Abstract
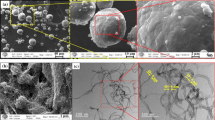
Porous magnesium/carbon nanofiber composites were produced using a powder metallurgic method to study the effect of ball milling time on their microstructure and hardness. Three ball milling times (240 min, 320 min, and 480 min) and two carbon nanofiber concentrations (0.05% and 1%) were utilized in the production of these porous composites. The increase of ball milling time led to the gradual decrease of the average size of magnesium powders from the initial 40 µm to about 26 µm after 480 min of ball milling. The powder size range first increased with the increase of ball milling time from 240 min to 320 min, and then decreased with the further increase of ball milling time to 480 min. Among the three ball milling times, the produced porous composites from the powders after 320 min of ball milling have the largest average pore size. With the increase of ball milling time from 240 min to 320 min and then to 480 min, the average Vickers microhardness data first decreased and then increased for Mg-1%C porous composites along the cross-sections parallel to the compact processing direction, increased for the cross-sections perpendicular to the compact processing direction for Mg-1%C porous composites, first increased and then decreased for the cross-sections parallel to the compact processing direction for Mg-0.05%C porous composites, and slightly decreased for the cross-sections perpendicular to the compact processing direction for Mg-0.05%C porous composites.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Liu, Y. Li, J. Wan, and H. Zhang, Mater Sci Eng, A 402, 47 (2005).
C. Wen, Y. Yamada, K. Shimojima, Y. Chino, H. Hosokawa, and M. Mabuchi, Mater Lett 58, 357 (2004).
M.P. Staiger, I. Kolbeinsson, N.T. Kirkland, T. Nguyen, G. Dias, and T.B. Woodfield, Mater Lett 64, 2572 (2010).
L. Tan, M. Gong, F. Zheng, B. Zhang, and K. Yang, Biomed Mater 4, 015016 (2009).
J. Čapek and D. Vojtěch, Mater Sci Eng, C 33, 564 (2013).
M.M. Zahrani, M. Meratian, and Y. Kabiri, Mater Lett 85, 14 (2012).
J. Banhart, Prog Mater Sci 46, 559 (2001).
G.J. Davies and S. Zhen, J Mater Sci 18, 1899 (1983).
H. Nakajima, Prog Mater Sci 52, 1091 (2007).
G. Ryan, A. Pandit, and D.P. Apatsidis, Biomaterials 27, 2651 (2006).
M. Sharma, G. Gupta, O. Modi, B. Prasad, and A.K. Gupta, Mater Lett 65, 3199 (2011).
C. Körner and R.F. Singer, Adv Eng Mater 2, 159 (2000).
G. Gunn, Critical Metals Handbook, 1st ed. (Oxford: Wiley, 2014), pp. 261–283.
D.C. Dunand, Adv Eng Mater 6, 369 (2004).
T. Kuromura, Y. Asao, Y. Chen, H. Kusuda, and M. Mabuchi, in MetFoam 2007: Porous Metals and Metallic Foams: Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference on Porous Metals and Metallic Foams (DEStech Publications, Inc, Lancaster, PA, 2008), p. 359.
H. Cay, H. Xu, and Q.Z. Li, Mater Sci Eng, A 574, 137 (2013).
Q.Z. Li, Mater Des 89, 978 (2016).
N. Zou and Q.Z. Li, J Mater Sci 51, 5232 (2016).
V.S. Ekinci, C. Bagci, and H. Arik, Exp. Tech. 38, 66 (2014).
M.R. Basariya, V.C. Srivastava, and N.K. Mukhopadhyay, Metall Mater Trans A 46, 1360 (2015).
Acknowledgement
The authors greatly appreciate the support for the research from the National Science Foundation under Award No. 1449607.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, H., Zou, N. & Li, Q. Effect of Ball Milling Time on Microstructure and Hardness of Porous Magnesium/Carbon Nanofiber Composites. JOM 69, 1236–1243 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-017-2361-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-017-2361-3