Abstract
Objective
Renal sympathetic denervation (RSD) is an emerging device based treatment for patients with resistant hypertension. Nocturnal dipping (ND) is defined as a decrease in BP of 10–20 % during sleep, and has been shown to be protective against cardiovascular disease. This study examined the effect of RSD on the 24 h BP profile of patients with resistant hypertension.
Methods and results
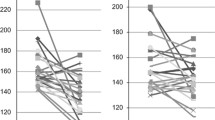
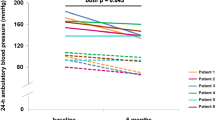
The first 23 consecutive patients with resistant hypertension scheduled for renal denervation in a single centre were included. 24 h ambulatory blood pressure monitors (ABPM) were given to patients pre-procedure and 9 months post-procedure. RSD led to a statistically non-significant reduction in overall 24 h ABPM BP (150/85 ± 12/9 vs. 143/84 ± 15/11 mmHg; P > 0.05) despite a reduction in the number of antihypertensive medications (4.9 ± 1.2 vs. 4.3 ± 1.2; P = 0.001). There were improvements in systolic ND 1.7 ± 8 vs. 5.2 ± 8 %; P < 0.05), diastolic ND (5.2 ± 8 vs. 10.2 ± 9 %; P < 0.05) and mean arterial pressure (MAP) ND (4.2 ± 8 vs. 8.0 ± 8 %; P < 0.05). Non-significant changes in ND status were observed in systolic (17 vs. 43 % of participants; P > 0.05), diastolic (30 vs. 43 % of participants; P > 0.05) and MAP (22 vs. 39 % of participants; P > 0.05) measurements.
Conclusions
These data suggest that RSD may lead to an improvement in nocturnal dipping in selected patients with resistant hypertension. This may have cardiovascular benefits even if reduction in BP is not achieved with RSD.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BP:
-
Blood pressure
- RSD:
-
Renal sympathetic denervation
- ND:
-
Nocturnal dipping
- ABPM:
-
Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring
- HR:
-
Heart rate
- BPM:
-
Beats per minute
- mmHg:
-
Millimetres of mercury
- SBP:
-
Systolic blood pressure
- DBP:
-
Diastolic blood pressure
- MAP:
-
Mean arterial pressure
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
References
Okamoto LE, Gamboa A, Shibao C, Black BK, Diedrich A, Raj SR et al (2009) Nocturnal blood pressure dipping in the hypertension of autonomic failure. Hypertension 53(2):363–369
Friedman O, Logan AG (2009) Nocturnal blood pressure profiles among normotensive, controlled hypertensive and refractory hypertensive subjects. Can J Cardiol 25(9):e312–e316
O’Brien E, Sheridan J, O’Malley K (1988) Dippers and non-dippers. Lancet 2:397
Henskens LH, Kroon AA, van Oostenbrugge RJ, Haest RJ, Lodder J, de Leeuw PW (2008) Different classifications of nocturnal blood pressure dipping affect the prevalence of dippers and nondippers and the relation with target-organ damage. J Hypertens 26:691–698
Verdecchia P, Schillaci G, Gatteschi C, Zampi I, Battistelli M, Bartoccini C et al (1993) Blunted nocturnal fall in blood pressure in hypertensive women with future cardiovascular morbid events. Circulation 88(3):986–992
Grassi G, Seravalle G, Quarti-Trevano F, Dell’Oro R, Bombelli M et al (2008) Adrenergic metabolic, and reflex abnormalities in reverse and extreme dipper hypertensives. Hypertension 52:925–931
Sherwood A, Steffen PR, Blumenthal JA, Kuhn C, Hinderliter AL (2002) Nighttime blood pressure dipping: the role of the sympathetic nervous system. Am J Hypertens 15:111–118
Esler MD, Krum H, Sobotka PA, Schlaich MP, Schmeider RE, Bohm M (2010) Renal sympathetic denervation in patients with treatment-resistant hypertension (the Symplicity HTN-2 trial): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 376:1903–1909
Katayama T, Sueta D, Kataoka K, Hasegawa Y, Koibuchi N, Toyama K et al (2013) Long-term renal denervation normalizes disrupted blood pressure circadian rhythm and ameliorates cardiovascular injury in a rat model of metabolic syndrome. J Am Heart Assoc 2(4):e000197. doi:10.1161/JAHA.113.000197
Kohara K, Nishida W, Maguchi M, Hiwada K (1995) Autonomic nervous function in non-dipper essential hypertensive subjects. Hypertension 26:808–814
Krum H, Sobotka P, Mahfoud F, Böhm M, Esler M, Schlaich M (2011) Device based antihypertensive therapy: therapeutic modulation of the autonomic nervous system. Circulation 123:209–215
Schlaich MP, Sobotka PA, Krum H, Lambert E, Esler MD (2009) Renal sympathetic-nerve ablation for uncontrolled hypertension. N Engl J Med 361:932–934
Schlaich MP, Lambert E, Kaye DM, Krozowski Z, Campbell DJ, Lambert G et al (2004) Sympathetic augmentation in hypertension: role of nerve firing, norepinephrine reuptake, and angiotensin neuromodulation. Hypertension 43:169–175
Hering D, Lambert EA, Marusic P, Ika-Sari C, Walton AS, Sabotka PA et al (2013) Renal nerve ablation reduces augmentation index in patients with resistant hypertension. J Hypertens 31(9):1893–1900
Mancia G, De Backer G, Dominiczak A, Cifkova R, Fagard R, Germano G et al (2007) Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: the Task Force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). J Hypertens 25:1105–1187
Calhoun DA, Jones D, Textor S, Goff DC, Murphy TP, Toto RD et al (2008) Resistant hypertension: diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment. A scientific statement from the American Heart Association Professional Education Committee of the Council for high blood pressure research. Hypertension 51:1403–1419
Krum H, Schlaich M, Whitbourn R, Sobotka PA, Sadowski J, Bartus K et al (2009) Catheter-based renal sympathetic denervation for resistant hypertension: a multicentre safety and proof-of-principle cohort study. Lancet 373:1275–1281
Grassi G, Bombelli M, Seravalle G, Dell’Oro R, Quarti-Trevano F (2010) Diurnal blood pressure variation and sympathetic activity. Hypertens Res 33:381–385
Mahfoud F, Ukena C, Schmieder RE, Cremers B, Rump LC, Vonend O et al (2013) Ambulatory blood pressure changes after renal sympathetic denervation in patients with resistant hypertension. Circulation 128(2):132–140
Howard J, Cole G, Sievert H, Bhatt D, Papademetriou V, Kandzari D, Davies J, Francis D (2014) Unintentional overestimation of an expected antihypertensive effect in drug and device trials: mechanisms and solutions. Int J Cardiol 172(1):29–35
Patel H, Hayward C, Ozdemir B, Rosen S, Krum H, Lyon A, Francis D, Di Mario C (2015) Magnitude of blood pressure reduction in the placebo arms of modern hypertension trials: implications for trials of renal denervation. Hypertension 65(2):401–406
Bhatt DL, Kandzari DE, O’Neill WW, D’Agostino R, Flack JM, Katzen BT et al (2014) A controlled trial of renal denervation for resistant hypertension. N Engl J Med 370(15):1393–1401
Patel H, Hayward C, Di Mario C (2014) SYMPLICITY HTN 3: the death knell for renal denervation in hypertension? Glob Cardiol Sci Pract 2014(1):94–98
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tuohy, S.T., Kyvelou, SM.G., Gleeson, P.J. et al. The effect of renal sympathetic denervation on nocturnal dipping in patients with resistant hypertension; observational data from a tertiary referral centre in the Republic of Ireland. Ir J Med Sci 185, 635–641 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11845-015-1324-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11845-015-1324-3