Abstract
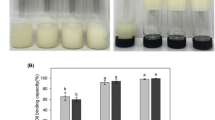
Virgin olive oil and beeswax were used to prepare four oleogel emulsions (EM1–EM4) through simultaneous oleogelation emulsification, and these oleogels were compared with breakfast margarine (BM). The melting temperatures of the oleogel emulsions ranged from 52.29 to 57.52 °C, while it was 40.36 °C for the BM sample. Similarly, the solid fat content (SFC) of the oleogel emulsions was between 3.57 and 3.68 % at 20 °C, and that of BM was 7.70 %. Except the EM3 sample, all oleogel emulsions exhibited mechanical stability. The firmness and stickiness values of the oleogel emulsion samples were lower than those of the BM sample, but they remained almost constant through 90 days of storage. Furthermore, the fine water droplets and needle-like beeswax crystals within the continuous oil phase were stable during the storage. The X-ray diffraction patterns of the samples revealed that the oleogel emulsions contain crystals similar to β′ polymorphs, characterized by a homogenous, smooth and fine texture. The presence of inter and intramolecular hydrogen bonds was proved by Fourier Transform Infrared (FT-IR) measurements. The developed oleogel emulsions were found to be stable in terms of texture, color and oxidation during 90 days of storage. In conclusion, these oleogel emulsion products can be used as margarine/spread stocks.










Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BM:
-
Breakfast margarine
- BW:
-
Beeswax
- CFT:
-
Crystal formation time
- FT-IR:
-
Fourier Transform Infrared
- HLB:
-
Hydrophilic-lipophilic balance
- MS:
-
Mechanical stability
- PLM:
-
Polarized light microscope
- SFC:
-
Solid fat content
- VOO:
-
Virgin olive oil
- XRD:
-
X-ray diffraction
References
McWilliams M (1993) Foods: experimental perspectives, 2nd edn. Macmillian, New York
O’Brien RD (2004) Fats and oils: formulating and processing for applications. CRC Press, New York
Chrysam MM (1996) Margarines and spreads. In: Hui YH (ed) Bailey’s industrial oil and fat products, vol 3. Wiley-Interscience, New York, pp 65–114
Codex (2008) Codex for margarines (number: 2008/21). Ankara, Turkey
Pernetti M, van Malssen KF, Flöter E, Bot A (2007) Structuring of edible oils by alternatives to crystalline fat. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 12:221–231
Bot A, Veldhuizen YSJ, den Adel R, Roijers EC (2009) Non-TAG structuring of edible oils and emulsions. Food Hydrocoll 23:1184–1189
Hughes NE, Marangoni AG, Wright AJ, Rogers MA, Rush JWE (2009) Potential food applications of edible oil oleogels. Trends Food Sci Technol 20:470–480
Marangoni A, Garti N (2011) Food oil gels: new strategies for structuring edible oils. Inform 22:317–320
Co ED, Marangoni AG (2012) Oleogels: an alternative edible oil-structuring method. J Am Oil Chem Soc 89:749–780
Duffy N, Blonk HCG, Beindorff CM, Cazade M, Bot A, Duchateau GSMJE (2009) Oleogel-based emulsion systems, micro-structural features and impact on in vitro digestion. J Am Oil Chem Soc 86:733–741
Bot A, den Adel R, Regkos C, Sawalha H, Venema P, Flöter E (2011) Structuring in β-sitosterol + γ-oryzanol-based emulsion gels during various stages of a temperature cycle. Food Hydrocolloid 25:639–646
Lupi FR, Gabriele D, de Cindio B, Sanchez MC, Gallegos C (2011) A rheological analysis of structured water-in-olive oil emulsions. J Food Eng 107:296–303
Toro-Vazquez JF, Mauricio-Pérez R, González-Chávez MM, Sánchez-Becerril M, Ornelas-Paz JJ, Pérez-Martínez JD (2013) Physical properties of oleogels and water in oil emulsions structured by mixtures of candelilla wax and monoglycerides. Food Res Int 54:1360–1368
Patel AR, Schatteman D, De Vos WH, Lesaffer A, Dewettinck K (2013) Preparation and rheological characterization of shellac oleogels and oleogel-based emulsions. J Colloid Interface Sci 411:114–121
Patel AR, Rodriguez Y, Lesaffer A, Dewettinck K (2014) High internal phase emulsion gels (HIPE-gels) prepared using food-grade components. RSC Adv 4:18136–18140
Patel AR, Rajarethinem PS, Cludts N, Lewille B, De Vos WH, Lesaffer A, Dewettinck K (2014) Biopolymer-based structuring of liquid oil into soft solids and oleogels using water-continuous emulsions as templates. Langmuir. doi:10.1021/la502829u
Pradhan S, Sagiri SS, Singh VK, Pal K, Ray SS, Pradhan DK (2014) Palm oil-based organogels and microemulsions for delivery of antimicrobial drugs. J Appl Polym Sci. doi:10.1002/APP.39979
Hwang HS, Singh M, Bakota EL, Winkler-Moser JK, Kim S (2013) Margarine from oleogels of plant wax and soybean oil. J Am Oil Chem Soc 90:1705–1712
Hwang HS, Singh M, Winkler-Moser JK, Bakota EL, Liu SX (2014) Preparation of margarines from organogels of sunflower wax and vegetable oils. J Food Sci 79(10):C1926–C1932
Öğütcü M, Yılmaz E (2014) Properties and stability of hazelnut oil organogels with beeswax and monoglyceride. J Am Oil Chem Soc 91:1007–1017
De Morais JM, dos Santos ODH, Delicato T, Gonçalves RA, da Rocha-Filho PA (2006) Physicochemical characterization of canola oil/water nano-emulsions obtained by determination of required HLB number and emulsion phase inversion methods. J Dispersion Sci Technol 27:109–115
Dassanayake LSK, Kodali DR, Ueno S, Sato K (2009) Physical properties of rice bran wax in bulk and oleogels. J Am Oil Chem Soc 86:1163–1173
Chen HH, Chiu EM, Huang JR (1997) Color and gel-forming properties of horse mackerel (Trachurus japonicus) as related to Washington conditions. J Food Sci 62:985–991
AOCS (1997) Peroxide value, acetic acid-chloroform method, Cd 8-53. Official Methods and Recommended Practices of the American Oil Chemists’ Society, 5th edn. AOCS Press, Champaign, IL
Minitab (2010) Minitab 16.1.1 Statistical Software. Minitab Inc, State College, Pennsylvania
ICI (1980) The HLB system—a time-saving guide to emulsifier selection. ICI Americas Inc, Wilmington
Garcia-Ochoa F, Santos VE, Casas JA, Gomez E (2000) Xanthan gum: production, recovery, and properties. Biotechnol Adv 18:549–579
Öğütcü M, Yılmaz E (2014) Comparison of the pomegranate seed oil organogels of carnauba wax and monoglyceride. J Appl Polym Sci. doi:10.1002/APP.41343
Moskowitz HR (1987) Food texture—instrumental and sensory measurements. Marcel Dekker, New York
Szydłowska-Czerniak A, Karlovits G, Lach M, Szłyk E (2005) X-ray diffraction and differential scanning calorimetry studies of β′-β transitions in fat mixtures. Food Chem 92:133–141
den Adel R, Heussen PCM, Bot A (2010) Effect of water on self-assembled tubules in β-sitosterol + γ-oryzanol-based oleogels. J Phys: Conf Ser 247:012025
Rogers MA, Bot A, Lam RSH, Pedersen T, May T (2010) Multicomponent hollow tubules formed using phytosterol and γ-oryzanol-based compounds: an understanding of their molecular embrace. J Phys Chem A 114:8278–8285
Codex (2012) Codex for vegetable oils (number: 2012/29). Ankara, Turkey
Acknowledgments
This research was funded by the Scientific and Technical Council (TÜBİTAK) of Turkey as the COST 112O038 project within COST FA 1001 Action. The authors are grateful for the support.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Öğütcü, M., Arifoğlu, N. & Yılmaz, E. Preparation and Characterization of Virgin Olive Oil-Beeswax Oleogel Emulsion Products. J Am Oil Chem Soc 92, 459–471 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11746-015-2615-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11746-015-2615-6