Abstract
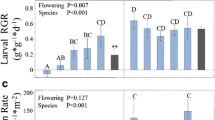
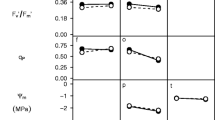
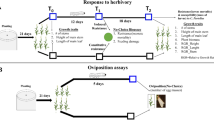
Climate change is predicted to cause continued increases in global temperatures, greater variability in precipitation and in some cases, more frequent insect pest outbreaks. Here we seek to understand how abiotic and biotic stresses associated with climate change can affect plant-herbivore interactions in a model crop species (soybean, Glycine max (L.) Merr.) by answering three questions: (1) Do the combined effects of abiotic and biotic stresses associated with climate change cause synergistic negative effects on plant biomass? (2) Can abiotic stress affect resistance of plants to insect herbivores? (3) Does genetic variation in plant traits modify a plant’s response to stress? We performed three experiments in controlled growth environments using up to 51 soybean genotypes selected to vary in numerous traits associated with drought and resistance against pests (e.g., insect herbivores, nematodes, and pathogenic fungi), and up to 3 generalist-feeding herbivorous noctuid moth species (Helicoverpa zea, Heliothis virescens, and Spodoptera exigua) that commonly feed on soybean in North America. Drought and herbivory had the largest and the most consistent negative effects on plant performance, reducing the above- and below-ground biomass by 10-45 %, whereas increased temperature had little to no effect on plants. Drought also increased susceptibility to generalist noctuid herbivores, but these results varied dramatically in magnitude and direction among plant genotypes. Our experiments show that the effects of abiotic and biotic stress on soybean biomass were largely due to the additive effects of these stresses, and there exists substantial genetic variation in the soybean germplasm pool we studied that could be used as a source of parental stock in breeding new crops that can more effectively tolerate and resist the combined negative effects of insect herbivory and drought.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams HD, Guardiola-Claramonte M, Barron-Gafford GA, Villegas JC, Breshears DD, Zou CB, Troch PA, Huxman TE (2009) Temperature sensitivity of drought-induced tree mortality portends increased regional die-off under global-change-type drought. Proceed Nat Acad Sci USA 106:7063–7066
Agrawal AA, Conner JK, Johnson MTJ, Wallsgrove R (2002) Ecological genetics of an induced plant defense against herbivores: additive genetic variance and costs of phenotypic plasticity. Evolution 56:2206–2213
Agrawal AA, Conner JK, Stinchcombe JR (2004) Evolution of plant resistance and tolerance to frost damage. Ecol Lett 7:1199–1208
American Soybean Association (2010) Soy Stats. URL: www.soystats.com/2010/Default-frames.htm
Battisti DS, Naylor RL (2009) Historical warnings of future food insecurity with unprecedented seasonal heat. Science 323:240–244
Burton JW, Carter TE (2005) Registration of ‘NC-Roy’ soybean. Crop Sci 45:2654–26545
Campitelli BE, Simonsen AK, Wolf AR, Manson JS, Stinchcombe JR (2008) Leaf shape variation and herbivore consumption and performance: a case study with Ipomoea hederacea and three generalists. Arthropod-Plant Interact 2:9–19
Carmona D, Lajeunesse MJ, Johnson MTJ (2011) Plant traits that predict resistance to herbivores. Funct Ecol 25:358–367
Carter TE, De Souza PI, Purcell LC (1999) Recent advances in breeding for drought and aluminum resistance in soybean. In: Kauffman H (ed) Proceedings of the world soybean conference VI. Superior Print, Champaign, pp 542
Carter TE Jr, Burton JW, Bowman DT, Cui Z, Zhou X, Villagarcia M, Niewoehner AS, Fountain MO (2003) Registration of ‘N7001’ soybean. Crop Sci 43:1126–1127
Carter TE Jr, Nelson RL, Sneller C, Cui Z (2004) Genetic diversity in soybean, 3rd edn. American Society of Agronomy, Madison
Charlson DV, Bhatnagar S, King CA, Ray JD, Sneller CH, Carter TE, Purcell LC (2009) Polygenic inheritance of canopy wilting in soybean Glycine max (L.) Merr. Theor Appl Genet 119:587–594
Chin G, Marathe T, Roberts L (2011) Doom or vroom? Science 333:539
Costamagna AC, Landis DA, Difonzo CD (2007) Suppression of soybean aphid by generalist predators results in a trophic cascade in soybeans. Ecol Appl 17:441–451
Cox WJ, Cherney JH (2011) Growth and yield responses of soybean to row spacing and seeding rate. Agron J 103:123–128
Daane KM, Williams LE (2003) Vineyard irrigation amounts to reduce insect pest damage. Ecol Appl 13:1650–1666
Darling ES, Cote IM (2008) Quantifying the evidence for ecological synergies. Ecol Lett 11:1278–1286
Easterling WE, Aggarwal PK, Batima P, Brander KM, Erda L, Howden SM, Kirilenko AP, Morton J, Soussana J-F, Schmidhuber J, Tubiello FN (2007) Food, fibre and forest products. In: Parry ML, Canziani OF, Palutikof JP, Van der Linden PJ, Hanson CE (eds) Climate change 2007: impacts, adaptation and vulnerability. Contribution of working group II to the fourth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 273–313
English-Loeb G, Stout MJ, Duffey SS (1997) Drought stress in tomatoes: changes in plant chemistry and potential nonlinear consequences for insect herbivores. Oikos 79:456–468
Fehr WR, Caviness CE (1977) Stages of soybean development, Special report 80, Ames, IA, Extension Services
Fry JD (2004) Chapter 2: estimation of genetic variances and covariances by restricted maximum likelihood using PROC MIXED. In: Saxton AM (ed) Genetic analysis of complex traits using SAS. SAS Institute, Cary
Geber MA, Griffen LR (2003) Inheritance and natural selection on functional traits. Int J Plant Sci 164:S21–S42
Glynn C, Ronnberg-Wastjung A, Julkunen-Tiitto R, Weih M (2004) Willow genotype, but not drought treatment, affects foliar phenolic concentrations and leaf-beetle resistance. J Chem Ecol 113:1–14
Gutbrodt B, Mody K, Dorn S (2011) Drought changes plant chemistry and causes contrasting responses in lepidopteran herbivores. Oikos 120:1732–1740
Hale BK, Herms DA, Hansen RC, Clausen TP, Arnold D (2005) Effects of drought stress and nutrient availability on dry matter allocation, phenolic glycosides, and rapid induced resistance of poplar to two lymantriid defoliators. J Chem Ecol 31:2601–2620
Hartwig EE (1973) Varietal development. In: Caldwell BE (ed) Soybean: improvement, production, and uses, vol 16. Madison, WI, pp 187–210
Hawkes CV, Sullivan JJ (2001) The impact of herbivory on plants in different resource conditions: a meta-analysis. Ecology 82:2045–2058
Hoffmann AA, Sgro CM (2011) Climate change and evolutionary adaptation. Nature 470:479–485
Hoogenboom G, Huck MG, Peterson CM (1987) Root growth rate of soybean as affected by drought stress. Agron J 79:607–614
Huberty AF, Denno RF (2004) Plant water stress and its consequences for herbivorous insects: a new synthesis. Ecology 85:1383–1398
IPCC (2007) Climate change 2007: synthesis report. Contribution of working groups I, II, and III to the fourth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. In: Core Writing Team, Pachauri RK, Reisinger A (eds) IPCC, Geneva, Switzerland, pp 104
James AT, Lawn RJ, Cooper M (2008) Genotypic variation for drought stress response traits in soybean. I. Variation in soybean and wild Glycine spp. for epidermal conductance, osmotic potential, and relative water content. Aust J Agric Res 59:656–669
Johnson MTJ, Agrawal AA (2005) Plant genotype and environment interact to shape a diverse arthropod community on evening primrose (Oenothera biennis). Ecology 86:874–885
Johnson MTJ, Agrawal AA (2007) Covariation and composition of arthropod species across plant genotypes of evening primrose (Oenothera biennis). Oikos 116:941–956
Johnson MTJ, Stinchcombe JR (2007) An emerging synthesis between community ecology and evolutionary biology. Trends Ecol Evol 22:250–257
Johnson MTJ, Smith SD, Rausher MD (2009) Plant sex and the evolution of plant defenses against herbivores. Proceed Nat Acad Sci USA 106:18079–18084
Kamalay JC, Barger JH, Pierson PE (1997) Survival and development of gypsy moths (Lepidoptera: Lymantriidae) on corn and soybean foliage. J Econ Entomol 90:147–153
Karban R, Baldwin IT (1997) Induced responses to herbivory. University of Chicago Press, Chicago
Kelly AE, Goulden ML (2008) Rapid shifts in plant distribution with recent climate change. Proceed Nat Acad Sci USA 105:11823–11826
Kim MY, Lee S, Van K, Kim TH, Jeong SC, Choi IY, Kim DS, Lee YS, Park D, Ma J, Kim WY, Kim BC, Park S, Lee KA, Kim DH, Kim KH, Shin JH, Jang YE, Do Kim K, Liu WX, Chaisan T, Kang YJ, Lee YH, Moon JK, Schmutz J, Jackson SA, Bhak J, Lee SH (2010) Whole-genome sequencing and intensive analysis of the undomesticated soybean (Glycine soja Sieb. and Zucc.) genome. Proceed Nat Acad Sci USA 107:22032–22037
Kogan M, Kuhlman DE (1982) Soybean insects: identification and management in Illinois. University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign
Kogan M, Turnipseed SG (1987) Ecology and management of soybean arthropods. Ann Rev Entomol 32:507–538
Koricheva J, Larsson S, Haukioja E (1998) Insect performance on experimentally stressed woody plants: a meta-analysis. Ann Rev Entomol 43:195–216
Kraemer ME, Rangappa M, Benepal PS, Mebrahtu T (1988) Field evaluation of soybeans for Mexican Bean Beetle resistance. I. Maturity groups VI, VII, and VIII. Crop Sci 28:497–499
Lam HM, Xu X, Liu X, Chen WB, Yang GH, Wong FL, Li MW, He WM, Qin N, Wang B, Li J, Jian M, Wang JA, Shao GH, Wang J, Sun SSM, Zhang GY (2010) Resequencing of 31 wild and cultivated soybean genomes identifies patterns of genetic diversity and selection. Nat Gen 42:1053–1059
Lee R (2011) The outlook for population growth. Science 333:569–573
Leimu R, Koricheva J (2006a) A meta-analysis of genetic correlations between plant resistances to multiple enemies. Am Nat 168:E15–E37
Leimu R, Koricheva J (2006b) A meta-analysis of tradeoffs between plant tolerance and resistance to herbivores: combining the evidence from ecological and agricultural studies. Oikos 112:1–9
Littell RC, Milliken GA, Stroup WW, Wolfinger RD (1996) SAS system for mixed models. SAS Institute, Cary
Liu FL, Andersen MN, Jensen CR (2003) Loss of pod set caused by drought stress is associated with water status and ABA content of reproductive structures in soybean. Funct Plant Biol 30:271–280
Logan JA, Regniere J, Powell JA (2003) Assessing the impacts of global warming on forest pest dynamics. Front Ecol Environ 1:130–137
Long SP, Ort DR (2010) More than taking the heat: crops and global change. Curr Opin Plant Biol 13:241–248
Matson PA, Parton WJ, Power AG, Swift MJ (1997) Agricultural intensification and ecosystem properties. Science 277:504–509
McPherson RM, Wells ML, Bundy CS (2001) Impact of the early soybean production system on arthropod pest populations in Georgia. Environ Entomol 30:76–81
Micinski S, Blouin DC, Waltman WF, Cookson C (2008) Abundance of Helicoverpa zea and Heliothis virescens in pheromone traps during the past twenty years in northwestern Louisiana. Southwest Entomol 33:139–149
Mody K, Eichenberger D, Dorn S (2009) Stress magnitude matters: different intensities of pulsed water stress produce non-monotonic resistance responses of host plants to insect herbivores. Ecol Entomol 34:133–143
Narvel JM, Carter TE Jr, Jakula LR, Bailey MA, Lee SH, Boerma HR (2004) Registration of NC113 soybean mapping population. Crop Sci 44:704–706
Núñez-Farfán J, Fornoni J, Valverde PL (2007) The evolution of resistance and tolerance to herbivores. Ann Rev Ecol Evol Syst 38:541–566
O’Connor MI (2009) Warming strengthens an herbivore-plant interaction. Ecology 90:388–398
Olson DM, Cortesero AM, Rains GC, Potter T, Lewis WJ (2009) Nitrogen and water affect direct and indirect plant systemic induced defense in cotton. Biol Control 49:239–244
Paritsis J, Veblen TT (2011) Dendroecological analysis of defoliator outbreaks on Nothofagus pumilio and their relation to climate variability in the Patagonian Andes. Global Change Biol 17:239–253
Parmesan C (2006) Ecological and evolutionary responses to recent climate change. Ann Rev Ecol Evol Syst 37:637–669
Portmann RW, Solomon S, Hegerl GC (2009) Spatial and seasonal patterns in climate change, temperatures, and precipitation across the United States. Proceed Nat Acad Sci USA 106:7324–7329
Relyea RA (2003) Predator cues and pesticides: a double dose of danger for amphibians. Ecol Appl 13:1515–1521
Roche BM, Fritz RS (1997) Genetics of resistance of Salix sericea to a diverse community of herbivores. Evolution 51:1490–1498
Rouault G, Candau J-N, Lieutier F, Nageleisen L-M, Martin J-C, Warzee N (2006) Effects of drought and heat on forest insect populations in relation to the 2003 drought in Western Europe. Ann For Sci 63:613–624
Roy BA, Gusewell S, Harte J (2004) Response of plant pathogens and herbivores to a warming experiment. Ecology 85:2570–2581
Rypstra AL, Marshall SD (2005) Augmentation of soil detritus affects the spider community and herbivory in a soybean agroecosystem. Entomol Exp Appl 116:149–157
SAS Institute Inc (2009) SAS/STAT user’s guide, 2nd edn. SAS Institute Inc, Cary
Shimada S, Kokubun M, Shibata H, Satsui S (1992) Effect of water supply and defoliation on photosynthesis, transpiration and yield of soybean. Jpn J Crop Sci 61:264–270
Showler AT, Moran PJ (2003) Effects of drought stressed cotton, Gossypium hirsutum L., on beet armyworm, Spodoptera exigua (Hubner), oviposition, and larval feeding preferences and growth. J Chem Ecol 29:1997–2011
Silva EN, Ferreira-Silva SL, Fontenele AD, Ribeiro RV, Viegas RA, Silveira JAG (2010) Photosynthetic changes and protective mechanisms against oxidative damage subjected to isolated and combined drought and heat stresses in Jatropha curcas plants. J Plant Physiol 167:1157–1164
Sinclair TR (2011) Challenges in breeding for yield increase for drought. Trends Plant Sci 16:289–293
Stinchcombe JR, Rausher MD (2001) Diffuse selection on resistance to deer herbivory in the ivy leaf morning glory, Ipomoea hederacea. Am Nat 158:376–388
Strauss SY, Siemens DH, Decher MB, Mitchell-Olds T (1999) Ecological costs of plant resistance to herbivores in the currency of pollination. Evolution 53:1105–1113
Turnipseed SG, Kogan M (1976) Soybean entomology. Ann Rev Entomol 21:247–282
Tylianakis JM, Didham RK, Bascompte J, Wardle DA (2008) Global change and species interactions in terrestrial ecosystems. Ecol Lett 11:1351–1363
UNFCCC (2009) Decision 2/CP.15 Copenhagen Accord pp 4–10. http://unfccc.int/documentation/documents/advanced_search/items/6911.php?priref=600005735#beg
van Mantgem PJ, Stephenson NL, Byrne JC, Daniels LD, Franklin JF, Fule PZ, Harmon ME, Larson AJ, Smith JM, Taylor AH, Veblen TT (2009) Widespread increase of tree mortality rates in the western United States. Science 323:521–524
Walter J, Hein R, Auge H, Beierkuhnlein C, Loeffler S, Reifenrath K, Schaedler M, Weber M, Jentsch A (2012) How do extreme drought and plant community composition affect host plant metabolites and herbivore performance? Arthropod-Plant Interact 6:15–25
Walther GR, Post E, Convey P, Menzel A, Parmesan C, Beebee TJC, Fromentin JM, Hoegh-Guldberg O, Bairlein F (2002) Ecological responses to recent climate change. Nature 416:389–395
White TCR (1984) The abundance of invertebrate herbivores in relation to the availability of nitrogen in stressed food plants. Oecologia 63:90–105
White TCR (2009) Plant vigour versus plant stress: a false dichotomy. Oikos 118:807–808
White JW, Hoogenboom G, Kimball BA, Wall GW (2011) Methodologies for simulating impacts of climate change on crop production. Field Crops Res 124:357–368
Whitham TG, Bailey JK, Schweitzer JA, Shuster SM, Bangert RK, LeRoy CJ, Lonsdorf EV, Allan GJ, diFazio SP, Potts BM, Fischer DG, Gehring CA, Lindroth RL, Marks JC, Hart SC, Wimp GM, Wooley SC (2006) A framework for community and ecosystem genetics: from genes to ecosystems. Nat Rev Gen 7:510–523
Williams JW, Jackson ST (2007) Novel climates, no-analog communities, and ecological surprises. Front Ecol Environ 5:475–482
Willis CG, Ruhfel B, Primack RB, Miller-Rushing AJ, Davis CC (2008) Phylogenetic patterns of species loss in Thoreau’s woods are driven by climate change. Proceed Nat Acad Sci USA 105:17029–17033
Wu XL, Ren CW, Joshi T, Vuong T, Xu D, Nguyen HT (2010) SNP discovery by high-throughput sequencing in soybean. BMC Genomics 11:469
Zavala JA, Casteel CL, DeLucia EH, Berenbaum MR (2008) Anthropogenic increase in carbon dioxide compromises plant defense against invasive insects. Proceed Nat Acad Sci USA 105:5129–5133
Zhu S, Walker DR, Boerma HR, All JN, Parrott WA (2006) Fine mapping of a major insect resistance QTL in soybean and its interaction with minor resistance QTLs. Crop Sci 46:1094–1099
Zhu S, Walker DR, Warrington CV, Parrott WA, All JN, Wood ED, Boerma HR (2007) Registration of four soybean germplasm lines containing defoliating insect resistance QTLs from PI 229358 introgressed into ‘Benning’. J Plant Regist 1:162–163
Acknowledgments
We thank the staff at the NCSU Phytotron and NCSU Method Road Greenhouse Facility who provided logistical support with experiments, especially Janet Shurtleff, Carole Saravitz, and Neal Robertson. Fred Gould supplied Heliothis virescens for Experiments 1 and 2. The USDA-ARS supplied seeds, and additional seed suppliers are identified in Online Supplemental Table 1. Ashley Childress, Diego Carmona, Erika Hersch-Green, Cassi Myburg, Robert San Miguel, and Nash Turley provided assistance with experiments. C. Thomsen provided comments on an earlier draft of the paper. This research was funded by USDA-ARS (TEC), North Carolina State University (RG, MTJJ), an NSERC Discovery grant, the Canadian Foundation for Innovation, and the Ontario Government (MTJJ).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling Editor: Michael Smith.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grinnan, R., Carter, T.E. & Johnson, M.T.J. Effects of drought, temperature, herbivory, and genotype on plant–insect interactions in soybean (Glycine max). Arthropod-Plant Interactions 7, 201–215 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11829-012-9234-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11829-012-9234-z