9, 2.1 to 4.8, 6.2 to 13.4 and 0.34 to 0.95 % with mean value (p = 0.05) of 14.1 ± 2.6, 1.2 ± 0.3, 2.3 ± 0.2, 3.3 ± 0.4, 9.4 ± 1.2 and 0.64 ± 0.11 %, respectively. The concentration of toxic metals, i.e. As, Cr, Ni, Cu, Zn, Cd and Pb, ranged from 13.8 to 47.3, 57 to 187, 36 to 89, 31 to 177, 208 to 472, 0.11 to 0.53 and 93 to 366 mg kg−1 with mean value (p = 0.05) of 21.5 ± 6.0, 111 ± 22, 59 ± 9, 102 ± 23, 306 ± 48, 0.28 ± 0.08 and 176 ± 48 mg kg−1, respectively. The cluster and factor analysis models were used to apportion sources of elements linked to several anthropogenic activities in the study area. The concentration variations, pollution indices and toxicities of the contaminants are described.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adachi K, Tainosho Y (2004) Characterization of heavy metal particles embedded in tire dust. Environ International 30(8):1009–1017. doi:10.1016/j.envint.2004.04.004
Awad AM, Mashat AWS (2016) Synoptic characteristics of spring dust days over northern Saudi Arabia. Air Qual Atmos Health 9(1):41–50. doi:10.1007/s11869-015-0320-0
Boch K, Schuster M, Risse G, Schwarzer M (2002) Microwave-assisted digestion procedure for the determination of palladium in road dust. Anal Chim Acta 459(2):257–265. doi:10.1016/S0003-2670(02)00123-X
Brimblecombe P (2003) The effects of air pollution on the built environment, Imperial College Press, London 428. ISBN: 978–1–86094-291-4
Charlesworth S, Everett M, McCarthy R, Ordo’n˜ezand A, de Miguel E (2003) A comparative study of heavy metal concentration and distribution in deposited street dusts in a large and a small urban area: Birmingham and Coventry, West Midlands, UK. Environ International 29(5):563–573. doi:10.1016/S0160-4120(03)00015-1
Councell TB, Duckenfield KU, Landa ER, Callender E (2004) Tire-wear particles as a source of zinc to the environment. Environ Sci Technol 38:4206–4214. doi:10.1021/es034631f
Duce RA, Hoffman EJ (1976) Chemical fractionation at the air/sea interface. Ann Review Earth Planetary Sci 4:187–228
Duong TT, Lee BK (2011) Determining contamination level of heavy metals in road dust from busy traffic areas with different characteristics. J Environ Manag 92(3):554–562. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2010.09.010
ECDGE (2004) Heavy metals and organic compounds from wastes used as organic fertilizers. Final Rep., July. WPA Consulting Engineers Inc. Ref. Nr. TEND/AML/2001/07/20, 73–74. http://ec.europa.eu/environment/waste/compost/ pdf/hm_finalreport.pdf
Faiz Y, Tufail M, Javed MT, Chaudhry MM, Siddique N (2009) Road dust pollution of Cd, Cu, Ni, Pb and Zn along Islamabad expressway, Pakistan. Microchem J 92(2):186–192. doi:10.1016/j.microc.2009.03.009
Guttikunda S, Lodoisamba S, Bulgansaikhan B, Dashdondog B (2013) Particulate pollution in Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia. Air Qual Atmos Health 6:589–601. doi:10.1007/s11869-013-0198-7
Han YM, Cao JJ, Chow JC, Watson JG, An ZS, Liu SX (2009) Elemental carbon in urban soils and road dusts in Xi'an, China and its implication for air pollution. Atmos Environ 43(15):2464–2470. doi:10.1016/j.atmosenv.2009.01.040
He Y, Zhang GL (2009) Historical record of black carbon in urban soils and its environmental implications. Environ Pollu 157(10):2684–2688
Inomata Y, Igarashi Y, Chiba M, Shinoda Y, Takahashi H (2009) Dry and wet deposition of water-insoluble dust and water-soluble chemical species during spring 2007 in Tsukuba, Japan. Atmos Environ 43(29):4503–4512
Jaiswal, NK (2009) Studies on black carbon distribution in air, sources and environmental impacts, PhD thesis, Submitted to Pt. Ravishankar Shukla University, Raipur, India
Kabata-Pendias A, Pendias H (1992) Trace elements in soils and plants. CRC Press, London
Knippertz P, Fink AH (2006) Synoptic and dynamic aspects of an extreme springtime Saharan dust outbreak. QJR Meteoro Soc 132:1153–1177. doi:10.1256/qj.05.109
Lebourg A, Sterckeman T, Ciesielski H, Proix N (1996) Intérêt de différentsréactifsd’extractionchimique pour l’évaluation de la biodisponibilité des métaux en traces du sol. Agronomy 16(4):201–215
Lefevre RA, Ausset P (2002) Atmospheric pollution and building material: stone and glass. Natural stones, weathering phenomena. Conservation strategies and case studies. Geological Society of London. Special Publication 205:329–345. doi:10.1144/GSL.SP.2002.205.01.24
Liu S, Xia X, Zhai Y, Wang R, Liu T, Zhang S (2011) Black carbon (BC) in urban and surrounding rural soils of Beijing, China: spatial distribution and relationship with polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). Chemosphere 82(2):223–228. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.10.017
Lu X, Li LY, Wang L, Lei K, Huang J, Zhai Y (2009a) Contamination assessment of mercury and arsenic in roadway dust from Baoji, China. Atmos Environ 43(15):2489–2496
Lu X, Wang L, Lei K, Huang J, Zhai Y (2009b) Contamination assessment of copper, lead, zinc, manganese and nickel in street dust of Baoji, NW China. J Hazard Mater 161(2–3):1058–1062. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.04.052
Lu X, Wang L, Li LY, Lei K, Huangand L, Kang D (2010) Multivariate statistical analysis of heavy metals in street dust of Baoji, NW China. J Hazard Mater 173(1–3):744–749. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.09.001
Manno E, Varrica D, Dongarra G (2006) Metal distribution in road dust samples collected in an urban area close to a petrochemical plant at Gela, Sicily. Atmos Environ 40(30):5929–5941. doi:10.1016/j.atmosenv.2006.05.020
McAlister JJ, Smith BJ, Torok A (2006) Element partitioning and potential mobility within surface dusts on buildings in a polluted urban environment, Budapest. Atmos Environ 40(35):6780–6790. doi:10.1016/j.atmosenv.2006.05.071
McAlister JJ, Smith BJ, Torok A (2008) Transition metals and water-soluble ions in deposits on a building and their potential catalysis of stone decay. Atmos Environ 42(33):7657–7668. doi:10.1016/j.atmosenv.2008.05.067
Muri G, Cermelj B, Faganeli J, Brancelj A (2002) Black carbon in Slovenian alpine lacustrine sediments. Chemosphere 46(8):1225–1234. doi:10.1016/S0045-6535(01)00295-8
Nastos PT (2012) Meteorological patterns associated with intense Saharan dust outbreaks over Greece in winter. Adv Meteorol ID 828301. http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2012/828301
Pagotto C, Remy N, Legret M, Le Cloirec P (2001) Heavy metal pollution of road dust and roadside soil near a major rural highway. Environ Tech 22(3):307–319. doi:10.1080/09593332208618280
Ramanathan V, Carmichael G (2008) Global and regional climate changes due to black carbon. Natural Geosci 1(4):221–227. doi:10.1038/ngeo156
Rao PS, Kumar A, Ansari MF, Pipalatkar P, Chakrabarti T (2009) Air quality impact of sponge iron industries in Central India. Bull Environ Conta Toxico 82(2):255–259
Rot RA (2000) Lead loading of urban streets by motor vehicle wheel weights. Environ Health Persp 108(10):937–940 PMCID: PMC1240125.
Rudnick RL, Gao S (2003) The composition of the continental crust. In: Holland H D, Turekian K K (eds) Treatise on geochemistry. Elsevier Ltd, Oxford, England SBN: 978-0-08-043751-4.
Sezgin N, HK O, Demir G, Nemlioglu S, Bayat C (2004) Determination of heavy metal concentrations in street dusts in Istanbul E-5 highway. Environ International 29(7):979–985. doi:10.1016/S0160-4120(03)00075-8
Shi X, Chen L, Wang J (2013) Multivariate analysis of heavy metal pollution in street dusts of Xianyang city, NW China. Environ Earth Sci 69(6):1973–1979. doi:10.1007/s12665-012-2032-1
Shinggu DY, Ogugbuaja VO, Barminasand JT, Toma I (2007) Analysis of street dust for heavy metal pollutants in Mubi, Adamawa state, Nigeria. International J Phys Sci 2(11):290–293
Sinex SA, Helz GR (1981) Regional geochemistry of trace elements in Chesapeake bay sediments. Environ Geology 3(6):315–323. doi:10.1007/BF02473521
Tyler G (2004) Vertical distribution of major, minor, and rare elements in a Haplic Podzol. Geoderma 119(3–4):277–290. doi:10.1016/j.geoderma.2003.08.005
Walkley A, Black IA (1934) An examination of the Degtjareff method for determining soil organic matter and a proposed modification of the chromic acid titration method. Soil Sci 37:29–38
Washington R, Bouet C, Cautenet G, Mackenzie E, Ashpole I, Engelstaedter S, Lizcano G, Henderson GM, Schepanski K, Tegen I (2009) Dust as a tipping element: the Bodélé depression, Chad. PANS 106:20564–20571
WHO/Europe (2007) Health risks of heavy metals from long range trans boundary air pollution, ISBN 978 92 890 7179 6F
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Patel, K.S., Rajak, M., Jaiswal, N.K. et al. Contamination of building roof dust in India. Air Qual Atmos Health 10, 287–295 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11869-016-0446-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11869-016-0446-8