Abstract
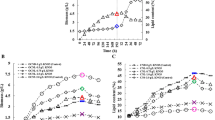
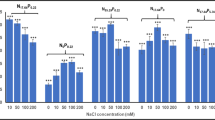
Scenedesmus sp. 14-3 was identified as a suitable candidate for producing biodiesel. The present work studied the effects of nitrogen concentration on the biomass and lipid productivity of algae, the consumption of sodium nitrate, and the two-stage N-deficient cultivation that could enhance dramatically the accumulation of biomass and lipids of Scenedesmus sp. 14-3. The two-stage N-deficient cultivation was described as follows: microalga Scenedesmus sp. 14-3 was cultured under low light intensity (LL) for 10 days in an N-deficient medium by 20 % inoculum concentration, and transferred to complete N-depletion BG11 under high light intensity (HL) for 8 days. The highest lipid content of Scenedesmus sp. 14-3 was 53.05 ± 0.08 % (10 % inoculum concentration) following the second stage of N-deficient cultivation after 8 days. For the second stage of N-deficient cultivation, the lipid content of Scenedesmus sp. 14-3 was 49.85 ± 0.22 %, which was 1.8 times higher than that under low light intensity (LL) (46–48 μmol m−2 s−1 ) in 10 days. Meanwhile, the high algal biomass productivity was around 0.10 g L−1 day−1 after the first stage of N-deficient cultivation (10 days) and the biomass productivity was around 0.037 g L−1 day−1 under the second stage of N-deficient cultivation (8 days). The comparison under different culture conditions showed a significant effect of the two-stage of N-deficient cultivation on lipid accumulation of Scenedesmus sp. 14-3. The two-stage N-deficient cultivation without centrifugation achieved a complete N-depletion condition, but the two-stage process required centrifugation which is unsuitable for commercialization and large-scale utilization. In summary, two-stage N-deficient cultivation is a more suitable and effective culture method for commercial applications and dramatic accumulation of lipids than the two-stage process.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Prabakaran P, Ravindran A (2012) Scenedesmus as a potential source of biodiesel among selected microalgae. Curr Sci 102(4):616–620
Weyer KM, Bush DR, Darzins A, Willson BD (2010) Theoretical maximum algal oil production. Bioenerg Res 3(2):204–213
Mutanda T, Ramesh D, Karthikeyan S, Kumari S, Anandraj A, Bux F (2011) Bioprospecting for hyper-lipid producing microalgal strains for sustainable biofuel production. Bioresour Technol 102(1):57–70
Chen Z, Gong Y, Fang X, Hu H (2012) Scenedesmus sp. NJ-1 isolated from Antarctica: a suitable renewable lipid source for biodiesel production. World J Microb Biot 28:3219–3225
Mandal S, Mallick N (2011) Waste utilization and biodiesel production by the green microalga Scenedesmus obliquus. Appl Environ Microb 77(1):374–377
de Queiroz JC, de Melo Ferreira AC, da Costa ACA (2012) The growth of Monoraphidium sp. and Scenedesmus sp. cells in the presence of thorium. Sci World J 2012:1–8. Art ID 592721
Yeesang C, Cheirsilp B (2011) Effect of nitrogen, salt, and iron content in the growth medium and light intensity on lipid production by microalgae isolated from freshwater sources in Thailand. Bioresour Technol 102(3):3034–3040
Chu FF, Chu PN, Cai PJ, Li WW, Lam PKS, Zeng RJ (2013) Phosphorus plays an important role in enhancing biodiesel productivity of Chlorella vulgaris under nitrogen deficiency. Bioresour Technol 134:341–346
Pokora W, Aksmann A, Tukaj Z (2011) Functional characteristics of green alga Scenedesmus obliquus (Chlorophyceae): 276-6 wild type and its two photosystems deficient mutants cultured under photoautotrophic, mixotrophic and heterotrophic conditions. Phycol Res 59(4):259–268
Jin H-F, Lim B-R, Lee K (2006) Influence of nitrate feeding on carbon dioxide fixation by microalgae. J Environ Sci Heal A 41(12):2813–2824
Feng D, Chen Z, Xue S, Zhang W (2011) Increased lipid production of the marine oleaginous microalga Isochrysis zhangjiangensis (Chrysophyta) by nitrogen supplement. Bioresour Technol 102(12):6710–6716
Li X, Liao X, Chen B, Wang (2014) Improvement of biomass and lipid content of Scenedesmus sp. by two-step cultivation. China Oil Fat 39(5):53–56
Sun X, Cao Y, Xu H, Liu Y, Sun JR, Qiao DR, Cao Y (2014) Effect of nitrogen-starvation, light intensity and iron on triacylglyceride/carbohydrate production and fatty acid profile of Neochloris oleoabundans HK-129 by a two-stage process. Bioresour Technol 155:204–212
Mujtaba G, Choi W, Lee C-G, Lee K (2012) Lipid production by Chlorella vulgaris after a shift from nutrient-rich to nitrogen starvation conditions. Bioresour Technol 123:279–283
Liu J, Yuan C, Hu G (2012) Li F (2012) Effects of light intensity on the growth and lipid accumulation of microalga Scenedesmus sp. 11–1 under nitrogen limitation. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 166:2127–2137
Li Y, Horsman M, Wang B, Wu N, Lan CQ (2008) Effects of nitrogen sources on cell growth and lipid accumulation of green alga Neochloris oleoabundans. Appl Microbiol Biot 81(4):629–636
Beschkov V, Velizarov S, Agathos S, Lukova V (2004) Bacterial denitrification of waste water stimulated by constant electric field. Biochem Eng J 17(2):141–145
Bligh EG, Dyer WJ (1959) A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Bioch Physiol 37(8):911–917
De la Jara A, Mendoza H, Martel A et al (2003) Flow cytometric determination of lipid content in a marine dinoflagellate Crypthecodinium cohnii. J Appl Phycol 15(5):433–438
Doan TTY, Sivaloganathan B, Obbard JP (2011) Screening of marine microalgae for biodiesel feedstock. Biomass Bioenerg 35(7):2534–2544
Lin Q, Lin J (2011) Effects of nitrogen source and concentration on biomass and oil production of a Scenedesmus rubescens like microalga. Bioresour Technol 102(2):1615–1621
Xin L, Hu HY, Ke G, Sun YX (2010) Effects of different nitrogen and phosphorus concentrations on the growth, nutrient uptake, and lipid accumulation of a freshwater microalga Scenedesmus sp. Bioresour Technol 101(14):5494–5500
Narendar P (2010) Screening and identification of everglades algal isolates for biodiesel production. FIU Electron Theses Dissertation 11(5):287–383
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by Development and Reform Commission of Fujian Province of China ([2011]1598), Agriculture Science Technology Achievement Transformation Fund of Ministry of Science and Technology of China (No.2013GB2C400228), and Southern Ocean Research Center of Xiamen.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Wang, M., Liao, X. et al. Two Stages of N-Deficient Cultivation Enhance the Lipid Content of Microalga Scenedesmus sp.. J Am Oil Chem Soc 92, 503–512 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11746-015-2613-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11746-015-2613-8