Abstract
Introduction
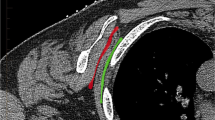
We describe a case report and technique for using an ultrasound scanner and a linear transducer to guide serratus posterior superior (SPS) muscle injection. A 43-year-old female presented with chronic pain centered under the right upper portion of her scapula impacting her activities of daily living.
Methods and materials
For the ultrasound-guided SPS muscle injection, the patient was placed in the prone position. The transducer was oriented in a transverse orientation at the level of the C6-T1 vertebrae. Here the SPS muscle attaches to the lower portion of the ligament nuchae and the intervening interspinous ligaments. The muscle fibers run inferiorly and laterally to attach to the 2nd–5th ribs which were identified along with the lateral portion of the serratus posterior superior muscle which is covered by the scapula. Real-time imaging was used to direct a spinal needle into the trigger points of the SPS muscle, where solution was injected under direct vision. The patient’s pain symptoms improved significantly.
Conclusion
Serratus posterior superior injection can confirm a diagnosis of scapulocostal syndrome and be therapeutically beneficial.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cohen CA (1980) Scapulocostal syndrome: diagnosis and treatment. South Med J 73(4):433–434
Rose DL, Novak EJ (1996) The painful shoulder. The scapulocostal syndrome in shoulder pain. J Kans Med Soc 167(3):112–114
Schmerl Sangster (2002) Therapeutic review, clinical update. Scapulocostal syndrome, The Academy of Chiropratcic Orthopedists 10(2):85–86
Gautschi R (2013) Manuelle triggerpunkt-therapie, 2nd edn. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 280–282
Fourie LJ (1991) The scapulocostal syndrome. S Afr Med J 79(12):721–724
Ormandy L (1994) Scapulocostal syndrome. Va Med Q 121(2):105–108
Kuhne M, Boniquit N, Ghodadra N, Romeo AA, Provencher MT (2009) The snapping scapula: diagnosis and treatment. Arthroscopy 25(11):1298–1311. doi:10.1016/j.arthro.2008.12.022 Epub 2009 Jun 24
Drenckhahn D, Waschke J (2008) Taschenbuch anatomie, 1st edn. Urban & Fischer Verlag/Elsevier, Germany, pp 134–136
Waldmann S (2013) Atlas of uncommon pain syndromes, 3rd edn. Elsevier Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 60–61
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Dr Ciana McCarthy and Dr Dominic Harmon reported no conflicts of interest.
Informed consent
The author states that the report describes the care of one or more patients. The patient consented to publication of the report. This is described in the report.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McCarthy, C., Harmon, D. A technical report on ultrasound-guided scapulocostal syndrome injection. Ir J Med Sci 185, 669–672 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11845-015-1336-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11845-015-1336-z