Abstract
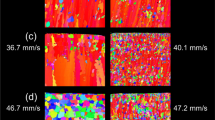
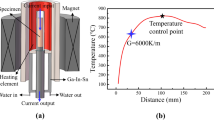
Directionally solidified Ti-47Al samples without contamination were obtained by the electromagnetic confinement and directional solidification technique. With increasing growth velocity, the solid/liquid interface was changed from cellular to dendritic. The grain boundary turned vague, and the lamellae within the grains became distorted. When the growth velocity increased to 200 μm/s, some γ phases and α phases appeared in local region owing to the enrichment of Al solute. The columnar grain size (λ), interdendritic spacing (λ 1), and interlamellar spacing (λ L) were measured, and the effects of growth velocity on these parameters were discussed. As the growth velocity increased, both the microhardness and the 0.2% offset compression yield stress increased continuously. However, the value of yield stress decreased slightly when the growth velocity increased to 200 μm/s, which resulted from the appearance of γ phases.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y.-W. Kim, JOM 46, 30 (1994).
M. Yamaguchi, H. Inui, and K. Ito, Acta Mater. 48, 307 (2000).
K.S. Chan, JOM 49(7), 53 (1997).
D.M. Dimiduk, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 263, 281 (1999).
X.F. Ding, J.P. Lin, L.Q. Zhang, Y.Q. Su, and G.L. Chen, Acta Mater. 60, 498 (2012).
D.R. Johnson, Y. Masuda, H. Inui, and M. Yamaguchi, Acta Mater. 45, 2523 (1997).
W.Z. Luo, J. Shen, Z.X. Min, and H.Z. Fu, Rare Metall. Mater. Eng. 38, 1441 (2009).
J. Lapin and L. Ondrus, Kovové Mater. 40, 161 (2002).
H.N. Lee, D.R. Johnson, H. Inui, M.H. Oh, D.M. Wee, and M. Yamaguchi, Acta Mater. 48, 3221 (2000).
N. Ge, H.S. Ding, R.R. Chen, J.J. Guo, and H.Z. Fu, Mater. Des. 39, 350 (2012).
S.R. Coriell, S.C. Hardy, and M.R. Cordes, J. Colloid Interface Sci. 60, 126 (1977).
H.Z. Fu, J. Shen, L. Liu, Q.T. Hao, S.M. Li, and J.S. Li, J. Mater. Process. Technol. 148, 25 (2004).
J. Shen, J.G. Li, and H.Z. Fu, J. Mater. Process. Technol. 102, 109 (2000).
C.J. Song, G.F. Liang, Z.M. Xu, J. Shen, and J.G. Li, J. Mater. Process. Technol. 180, 179 (2006).
S.M. Li, L. Liu, J.S. Li, Q.T. Hao, and H.Z. Fu, J. Mater. Process. Technol. 166, 449 (2005).
U. Bőyük and N. Maraşlı, J. Alloy Compd. 485, 264 (2009).
M. Gündüz, H. Kaya, E. Çadırlı, and A. Özmen, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 369, 215 (2004).
K. Kitamura, S. Kimura, and K. Watanabe, J. Cryst. Growth 57, 475 (1982).
M.C. Kim, M.H. Oh, J.H. Lee, H. Inui, M. Yamaguchi, and D.M. Wee, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 239, 570 (1997).
X.Z. Li, T. Sun, C.X. Yu, Y.Q. Su, Y.Z. Cao, J.J. Guo, and H.Z. Fu, Acta Metall. 45, 1479 (2009).
M. Oehring, V. Küstner, F. Appel, and U. Lorenz, Mater. Sci. Forum 539, 1475 (2007).
J.C. Schuster and M. Palm, J. Phase Equilib. Diffus. 27, 255 (2006).
C. McCullough, J.J. Valencia, C.G. Levi, and R. Mehrabian, Acta Metall. 37, 1321 (1989).
C. Stelian, Y. Delannoy, Y. Fautrelle, and T. Duffar, J. Cryst. Growth 266, 207 (2004).
L.S. Wang, J. Shen, Z. Shang, and H.Z. Fu, J. Cryst. Growth 375, 32 (2013).
X.Y. Yan, F.Y. Xie, M. Chu, and Y.A. Chang, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 302, 268 (2001).
J. Lapin, L. Ondrúš, and M. Nazmy, Intermetallics 10, 1019 (2002).
M.A. Eshelman, V. Seetharaman, and R. Trivedi, Acta Metall. 36, 1165 (1988).
W. Kurz and D.J. Fisher, Acta Metall. 29, 11 (1981).
R. Trivedi, Metall. Trans A. 611 (1984).
J.L. Fan, X.Z. Li, Y.Q. Su, J.J. Guo, and H.Z. Fu, J. Alloy Compd. 504, 60 (2010).
J.L. Fan, X.Z. Li, Y.Q. Su, J.J. Guo, and H.Z. Fu, Mater. Des. 34, 552 (2011).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 51174167, and the Research Fund of State Key Laboratory of Solidification Processing (NWPU), China under Grant No. 63-TP-2011. It is also supported by the Doctorate Foundation of Northwestern Polytechnical University under contract No. CX201308.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Du, Y., Shen, J., Xiong, Y. et al. Determining the Effects of Growth Velocity on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Ti-47Al Alloy using Electromagnetic Confinement and Directional Solidification. JOM 66, 1914–1922 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-014-1051-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-014-1051-7