Abstract
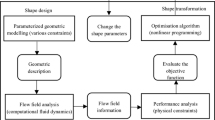
Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) plays a major role in predicting the flow behavior of a ship. With the development of fast computers and robust CFD software, CFD has become an important tool for designers and engineers in the ship industry. In this paper, the hull form of a ship was optimized for total resistance using CFD as a calculation tool and a genetic algorithm as an optimization tool. CFD based optimization consists of major steps involving automatic generation of geometry based on design parameters, automatic generation of mesh, automatic analysis of fluid flow to calculate the required objective/cost function, and finally an optimization tool to evaluate the cost for optimization. In this paper, integration of a genetic algorithm program, written in MATLAB, was carried out with the geometry and meshing software GAMBIT and CFD analysis software FLUENT. Different geometries of additive bulbous bow were incorporated in the original hull based on design parameters. These design variables were optimized to achieve a minimum cost function of “total resistance”. Integration of a genetic algorithm with CFD tools proves to be effective for hull form optimization.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen YJ, Chau SW, Kouth JS (2002). Application of two-phase fluid approach for free-surface ship flow simulation. Journal of the Chinese Institute of Engineers, 25(2), 179–188.
Dejhalla R, Mrša Z, Vuković S (2001). Application of genetic algorithm for ship hull form optimization. Int. Shipbuild. Progr., 48(2), 117–133.
Dejhalla R, Mrša Z, Vuković S (2002). A genetic algorithm approach to the problem of minimum ship wave resistance. Marine Technology, 39(2), 187–195.
Fonfach JM, Soares CG (2010). Improving the resistance of a series 60 vessel with a CFD code. Proceedings of the Fifth European Conference on Computational Fluid Dynamics (ECCOMAS CFD), Lisbon, Portugal, 1–14.
Holland JH (1975). Adaptation in natural and artificial systems. University of Michigan Press, Ann Arbor, Michigan.
Jacquin E, Bellevere D, Alessandrini B, Cordier S (2002). Yacht optimisation based on genetic algorithm using RANSE solver. High Performance Yacht Design Conference, Auckland, 1–8.
Kracht AM (1978). Design of bulbous bows. SNAME Transactions, 86, 197–217.
Lin CW, Percival S, Gotimer EH (1995). Viscous drag calculations for ship hull geometry. 9th International Conference on Numerical Methods in Laminar and Turbulent Flow, Atlanta, GA, 1209–1222.
Özdemir YH, Bayraktar S, Yılmaz T (2007). Computational investigation of a hull. 2nd International Conference on Maritime Research and Transportation ICMRT, Ischia, Naples, Italy, 145–149.
Perez F, Suarez JA, Clemente JA (2007). Geometric modelling of bulbous bows with the use of non-uniform rational B-spline surfaces. Journal of Marine Science and Technology, 12, 83–94.
Shahid M, Huang DB (2011). Resistance calculations of trimaran hull form using computational fluid dynamics. Fourth International Joint Conference on Computational Sciences and Optimization, Kunming/Lijiang, 81–85.
Takeshi H, Hino T, Hinatsu M, Tsukada Y, Fujisawa J (1987). ITTC cooperative expreiments on series 60 model at ship research institute — flow measurements and resistance tests. Ship Res. Inst. Japan (Papers), Suppt. 9, 1–48.
Zhang ZR, Liu H, Zhu SP, Zhao F (2006). Application of CFD in ship engineering design practice and ship hydrodynamics. Journal of Hydrodynamics, 18(3), 315–322.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Shahid Mahmood is a PhD candidate at Harbin Engineering University. He received a Bachelor and a Master of Science degree in Mechanical Engineering from Eastern Mediterranean University. His research interests are in computational fluid dynamics, marine hydrodynamics, ship resistance, and shape optimization.
Debo Huang was born in 1943. He is a Professor at Harbin Engineering University. His current research interests include ship hydrodynamics and resistance, high performance vessels, and optimization.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mahmood, S., Huang, D. Computational fluid dynamics based bulbous bow optimization using a genetic algorithm. J. Marine. Sci. Appl. 11, 286–294 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11804-012-1134-1
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11804-012-1134-1