Abstract
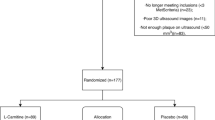
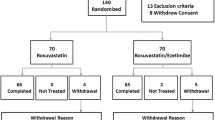
Lipoprotein (a) [Lp(a)] is an independent risk factor for cardiovascular disease. There are currently limited therapeutic options to lower Lp(a) levels. l-Carnitine has been reported to reduce Lp(a) levels. The aim of this study was to compare the effect of l-carnitine/simvastatin co-administration with that of simvastatin monotherapy on Lp(a) levels in subjects with mixed hyperlipidemia and elevated Lp(a) concentration. Subjects with levels of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) >160 mg/dL, triacylglycerol (TAG) >150 mg/dL and Lp(a) >20 mg/dL were included in this study. Subjects were randomly allocated to receive l-carnitine 2 g/day plus simvastatin 20 mg/day (N = 29) or placebo plus simvastatin 20 mg/day (N = 29) for a total of 12 weeks. Lp(a) was significantly reduced in the l-carnitine/simvastatin group [−19.4%, from 52 (20–171) to 42 (15–102) mg/dL; p = 0.01], but not in the placebo/simvastatin group [−6.7%, from 56 (26–108) to 52 (27–93) mg/dL, p = NS versus baseline and p = 0.016 for the comparison between groups]. Similar significant reductions in total cholesterol, LDL-C, apolipoprotein (apo) B and TAG were observed in both groups. Co-administration of l-carnitine with simvastatin was associated with a significant, albeit modest, reduction in Lp(a) compared with simvastatin monotherapy in subjects with mixed hyperlipidemia and elevated baseline Lp(a) levels.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ALT:
-
Alanine aspartate aminotransferase
- ANCOVA:
-
Analysis of covariance
- apo:
-
Apolipoprotein
- AST:
-
Aspartate aminotransferase
- ATP:
-
Adenosine triphosphate
- CETP:
-
Cholesteryl ester transfer protein
- CK:
-
Creatine phosphokinase
- eGFR:
-
Estimated glomerular filtration rate
- HDL-C:
-
High-density lipoprotein cholesterol
- HOMA:
-
Homeostasis model assessment
- LDL-C:
-
Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol
- LDL-Ccor:
-
LDL-C levels corrected for Lp(a) concentration
- Lp(a):
-
Lipoprotein (a)
- MDRD:
-
Modification of diet in renal disease
- PCSK9:
-
Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
- T2DM:
-
Type 2 diabetes mellitus
- TC:
-
Total cholesterol
- TAG:
-
Triacylglycerol
- TSH:
-
Thyroid stimulating hormone
- ULN:
-
Upper limit of normal
References
Collaboration Cholesterol Treatment Trialists, Fulcher J, O’Connell R, Voysey M, Emberson J, Blackwell L, Mihaylova B, Simes J, Collins R, Kirby A, Colhoun H, Braunwald E, La Rosa J, Pedersen TR, Tonkin A, Davis B, Sleight P, Franzosi MG, Baigent C, Keech A (2015) Efficacy and safety of LDL-lowering therapy among men and women: meta-analysis of individual data from 174,000 participants in 27 randomised trials. Lancet 385:1397–1405
Marcovina SM, Albers JJ (2016) Lipoprotein (a) measurements for clinical application. J Lipid Res 57:526–537
Kronenberg F, Utermann G (2013) Lipoprotein(a): resurrected by genetics. J Intern Med 273:6–30
Tsimikas S, Hall JL (2012) Lipoprotein(a) as a potential causal genetic risk factor of cardiovascular disease: a rationale for increased efforts to understand its pathophysiology and develop targeted therapies. J Am Coll Cardiol 60:716–721
Kronenberg F (2016) Human genetics and the causal role of lipoprotein(a) for various diseases. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther 30:87–100
Enkhmaa B, Anuurad E, Berglund L (2016) Lipoprotein (a): impact by ethnicity and environmental and medical conditions. J Lipid Res 57:1111–1125
Banach M (2016) Lipoprotein (a)—we know so much yet still have much to learn. J Am Heart Assoc 5(4). doi:10.1161/JAHA.116.003597
Galvano F, Malaguarnera M, Vacante M, Motta M, Russo C, Malaguarnera G, D’Orazio N, Malaguarnera L (2010) The physiopathology of lipoprotein (a). Front Biosci (Schol Ed) 2:866–875
Kotani K, Serban MC, Penson P, Lippi G, Banach M (2016) Evidence-based assessment of lipoprotein(a) as a risk biomarker for cardiovascular diseases—Some answers and still many questions. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci 53:370–378
Nordestgaard BG, Chapman MJ, Ray K, Boren J, Andreotti F, Watts GF, Ginsberg H, Amarenco P, Catapano A, Descamps OS, Fisher E, Kovanen PT, Kuivenhoven JA, Lesnik P, Masana L, Reiner Z, Taskinen MR, Tokgozoglu L, Tybjaerg-Hansen A, European Atherosclerosis Society Consensus P (2010) Lipoprotein(a) as a cardiovascular risk factor: current status. Eur Heart J 31:2844–2853
Emerging Risk Factors Collaboration, Erqou S, Kaptoge S, Perry PL, Di Angelantonio E, Thompson A, White IR, Marcovina SM, Collins R, Thompson SG, Danesh J (2009) Lipoprotein(a) concentration and the risk of coronary heart disease, stroke, and nonvascular mortality. JAMA 302:412–423
Forbes CA, Quek RG, Deshpande S, Worthy G, Wolff R, Stirk L, Kleijnen J, Gandra SR, Djedjos S, Wong ND (2016) The relationship between Lp(a) and CVD outcomes: a systematic review. Lipids Health Dis 15:95
Malaguarnera M, Vacante M, Russo C, Malaguarnera G, Antic T, Malaguarnera L, Bella R, Pennisi G, Galvano F, Frigiola A (2013) Lipoprotein(a) in cardiovascular diseases. Biomed Res Int 2013:650989
Thanassoulis G (2016) Lipoprotein (a) in calcific aortic valve disease: from genomics to novel drug target for aortic stenosis. J Lipid Res 57:917–924
Malaguarnera G, Gagliano C, Bucolo C, Vacante M, Salomone S, Malaguarnera M, Leonardi DG, Motta M, Drago F, Avitabile T (2013) Lipoprotein(a) serum levels in diabetic patients with retinopathy. Biomed Res Int 2013:943505
Erqou S, Thompson A, Di Angelantonio E, Saleheen D, Kaptoge S, Marcovina S, Danesh J (2010) Apolipoprotein(a) isoforms and the risk of vascular disease: systematic review of 40 studies involving 58,000 participants. J Am Coll Cardiol 55:2160–2167
Clarke R, Peden JF, Hopewell JC, Kyriakou T, Goel A, Heath SC, Parish S, Barlera S, Franzosi MG, Rust S, Bennett D, Silveira A, Malarstig A, Green FR, Lathrop M, Gigante B, Leander K, de Faire U, Seedorf U, Hamsten A, Collins R, Watkins H, Farrall M, Consortium P (2009) Genetic variants associated with Lp(a) lipoprotein level and coronary disease. N Engl J Med 361:2518–2528
Nordestgaard BG, Chapman MJ, Humphries SE, Ginsberg HN, Masana L, Descamps OS, Wiklund O, Hegele RA, Raal FJ, Defesche JC, Wiegman A, Santos RD, Watts GF, Parhofer KG, Hovingh GK, Kovanen PT, Boileau C, Averna M, Boren J, Bruckert E, Catapano AL, Kuivenhoven JA, Pajukanta P, Ray K, Stalenhoef AF, Stroes E, Taskinen MR, Tybjaerg-Hansen A, European Atherosclerosis Society Consensus P (2013) Familial hypercholesterolaemia is underdiagnosed and undertreated in the general population: guidance for clinicians to prevent coronary heart disease: consensus statement of the European Atherosclerosis Society. Eur Heart J 34:3478–3490a
Irudayam J, Sivaraj S, Nirmala P (2014) Effect of statins on lipoprotein (a) in dyslipidemic patients. Int J Basic Clin Pharmacol 3:1024–1029
Raal FJ, Giugliano RP, Sabatine MS, Koren MJ, Langslet G, Bays H, Blom D, Eriksson M, Dent R, Wasserman SM, Huang F, Xue A, Albizem M, Scott R, Stein EA (2014) Reduction in lipoprotein(a) with PCSK9 monoclonal antibody evolocumab (AMG 145): a pooled analysis of more than 1,300 patients in 4 phase II trials. J Am Coll Cardiol 63:1278–1288
Tsimikas S, Viney NJ, Hughes SG, Singleton W, Graham MJ, Baker BF, Burkey JL, Yang Q, Marcovina SM, Geary RS, Crooke RM, Witztum JL (2015) Antisense therapy targeting apolipoprotein(a): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 1 study. Lancet 386:1472–1483
Nicholls SJ, Ruotolo G, Brewer HB, Wang MD, Liu L, Willey MB, Deeg MA, Krueger KA, Nissen SE (2016) Evacetrapib alone or in combination with statins lowers lipoprotein(a) and total and small LDL particle concentrations in mildly hypercholesterolemic patients. J Clin Lipidol 10(519–527):e514
Serban MC, Sahebkar A, Mikhailidis DP, Toth PP, Jones SR, Muntner P, Blaha MJ, Andrica F, Martin SS, Borza C, Lip GY, Ray KK, Rysz J, Hazen SL, Banach M (2016) Impact of l-carnitine on plasma lipoprotein(a) concentrations: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Sci Rep 6:19188
Li KM, Wilcken DE, Dudman NP (1994) Effect of serum lipoprotein(a) on estimation of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol by the Friedewald formula. Clin Chem 40:571–573
Galvano F, Volti GL, Malaguarnera M, Avitabile T, Antic T, Vacante M (2009) Effects of simvastatin and carnitine versus simvastatin on lipoprotein(a) and apoprotein(a) in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Expert Opin Pharmacother 10:1875–1882
Solfrizzi V, Capurso C, Colacicco AM, D’Introno A, Fontana C, Capurso SA, Torres F, Gadaleta AM, Koverech A, Capurso A, Panza F (2006) Efficacy and tolerability of combined treatment with l-carnitine and simvastatin in lowering lipoprotein(a) serum levels in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Atherosclerosis 188:455–461
Maebashi M, Kawamura N, Sato M, Imamura A, Yoshinaga K (1978) Lipid-lowering effect of carnitine in patients with type-IV hyperlipoproteinaemia. Lancet 2:805–807
Brescia F, Balestra E, Iasella MG, Damato AB (2002) Effects of combined treatment with simvastatin and l-carnitine on triglyceride levels in diabetic patients with hyperlipidaemia. Clin Drug Investig 22:23–28
Sirtori CR, Calabresi L, Ferrara S, Pazzucconi F, Bondioli A, Baldassarre D, Birreci A, Koverech A (2000) l-Carnitine reduces plasma lipoprotein(a) levels in patients with hyper Lp(a). Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 10:247–251
Derosa G, Cicero AF, Gaddi A, Mugellini A, Ciccarelli L, Fogari R (2003) The effect of l-carnitine on plasma lipoprotein(a) levels in hypercholesterolemic patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Clin Ther 25:1429–1439
McTaggart F, Jones P (2008) Effects of statins on high-density lipoproteins: a potential contribution to cardiovascular benefit. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther 22:321–338
Hasvold P, Thuresson M, Sundstrom J, Hammar N, Kjeldsen SE, Johansson G, Holme I, Bodegard J (2016) Association between paradoxical HDL cholesterol decrease and risk of major adverse cardiovascular events in patients initiated on statin treatment in a primary care setting. Clin Drug Investig 36:225–233
Power RA, Hulver MW, Zhang JY, Dubois J, Marchand RM, Ilkayeva O, Muoio DM, Mynatt RL (2007) Carnitine revisited: potential use as adjunctive treatment in diabetes. Diabetologia 50:824–832
Malaguarnera M, Vacante M, Avitabile T, Cammalleri L, Motta M (2009) l-Carnitine supplementation reduces oxidized LDL cholesterol in patients with diabetes. Am J Clin Nutr 89:71–76
Malaguarnera M, Vacante M, Motta M, Li Volti G, Galvano F (2009) Effect of l-carnitine on the size of low-density lipoprotein particles in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients treated with simvastatin. Metabolism 58:1618–1623
Malaguarnera M, Gargante MP, Russo C, Antic T, Vacante M, Avitabile T, Volti GL, Galvano F (2010) l-Carnitine supplementation to diet: a new tool in treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis—a randomized and controlled clinical trial. Am J Gastroenterol 105:1338–1345
Elisaf M, Bairaktari E, Katopodis K, Pappas M, Sferopoulos G, Tzallas C, Tsolas O, Siamopoulos KC (1998) Effect of l-carnitine supplementation on lipid parameters in hemodialysis patients. Am J Nephrol 18:416–421
Schmidt K, Noureen A, Kronenberg F, Utermann G (2016) Structure, function, and genetics of lipoprotein (a). J Lipid Res 57:1339–1359
Chang B, Nishikawa M, Nishiguchi S, Inoue M (2005) l-Carnitine inhibits hepatocarcinogenesis via protection of mitochondria. Int J Cancer 113:719–729
Rajasekar P, Anuradha CV (2007) l-Carnitine inhibits protein glycation in vitro and in vivo: evidence for a role in diabetic management. Acta Diabetol 44:83–90
Riches K, Porter KE (2012) Lipoprotein(a): cellular effects and molecular mechanisms. Cholesterol 2012:923289
Boffa MB, Koschinsky ML (2016) Lipoprotein (a): truly a direct prothrombotic factor in cardiovascular disease? J Lipid Res 57:745–757
Kotani K, Sahebkar A, Serban C, Andrica F, Toth PP, Jones SR, Kostner K, Blaha MJ, Martin S, Rysz J, Glasser S, Ray KK, Watts GF, Mikhailidis DP, Banach M, Lipid, and Blood Pressure Meta-analysis Collaboration G (2015) Tibolone decreases lipoprotein(a) levels in postmenopausal women: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 12 studies with 1009 patients. Atherosclerosis 242:87–96
Sahebkar A, Serban C, Ursoniu S, Banach M (2016) Effect of garlic on plasma lipoprotein(a) concentrations: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled clinical trials. Nutrition 32:33–40
Dinicolantonio JJ, Niazi AK, McCarty MF, Lavie CJ, Liberopoulos E, O’Keefe JH (2014) l-Carnitine for the treatment of acute myocardial infarction. Rev Cardiovasc Med 15:52–62
Koeth RA, Levison BS, Culley MK, Buffa JA, Wang Z, Gregory JC, Org E, Wu Y, Li L, Smith JD, Tang WH, DiDonato JA, Lusis AJ, Hazen SL (2014) γ-Butyrobetaine is a proatherogenic intermediate in gut microbial metabolism of l-carnitine to TMAO. Cell Metab 20:799–812
Koeth RA, Wang Z, Levison BS, Buffa JA, Org E, Sheehy BT, Britt EB, Fu X, Wu Y, Li L, Smith JD, DiDonato JA, Chen J, Li H, Wu GD, Lewis JD, Warrier M, Brown JM, Krauss RM, Tang WH, Bushman FD, Lusis AJ, Hazen SL (2013) Intestinal microbiota metabolism of l-carnitine, a nutrient in red meat, promotes atherosclerosis. Nat Med 19:576–585
Seldin MM, Meng Y, Qi H, Zhu W, Wang Z, Hazen SL, Lusis AJ, Shih DM (2016) Trimethylamine N-oxide promotes vascular inflammation through signaling of mitogen-activated protein kinase and nuclear factor-κB. J Am Heart Assoc 5(2). doi:10.1161/JAHA.115.002767
Skagen K, Troseid M, Ueland T, Holm S, Abbas A, Gregersen I, Kummen M, Bjerkeli V, Reier-Nilsen F, Russell D, Svardal A, Karlsen TH, Aukrust P, Berge RK, Hov JE, Halvorsen B, Skjelland M (2016) The carnitine-butyrobetaine-trimethylamine-N-oxide pathway and its association with cardiovascular mortality in patients with carotid atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis 247:64–69
Collins HL, Drazul-Schrader D, Sulpizio AC, Koster PD, Williamson Y, Adelman SJ, Owen K, Sanli T, Bellamine A (2016) l-Carnitine intake and high trimethylamine N-oxide plasma levels correlate with low aortic lesions in ApoE(−/− transgenic mice expressing CETP. Atherosclerosis 244:29–37
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
About this article
Cite this article
Florentin, M., Elisaf, M.S., Rizos, C.V. et al. l-Carnitine/Simvastatin Reduces Lipoprotein (a) Levels Compared with Simvastatin Monotherapy: A Randomized Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Study. Lipids 52, 1–9 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-016-4216-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-016-4216-z