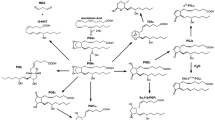
Abstract
The isoprenoid biosynthetic pathway is the source of a wide array of products. The pathway has been highly conserved throughout evolution, and isoprenoids are some of the most ancient biomolecules ever identified, playing key roles in many life forms. In this review we focus on C-10 mono-, C-15 sesqui-, and C-20 diterpenes. Evidence for interconversion between the pathway intermediates farnesyl pyrophosphate and geranylgeranly pyrophosphate and their respective metabolites is examined. The diverse functions of these molecules are discussed in detail, including their ability to regulate expression of the β-HMG-CoA reductase and Ras-related proteins. Additional topics include the mechanisms underlying the apoptotic effects of select isoprenoids, antiulcer activities, and the disposition and degradation of isoprenoids in the environment. Finally, the significance of pharmacological manipulation of the isoprenoid pathway and clinical correlations are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CPT:
-
cholinephosphotransferase
- DMAPP:
-
dimethylallyl pyrophosphate
- DOXP:
-
deoxy-d-xylulose 5-phosphate
- DXPS:
-
deoxyxylulose 5-phosphate synthase
- FOH:
-
farnesol
- FPP:
-
farnesyl pyrophosphate
- FPPase:
-
farnesyl pyrophosphatase
- FPTase:
-
farnesyl protein transferase
- FXR:
-
farnesoid X receptor
- GGA:
-
geranylgeranylacetone
- GGOH:
-
geranylgeraniol
- GGPP:
-
geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate
- GGPTase:
-
geranylgeranyl protein transferase
- GOH:
-
geraniol
- GPP:
-
geranyl pyrophosphate
- HIDS:
-
hyper-IgD and periodic fever syndrome
- HMGR:
-
HMG-CoA reductase
- IDS:
-
isoprenyl diphosphate synthases
- IPP:
-
isopentenyl pyrophosphate
- JH:
-
juvenile hormone
- LXR:
-
liver X receptor
- MA:
-
mevalonic aciduria
- MK:
-
mevalonate kinase
- PKC:
-
protein kinase C
- PPAR:
-
peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor
- RAR:
-
retinoic acid receptor
- ROS:
-
reactive oxygen species
- RXR:
-
retinoid X receptor
References
Sacchettini, J.C., and Poulter, C.D. (1997) Creating Isoprenoid Diversity, Science 277, 1788–1789.
Summouns, R.E., Jahnke, L.L., Hope, J.M., and Logan, G.A. (1999) 2-Methylhopanoids as Biomarkers for Cyanobacterial Oxygenic Photosynthesis, Nature 400, 554–557.
Ferguson, J.J., Durr, I.F., and Rudney, H. (1959) The Biosynthesis of Mevalonic Acid, Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 45, 499–504.
Tchen, T.T. (1958) Mevalonic Kinase: Purification and Properties, J. Biol. Chem. 233, 1100–1103.
Tada, M., and Lynen, F. (1961) On the Biosynthesis of Terpenes. XIV. On the Determination of Phosphomevalonic Acid Kinase and Pyrophosphomevalonic Acid Decarboxylase in Cell Extracts, J. Biochem. 49, 758–764.
Agranoff, B.W., Eggerer, H., Henning, U., and Lynen, F. (1960) Biosynthesis of Terpenes. VII. Isopentenyl Pyrophosphate Isomerase, J. Biol. Chem. 235, 326–332.
Milstone, D.S., Vold, B.S., Glitz, D.G., and Shutt, N. (1978) Antibodies to N6-(Δ2-isopentenyl) Adenosine and Its Nucleotide: Interaction with Purified tRNAs and with Bases, Nucleosides and Nucleotides of the Isopentenyladenosine Family, Nucleic Acids Res. 5, 3439–3455.
Taya, Y., Tanaka, Y., and Nishimura, S. (1978) 5′-AMP Is a Direct Precursor of Cytokinin in Dictyostelium discoideum, Nature 271, 545–547.
Poulter, C.D., and Rilling, H.C. (1978) The Prenyl Transfer Reaction: Enzymic and Mechanistic Studies on the 1′-4 Coupling Reaction in the Terpene Biosynthetic Pathway, Acc. Chem. Res. 11, 307–313.
Croteau, R., and Purkett, P.T. (1989) Geranyl Pyrophosphate Synthase: Characterization of the Enzyme and Evidence That This Chain-Length-Specific Prenyltransferase Is Associated with Monoterpene Biosynthesis in Sage (Salvia officinalis), Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 271, 524–535.
Beytia, E., Qureshi, A.A., and Porter, J.W. (1973) Squalene Synthetase. 3. Mechanism of the Reaction, J. Biol. Chem. 248, 1856–1867.
Koyama, T., Matsubara, M., and Ogura, K. (1985) Isoprenoid Enzyme Systems of Silkworm. II. Formation of the Juvenile Hormone Skeletons by Farnesyl Pyrophosphate Synthetase II, J. Biochem. 98 (Tokyo), 457–463.
Kandutsch, A.A., Paulus, H., Levin, E., and Bloch, K. (1964) Purification of Geranylgeranyl Pyrophosphate Synthetase from Micrococcus lysodeikticus, J. Biol. Chem. 239, 2507–2515.
Reiss, Y., Goldstein, J.L., Seabra, M.C., Casey, P.J., and Brown, M.S. (1990) Inhibition of Purified p21ras Farnesyl:Protein Transferase by Cys-AAX Tetrapeptides, Cell 62, 81–88.
Moomaw, J.F., and Casey, P.J. (1992) Mammalian Protein Geranylgeranyltransferase. Subunit Composition and Metal Requirements, J. Biol. Chem. 267, 17438–17443.
Yokoyama, K., and Gelb, M.H. (1993) Purification of a Mammalian Protein Geranylgeranyltransferase. Formation and Catalytic Properties of an Enzyme-Geranylgeranyl Pyrophosphate Complex, J. Biol. Chem. 268, 4055–4060.
Armstrong, S.A., Seabra, M.C., Sudhof, T.C., Goldstein, J.L., and Brown, M.S. (1993) cDNA Cloning and Expression of the Alpha and Beta Subunits of Rat Rab Geranylgeranyl Transferase, J. Biol. Chem. 268, 12221–12229.
Wang, K.C., and Ohnuma, S. (2000) Isoprenyl Diphosphate Synthases, Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1529, 33–48.
Teclebrhan, H., Olsson, J., Swiezewska, E., and Dallner, G. (1993) Biosynthesis of the Side Chain of Ubiquinone: trans-Prenyltransferase in Rat Liver Microsomes, J. Biol. Chem. 268, 23081–23086.
Matsuoka, S., Sagami, H., Kurisaki, A., and Ogura, K. (1991) Variable Product Specificity of Microsomal Dehydrodolichyl Diphosphate Synthase from Rat Liver, J. Biol. Chem. 266, 3464–3468.
Ibata, K., Mizuno, M., Takigawa, T., and Tanaka, Y. (1983) Long-Chain Betulaprenol-Type Polyprenols from the Leaves of Ginkgo biloba, Biochem. J. 213, 305–311.
Fujisaki, S., Hara, H., Nishimura, Y., Horiuchi, K., and Nishino, T. (1990) Cloning and Nucleotide Sequence of the ispA Gene Responsible for Farnesyl Diphosphate Synthase Activity in Escherichia coli, J. Biochem. (Tokyo) 108, 995–1000.
Apfel, C.M., Takacs, B., Fountoulakis, M., Stieger, M., and Keck, W. (1999) Use of Genomics to Identify Bacterial Undecaprenyl Pyrophosphate Synthetase: Cloning, Expression, and Characterization of the Essential uppS Gene, J. Bacteriol. 181, 483–492.
Ogura, K., Koyama, T., and Sagami, H. (1997) Polyprenyl Diphosphate Synthases, Subcell. Biochem. 28, 57–87.
Kuntz, M., Romer, S., Suire, C., Hugueney, P., Weil, J.H., Schantz, R., and Camara, B. (1992) Identification of a cDNA for the Plastid-Located Geranylgeranyl Pyrophosphate Synthase from Capsicum annuum: Correlative Increase in Enzyme Activity and Transcript Level During Fruit Ripening, Plant J. 2, 25–34.
Sprenger, G.A., Schorken, U., Wiegert, T., Grolle, S., de Graaf, A.A., Taylor, S.V., Begley, T.P., Bringer-Meyer, S., and Sahm, H. (1997) Identification of a Thiamin-Dependent Synthase in Escherichia coli Required for the Formation of the 1-Deoxy-d-xylulose 5-phosphate Precursor to Isoprenoids, Thiamin, and Pyridoxol, Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 94, 12857–12862.
Lange, B.M., Wildung, M.R., McCaskill, D., and Croteau, R. (1998) A Family of Transketolases That Directs Isoprenoid Biosynthesis via a Mevalonate-Independent Pathway, Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 2100–2104.
Eisenreich, W., Schwarz, M., Cartayrade, A., Arigoni, D., Zenk, M.H., and Bacher, A. (1998) The Deoxyxylulose Phosphate Pathway of Terpenoid Biosynthesis in Plants and Microorganisms, Chem. Biol. 5, R221-R233.
Flesch, G., and Rohmer, M. (1988) Prokaryotic Hopanoids: The Biosynthesis of the Bacteriohopane Skeleton. Formation of Isoprenic Units from Two Distinct Acetate Pools and a Novel Type of Carbon/Carbon Linkage Between a Triterpene and d-Ribose, Eur. J. Biochem. 175, 405–411.
Lange, B.M., and Croteau, R. (1999) Isopentenyl Diphosphate Biosynthesis via a Mevalonate-Independent Pathway: Isopentenyl Monophosphate Kinase Catalyzes the Terminal Enzymatic Step, Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 96, 13714–13719.
Lichtenthaler, H.K., Rohmer, M., and Schwender, J. (1997) Two Independent Biochemical Pathways for Isopentenyl Diphosphate and Isoprenoid Biosynthesis in Higher Plants, Physiol. Plant. 101, 643–652.
Lange, B.M., Rujan, T., Martin, W., and Croteau, R. (2000) Isoprenoid Biosynthesis: The Evolution of Two Ancient and Distinct Pathways Across Genomes, Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 13172–13177.
Boucher, Y., and Doolittle, W.F. (2000) The Role of Lateral Gene Transfer in the Evolution of Isoprenoid Biosynthesis Pathways, Mol. Microbiol. 37, 703–716.
Flesch, G., and Rohmer, M. (1989) Prokaryotic Triterpenoids. A Novel Hopanoid from the Ethanol-Producing Bacterium Zymomonas mobilis, Biochem. J. 262, 673–675.
Rohmer, M., Knani, M., Simonin, P., Sutter, B., and Sahm, H. (1993) Isoprenoid Biosynthesis in Bacteria: A Novel Pathway for the Early Steps Leading to Isopentenyl Diphosphate, Biochem. J. 295, 517–524.
Putra, S.R., Disch, A., Bravo, J.M., and Rohmer, M. (1998) Distribution of Mevalonate and Glyceraldehyde 3-Phosphate/Pyruvate Routes for Isoprenoid Biosynthesis in Some Gram-Negative Bacteria and Mycobacteria, FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 164, 169–175.
Knöss, W., Reuter, B., and Zapp, J. (1997) Biosynthesis of the Labdane Diterpene Marrubiin in Marrubium vulgare via a Non-mevalonate Pathway, Biochem. J. 326, 449–454.
Schwender, J., Seemann, M., Lichtenthaler, H.K., and Rohmer, M. (1996) Biosynthesis of Isoprenoids (carotenoids, sterols, prenyl side-chains of chlorophylls and plastoquinone) via a Novel Pyruvate/Glyceraldehyde 3-Phosphate Non-mevalonate Pathway in the Green Alga Scenedesmus obliquus, Biochem. J. 316, 73–80.
Disch, A., and Rohmer, M. (1998) On the Absence of the Glyceraldehyde 3-Phosphate/Pyruvate Pathway for Isoprenoid Biosynthesis in Fungi and Yeasts, FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 168, 201–208.
Mahmoud, S.S., and Croteau, R.B. (2002) Strategies for Transgenic Manipulation of Monoterpene Biosynthesis in Plants, Trends Plant Sci. 7, 366–373.
Porter, J.W., and Spurgeon, S.L. (1981) Biosynthesis of Isoprenoid Compounds, Vol. 1, John Wiley & Sons, New York.
Harrewijn, P., van Oosten, A.M., and Piron, P.G.M. (2001) Natural Terpenoids as Messengers: A Multidisciplinary Study of Their Production, Biological Functions and Practical Applications, pp. 1–9, Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht.
Crowell, P.L. (1999) Prevention and Therapy of Cancer by Dietary Monoterpenes, J. Nutr. 129, 775S-778S.
Gould, M.N., Moore, C.J., Zhang, R., Wang, B., Kennan, W.S., and Haag, J.D. (1994) Limonene Chemoprevention of Mammary Carcinoma Induction Following Direct in situ Transfer of v-Ha-ras, Cancer Res. 54, 3540–3543.
Elegbede, J.A., Elson, C.E., Tanner, M.A., Qureshi, A., and Gould, M.N. (1986) Regression of Rat Primary Mammary Tumors Following Dietary d-Limonene, J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 76, 323–325.
Haag, J.D., and Gould, M.N. (1994) Mammary Carcinoma Regression Induced by Perillyl Alcohol, a Hydroxylated Analog of Limonene, Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 34, 477–483.
Stark, M.J., Burke, Y.D., McKinzie, J.H., Ayoubi, A.S., and Crowell, P.L. (1995) Chemotherapy of Pancreatic Cancer with the Monoterpene Perillyl Alcohol, Cancer Lett. 96, 15–21.
Elegbede, J.A., Flores, R., and Wang, R.C. (2003) Perillyl Alcohol and Perillaldehyde Induced Cell Cycle Arrest and Cell Death in Bro To and A549 Cells Cultured in vitro, Life Sci. 73, 2831–2840.
Ahn, K.J., Lee, C.K., Choi, E.K., Griffin, R., Song, C.W., and Park, H.J. (2003) Cytotoxicity of Perillyl Alcohol Against Cancer Cells Is Potentiated by Hyperthermia, Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 57, 813–819.
Unlu, S., Mason, C.D., Schachter, M., and Hughes, A.D. (2000) Perillyl Alcohol, an Inhibitor of Geranylgeranyl Transferase, Induces Apoptosis of Immortalized Human Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells in vitro, J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 35, 341–344.
Sahin, M.B., Perman, S.M., Jenkins, G., and Clark, S.S. (1999) Perillyl Alcohol Selectively Induces G0/G1 Arrest and Apoptosis in Bcr/Abl-Transformed Myeloid Cell Lines, Leukemia. 13, 1581–1591.
Ripple, G.H., Gould, M.N., Stewart, J.A., Tutsch, K.D., Arzoomanian, R.Z., Alberti, D., Feierabend, C., Pomplun, M., Wilding, G., and Bailey, H.H. (1998) Phase I Clinical Trial of Perillyl Alcohol Administered Daily, Clin. Cancer Res. 4, 1159–1164.
Vigushin, D.M., Poon, G.K., Boddy, A., English, J., Halbert, G.W., Pagonis, C., Jarman, M., and Coombes, R.C. (1998) Phase I and Pharmacokinetic Study of d-Limonene in Patients with Advanced Cancer. Cancer Research Campaign Phase I/II Clinical Trials Committee, Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 42, 111–117.
Hudes, G.R., Szarka, C.E., Adams, A., Ranganathan, S., McCauley, R.A., Weiner, L.M., Langer, C.J., Litwin, S., Yeslow, G., Halberr, T., et al. (2000) Phase I Pharmacokinetic Trial of Perillyl Alcohol (NSC 641066) in Patients with Refractory Solid Malignancies, Clin. Cancer Res. 6, 3071–3080.
Ripple, G.H., Gould, M.N., Arzoomanian, R.Z., Alberti, D., Feierabend, C., Simon, K., Binger, K., Tutsch, K.D., Pomplun, M., Wahamaki, A., et al. (2000) Phase I Clinical and Pharmacokinetic Study of Perillyl Alcohol Administered Four Times a Day, Clin. Cancer Res. 6, 390–396.
Murren, J.R., Pizzorno, G., DiStasio, S.A., McKeon, A., Peccerillo, K., Gollerkari, A., McMurray, W., Burtness, B.A., Rutherford, T., Li, X., et al. (2002) Phase I Study of Perillyl Alcohol in Patients with Refractory Malignancies, Cancer Biol. Ther. 1, 130–135.
Bailey, H.H., Wilding, G., Tutsch, K.D., Arzoomanian, R.Z., Alberti, D., Feierabend, K.S., Marnocha, R., Holstein, S.A., Stewart, J., Lewis, K.A., and Hohl, R.J. (2004) A Phase I Trial of Perillyl Alcohol Administered 4 Times Daily for 14 Days out of 28 Days, Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol., in press.
Crowell, P.L., Chang, R.R., Ren, Z.B., Elson, C.E., and Gould, M.N. (1991) Selective Inhibition of Isoprenylation of 21–26 kDa Proteins by the Anticarcinogen d-Limonene and Its Metabolites, J. Biol. Chem. 266, 17679–17685.
Hohl, R.J., and Lewis, K. (1995) Differential Effects of Monoterpenes and Lovastatin on RAS Processing, J. Biol. Chem. 270, 17508–17512.
Holstein, S.A., and Hohl, R.J. (2003) Monoterpene Regulation of Ras and Ras-Related Protein Expression, J. Lipid Res. 44, 1209–1215.
Goodwin, T.E., Rasmussen, E.L., Guinn, A.C., McKelvey, S.S., Gunawardena, R., Riddle, S.W., and Riddle, H.S. (1999) African Elephant Sesquiterpenes, J. Nat. Prod. 62, 1570–1572.
Schulz, S., Kruckert, K., and Weldon, P.J. (2003) New Terpene Hydrocarbons from the Alligatoridae (Crocodylia, Reptilia), J. Nat. Prod. 66, 34–38.
Novotny, M., Harvey, S., and Jemiolo, B. (1990) Chemistry of Male Dominance in the House Mouse, Mus domesticus, Experientia 46, 109–113.
McBrien, H.L., Millar, J.G., Rice, R.E., McElfresh, J.S., Cullen, E., and Zalom, F.G. (2002) Sex Attractant Pheromone of the Red-Shouldered Stink Bug Thyanta pallidovirens: A Pheromone Blend with Multiple Redundant Components, J. Chem. Ecol. 28, 1797–1818.
Tesh, R.B., Guzman, H., and Wilson, M.L. (1992) Trans-Beta-Farnesene as a Feeding Stimulant for the Sand Fly Lutzomyia longipalpis (Diptera: Psychodidae), J. Med. Entomol. 29, 226–231.
Quintana, A., Reinhard, J., Faure, R., Uva, P., Bagnères, A.G., Massiot, G., and Clément, J.L. (2003) Interspecific Variation in Terpenoid Composition of Defensive Secretions of European Reticulitermes Termites, J. Chem. Ecol., 29, 639–652.
Rowan, D.D., Hunt, M.B., Fielder, S., Norris, J., and Sherburn, M.S. (2001) Conjugated Triene Oxidation Products of α-Farnesene Induce Symptoms of Superficial Scald on Stored Apples, J. Agric. Food. Chem. 49, 2780–2787.
Kuriyama, T., Schmidt, T.J., Okuyama, E., and Ozoe, Y. (2002) Structure-Activity Relationships of seco-Prezizaane Terpenoids in γ-Aminobutyric Acid Receptors of Houseflies and Rats, Bioorg. Med. Chem. 10, 1873–1881.
Castro, V., Murillo, R., Klaas, C.A., Meunier, C., Mora, G., Pahl, H.L., and Merfort, I. (2000) Inhibition of the Transcription Factor NF-κB by Sesquiterpene Lactones from Podachaenium eminens, Planta Med. 66, 591–595.
Duan, H., Takaishi, Y., Momota, H., Ohmoto, Y., Taki, T., Jia, Y., and Li, D. (2001) Immunosuppressive Sesquiterpene Alkaloids from Tripterygium wilfordii, J. Nat. Prod. 64, 582–587.
Appendino, G., Spagliardi, P., Cravotto, G., Pocock, V., and Milligan, S. (2002) Daucane Phytoestrogens: A Structure-Activity Study, J. Nat. Prod. 65, 1612–1615.
Chang, F.R., Hayashi, K., Chen, I.H., Liaw, C.C., Bastow, K.F., Nakanishi, Y., Nozaki, H., Cragg, G.M., Wu, Y.C., and Lee, K.H. (2003) Antitumor Agents. 228. Five New Agarofurans, Reissantins A-E, and Cytotoxic Principles from Reissantia buchananii, J. Nat. Prod. 66, 1416–1420.
Jeong, S.J., Itokawa, T., Shibuya, M., Kuwano, M., Ono, M., Higuchi, R., and Miyamoto, T. (2002) Costunolide, a Sesquiterpene Lactone from Saussurea lappa, Inhibits the VEGFR KDR/Flk-1 Signaling Pathway, Cancer Lett. 187, 129–133.
Duan, H., Takaishi, Y., Imakura, Y., Jia, Y., Li, D., Cosentino, L.M., and Lee, K.H. (2000) Sequiterpene Alkaloids from Tripterygium hypoglaucum and Tripterygium wilfordii: A New Class of Potent Anti-HIV Agents, J. Nat. Prod. 63, 357–361.
Christophe, J., and Popják, G. (1961) Studies on the Biosynthesis of Cholesterol: XIV. The Origin of Prenoic Acids from Allyl Pyrophosphates in Liver Enzyme Systems, J. Lipid Res. 2, 244–257.
Bansal, V.S., and Vaidya, S. (1994) Characterization of Two Distinct Allyl Pyrophosphatase Activities from Rat Liver Microsomes, Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 315, 393–399.
Meigs, T.E., and Simoni, R.D. (1997) Farnesol as a Regulator of HMG-CoA Reductase Degradation: Characterization and Role of Farnesyl Pyrophosphatase, Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 345, 1–9.
Huang, Z., and Poulter, C.D. (1989) Stereochemical Studies of Botryococcene Biosynthesis: Analogies Between 1′-1 and 1′-3 Condensations in the Isoprenoid Pathway, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 111, 2713–2715.
Crick, D.C., Andres, D.A., and Waechter, C.J. (1995) Farnesol Is Utilized for Protein Isoprenylation and the Biosynthesis of Cholesterol in Mammalian Cells, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 211, 590–599.
Fliesler, S.J., and Keller, R.K. (1995) Metabolism of [3H]Farnesol to Cholesterol and Cholesterogenic Intermediates in the Living Rat Eye, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 210, 695–702.
Westfall, D., Aboushadi, N., Shackelford, J.E., and Krisans, S.K. (1997) Metabolism of Farnesol: Phosphorylation of Farnesol by Rat Liver Microsomal and Peroxisomal Fractions, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 210, 562–568.
Tachibana, A., Tanaka, T., Taniguchi, M., and Oi, S. (1996) Evidence for Farnesol-Mediated Isoprenoid Synthesis Regulation in a Halophilic Archaeon, Haloferax volcanii, FEBS Lett. 379, 43–46.
Bentinger, M., Grunler, J., Peterson, E., Swiezewska, E., and Dallner, G. (1998) Phosphorylation of Farnesol in Rat Liver Microsomes: Properties of Farnesol Kinase and Farnesyl Phosphate Kinase, Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 353, 191–198.
Thai, L., Rush, J.S., Maul, J.E., Devarenne, T., Rodgers, D.L., Chappell, J., and Waechter, C.J. (1999) Farnesol Is Utilized for Isoprenoid Biosynthesis in Plant Cells via Farnesyl Pyrophosphate Formed by Successive Monophosphorylation Reactions, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96, 13080–13085.
Wagner, P.D., and Wu, N.D. (2000) Phosphorylation of Geranyl and Farnesyl Pyrophosphates by Nm23 Proteins/Nucleoside Diphosphate Kinases, J. Biol. Chem. 275, 35570–35576.
Gonzalez-Pacanowska, D., Arison, B., Havel, C.M., and Watson, J.A. (1988) Isopentenoid Synthesis in Isolated Embryonic Drosophila Cells. Farnesol Catabolism and Omega-Oxidation, J. Biol. Chem. 263, 1301–1306.
Fliesler, S.J., and Schroepfer, G.J., Jr. (1983) Metabolism of Mevalonic Acid in Cell-Free Homogenates of Bovine Retinas. Formation of Novel Isoprenoid Acids, J. Biol. Chem. 258, 15062–15070.
Keung, W.M. (1991) Human Liver Alcohol Dehydrogenases Catalyze the Oxidation of the Intermediary Alcohols of the Shunt Pathway of Mevalonate Metabolism, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 174, 701–707.
Zhang, L., Tschantz, W.R., and Casey, P.J. (1997) Isolation and Characterization of a Prenylcysteine Lyase from Bovine Brain, J. Biol. Chem. 272, 23354–23359.
Bostedor, R.G., Karkas, J.D., Arison, B.H., Bansal, V.S., Vaidya, S., Germershausen, J.I., Kurtz, M.M., and Bergstrom, J.D. (1997) Farnesol-Derived Dicarboxylic Acids in the Urine of Animals Treated with Zaragozic Acid A or with Farnesol, J. Biol. Chem. 272, 9197–9203.
Vaidya, S., Bostedor, R., Kurtz, M.M., Bergstrom, J.D., and Bansal, V.S. (1998) Massive Production of Farnesol-Derived Dicarboxylic Acids in Mice Treated with the Squalene Synthase Inhibitor Zaragozic Acid A, Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 355, 84–92.
Baker, F.C., Mauchamp, B., Tsai, L.W., and Schooley, D.A. (1983) Farnesol and Farnesal Dehydrogenase(s) in Corpora Allata of the Tobacco Hornworm Moth, Manduca sexta, J. Lipid Res. 24, 1586–1594.
Keller, R.K., Zhao, Z., Chambers, C., and Ness, G.C. (1996) Farnesol Is Not the Nonsterol Regulator Mediating Degradation of HMG-CoA Reductase in Rat Liver, Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 328, 324–330.
Roullet, J.B., Spaetgens, R.L., Burlingame, T., Feng, Z.P., and Zamponi, G.W. (1999) Modulation of Neuronal Voltage-Gated Calcium Channels by Farnesol, J. Biol. Chem. 274, 25439–25446.
Saisho, Y., Morimoto, A., and Umeda, T. (1997) Determination of Farnesyl Pyrophosphate in Dog and Human Plasma by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography with Fluorescence Detection, Anal. Biochem. 252, 89–95.
Bruenger, E., and Rilling, H.C. (1988) Determination of Isopentenyl Diphosphate and Farnesyl Diphosphate in Tissue Samples with a Comment on Secondary Regulation of Polyisoprenoid Biosynthesis, Anal. Biochem. 173, 321–327.
Raner, G.M., Muir, A.Q., Lowry, C.W., and Davis, B.A. (2002) Farnesol as an Inhibitor and Substrate for Rabbit Liver Microsomal P450 Enzymes, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 293, 1–6.
Feyereisen, R., Pratt, G.E., and Hamnett, A.F. (1981) Enzymic Synthesis of Juvenile Hormone in Locust Corpora Allata: Evidence for a Microsomal Cytochrome P-450 Linked Methyl Farnesoate Epoxidase, Eur. J. Biochem. 118, 231–238.
Andersen, J.F., Walding, J.K., Evans, P.H., Bowers, W.S., and Feyereisen, R. (1997) Substrate Specificity for the Epoxidation of Terpenoids and Active Site Topology of House Fly Cytochrome P450 6A1, Chem. Res. Toxicol. 10, 156–164.
Sutherland, T.D., Unnithan, G.C., Andersen, J.F., Evans, P.H., Murataliev, M.B., Szabo, L.Z., Mash, E.A., Bowers, W.S., and Feyereisen, R. (1998) A Cytochrome P450 Terpenoid Hydroxylase Linked to the Suppression of Insect Juvenile Hormone Synthesis, Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 12884–12889.
Bucher, N.L.R., McGarrahan, K., Gould, E., and Loud, A.V. (1959) Cholesterol Biosynthesis in Preparations of Liver from Normal, Fasting, X-Irradiated Cholesterol-Fed, Triton, or Δ4-Cholesten-3-one- Treated Rats, J. Biol. Chem. 234, 262–267.
Siperstein, M.D., and Fagan, V.M. (1966) Feedback Control of Mevalonate Synthesis by Dietary Cholesterol, J. Biol. Chem. 241, 602–609.
Brown, M.S., Faust, J.R., and Goldstein, J.L. (1978) Induction of 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl Coenzyme A Reductase Activity in Human Fibroblasts Incubated with Compactin (ML-236B), a Competitive Inhibitor of the Reductase, J. Biol. Chem. 253, 1121–1128.
Sakakura, Y., Shimano, H., Sone, H., Takahashi, A., Inoue, N., Toyoshima, H., Suzuki, S., Yamada, N., and Inoue, K. (2001) Sterol Regulatory Element-Binding Proteins Induce an Entire Pathway of Cholesterol Synthesis, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 286, 176–183.
Panini, S.R., Delate, T.A., and Sinensky, M. (1992) Post-transcriptional Regulation of 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl Coenzyme A Reductase by 24(S),25-Oxidolanosterol, J. Biol. Chem. 267, 12647–12654.
Dawson, P.A., Metherall, J.E., Ridgway, N.D., Brown, M.S., and Goldstein, J.L. (1991) Genetic Distinction Between Sterol-Mediated Transcriptional and Posttranscriptional Control of 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-Coenzyme A Reductase, J. Biol. Chem. 266, 9128–9134.
Nakanishi, M., Goldstein, J.L., and Brown, M.S. (1988) Multivalent Control of 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl Coenzyme A Reductase. Mevalonate-Derived Product Inhibits Translation of mRNA and Accelerates Degradation of Enzyme, J. Biol. Chem. 263, 8929–8937.
Roitelman, J., and Simoni, R.D. (1992) Distinct Sterol and Nonsterol Signals for the Regulated Degradation of 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA Reductase, J. Biol. Chem. 267, 25264–25273.
Correll, C.C., and Edwards, P.A. (1994) Mevalonic Acid-Dependent Degradation of 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A Reductase in vivo and in vitro, J. Biol. Chem. 269, 633–638.
Correll, C.C., Ng, L., and Edwards, P.A. (1994) Identification of Farnesol as the Non-sterol Derivative of Mevalonic Acid Required for the Accelerated Degradation of 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A Reductase, J. Biol. Chem. 269, 17390–17393.
Bradfute, D.L., and Simoni, R.D. (1994) Non-sterol Compounds That Regulate Cholesterogenesis. Analogues of Farnesyl Pyrophosphate Reduce 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A Reductase Levels, J. Biol. Chem. 269, 6645–6650.
Parker, R.A., Pearce, B.C., Clark, R.W., Gordon, D.A., and Wright, J.J. (1993) Tocotrienols Regulate Cholesterol Production in Mammalian Cells by Post-transcriptional Suppression of 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A Reductase, J. Biol. Chem. 268, 11230–11238.
Gardner, R.G., and Hampton, R.Y. (1999) A Highly Conserved Signal Controls Degradation of 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-Coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) Reductase in Eukaryotes, J. Biol. Chem. 274, 31671–31678.
Sever, N., Song, B.L., Yabe, D., Goldstein, J.L., Brown, M.S., and DeBose-Boyd, R.A. (2003) Insig-Dependent Ubiquitination and Degradation of Mammalian 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA Reductase Stimulated by Sterols and Geranylgeraniol, J. Biol. Chem. 278, 52479–52490.
Peffley, D.M., and Gayen, A.K. (2003) Plant-Derived Monoterpenes Suppress Hamster Kidney Cell 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl Coenzyme A Reductase Synthesis at the Post-transcriptional Level, J. Nutr. 133, 38–44.
Seybold, S.J., and Tittiger, C. (2003) Biochemistry and Molecular Biology of de novo Isoprenoid Pheromone Production in the Scolytidae, Annu. Rev. Entomol. 48, 425–453.
Hall, G.M., Tittiger, C., Blomquist, G.J., Andrews, G.L., Mastick, G.S., Barkawi, L.S., Bengoa, C., and Seybold, S.J. (2002) Male Jeffrey Pine Beetle, Dendroctonus jeffreyi, Synthesizes the Pheromone Component Frontalin in Anterior Midgut Tissue, Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 32, 1525–1532.
Tittiger, C., Barkawi, L.S., Bengoa, C.S., Blomquist, G.J., and Seybold, S.J. (2003) Structure and Juvenile Hormone-Mediated Regulation of the HMG-CoA Reductase Gene from the Jeffrey Pine Beetle, Dendroctonus jeffreyi, Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 199, 11–21.
Stermer, B.A., Bianchini, G.M., and Korth, K.L. (1994) Regulation of HMG-CoA Reductase Activity in Plants, J. Lipid Res. 35, 1133–1140.
Wentzinger, L.F., Bach, T.J., and Hartmann, M.A. (2002) Inhibition of Squalene Synthase and Squalene Epoxidase in Tobacco Cells Triggers an Up-regulation of 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl Coenzyme A Reductase, Plant Physiol. 130, 334–346.
Hemmerlin, A., and Bach, T.J. (2000) Farnesol-Induced Cell Death and Stimulation of 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A Reductase Activity in Tobacco cv Bright Yellow-2 Cells, Plant Physiol. 123, 1257–1268.
Endo, A., Kuroda, M., and Tsujita, Y. (1976) ML-236A, ML-236B, and ML-236C, New Inhibitors of Cholesterogenesis Produced by Penicillium citrinium, J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 29, 1346–1348.
Schafer, W.R., Kim, R., Sterne, R., Thorner, J., Kim, S.H., and Rine, J. (1989) Genetic and Pharmacological Suppression of Oncogenic Mutations in RAS Genes of Yeast and Humans, Science 245, 379–385.
Leonard, S., Beck, L., and Sinensky, M. (1990) Inhibition of Isoprenoid Biosynthesis and the Post-translational Modification of pro-p21, J. Biol. Chem. 265, 5157–5160.
Holstein, S.A., Wohlford-Lenane, C.L., and Hohl, R.J. (2002) Consequences of Mevalonate Depletion. Differential transcriptional, Translational, and Post-translational Up-regulation of Ras, Rap1a, RhoA, and RhoB, J. Biol. Chem. 277, 10678–10682.
Laezza, C., Bucci, C., Santillo, M., Bruni, C.B., and Bifulco, M. (1998) Control of Rab5 and Rab7 Expression by the Isoprenoid Pathway, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 248, 469–472.
Dimster-Denk, D., Schafer, W.R., and Rine, J. (1995) Control of RAS mRNA Level by the Mevalonate Pathway, Mol. Biol. Cell. 6, 59–70.
Holstein, S.A., Wohlford-Lenane, C.L., and Hohl, R.J. (2002) Isoprenoids Influence the Expression of Ras and Ras-Related Proteins, Biochemistry 41, 13698–13704.
Holstein, S.A., Wohlford-Lenane, C.L., Wiemer, D.F., and Hohl, R.J. (2003) Isoprenoid Pyrophosphate Analogues Regulate Expression of Ras-Related Proteins, Biochemistry 42, 4384–4391.
Forman, B.M., Goode, E., Chen, J., Oro, A.E., Bradley, D.J., Perlmann, T., Noonan, D.J., Burka, L.T., McMorris, T., Lamph, W.W., et al. (1995) Identification of a Nuclear Receptor That Is Activated by Farnesol Metabolites, Cell 81, 687–693.
Wang, H., Chen, J., Hollister, K., Sowers, L.C., and Forman, B.M. (1999) Endogenous Bile Acids Are Ligands for the Nuclear Receptor FXR/BAR, Mol. Cell. 3, 543–553.
Parks, D.J., Blanchard, S.G., Bledsoe, R.K., Chandra, G., Consler, T.G., Kliewer, S.A., Stimmel, J.B., Willson, T.M., Zavacki, A.M., Moore, D.D., and Lehmann, J.M. (1999) Bile Acids: Natural Ligands for an Orphan Nuclear Receptor, Science 284, 1365–1368.
Makishima, M., Okamoto, A.Y., Repa, J.J., Tu, H., Learned, R.M., Luk, A., Hull, M.V., Lustig, K.D., Mangelsdorf, D.J., and Shan, B. (1999) Identification of a Nuclear Receptor for Bile Acids, Science 284, 1362–1365.
Hanley, K., Komuves, L.G., Ng, D.C., Schoonjans, K., He, S.S., Lau, P., Bikle, D.D., Williams, M.L., Elias, P.M., Auwerx, J., and Feingold, K.R. (2000) Farnesol Stimulates Differentiation in Epidermal Keratinocytes via PPARα, J. Biol. Chem. 275, 11484–11491.
Mangelsdorf, D.J., Kliewer, S.A., Kakizuka, A., Umesono K., and Evans, R.M. (1993) Retinoid Receptors, Recent Prog. Horm. Res. 48, 99–121.
Harmon, M.A., Boehm, M.F., Heyman, R.A., and Mangelsdorf, D.J. (1995) Activation of Mammalian Retinoid X Receptors by the Insect Growth Regulator Methoprene, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92, 6157–6160.
Gan, X., Kaplan, R., Menke, J.G., MacNaul, K., Chen, Y., Sparrow, C.P., Zhou, G., Wright, S.D., and Cai, T.Q. (2001) Dual Mechanisms of ABCA1 Regulation by Geranylgeranyl Pyrophosphate, J. Biol. Chem. 276, 48702–48708.
Rioja, A., Pizzey, A.R., Marson, C.M., and Thomas, N.S. (2000) Preferential Induction of Apoptosis of Leukaemic Cells by Farnesol, FEBS. Lett. 467, 291–295.
Voziyan, P.A., Haug, J.S., and Melnykovych, G. (1995) Mechanism of Farnesol Cytotoxicity: Further Evidence for the Role of PKC-Dependent Signal Transduction in Farnesol-Induced Apoptotic Cell Death, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 212, 479–486.
Yasugi, E., Nakata, K., Yokoyama, Y., Kano, K., Dohi, T., and Oshima, M. (1998) Dihydroheptaprenyl and Dihydrodecaprenyl Monophosphates Induce Apoptosis Mediated by Activation of Caspase-3-like Protease, Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1389, 132–140.
Miquel, K., Pradines, A., Terce, F., Selmi, S. and Favre, G. (1998) Competitive Inhibition of Choline Phosphotransferase by Geranylgeraniol and Farnesol Inhibits Phosphatidylcholine Synthesis and Induces Apoptosis in Human Lung Adenocarcinoma A549 Cells, J. Biol. Chem. 273, 26179–26186.
Burke, Y.D., Stark, M.J., Roach, S.L., Sen, S.E., and Crowell, P.L. (1997) Inhibition of Pancreatic Cancer Growth by the Dietary Isoprenoids Farnesol and Geraniol, Lipids 32, 151–156.
Machida, K., Tanaka, T., Fujita, K., and Taniguchi, M. (1998) Farnesol-Induced Generation of Reactive Oxygen Species via Indirect Inhibition of the Mitochondrial Electron Transport Chain in the Yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae, J. Bacteriol. 180, 4460–4465.
Voziyan, P.A., Goldner, C.M., and Melnykovych, G. (1993) Farnesol Inhibits Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis in Cultured Cells by Decreasing Cholinephosphotransferase Activity, Biochem. J. 295, 757–762.
Wright, M.M., Henneberry, A.L., Lagace, T.A., Ridgway, N.D., and McMaster, C.R. (2001) Uncoupling Farnesol-Induced Apoptosis from Its Inhibition of Phosphatidylcholine Synthesis, J. Biol. Chem. 276, 25254–25261.
Yazlovitskaya, E.M., and Melnykovych, G. (1995) Selective Farnesol Toxicity and Translocation of Protein Kinase C in Neoplastic HeLa-S3K and Non-neoplastic CF-3 Cells, Cancer Lett. 88, 179–183.
Machida, K., and Tanaka, T. (1999) Farnesol-Induced Generation of Reactive Oxygen Species Dependent on Mitochondrial Transmembrane Potential Hyperpolarization Mediated by F(0)F(1)-ATPase in Yeast, FEBS Lett. 462, 108–112.
Rajbhandari, I., Takamatsu, S., and Nagle, D.G. (2001) A New Dehydrogeranylgeraniol Antioxidant from Saururus cernuus That Inhibits Intracellular Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)-Catalyzed Oxidation Within HL-60 Cells, J. Nat. Prod. 64, 693–695.
Roullet, J.B., Xue, H., Chapman, J., McDougal, P., Roullet, C.M., and McCarron, D.A. (1996) Farnesyl Analogues Inhibit Vasoconstriction in Animal and Human Arteries, J. Clin. Invest. 97, 2384–2390.
Roullet, J.B., Luft, U.C., Xue, H., Chapman, J., Bychkov, R., Roullet, C.M., Luft, F.C., Haller, H., and McCarron, D.A. (1997) Farnesol Inhibits L-Type Ca2+ Channels in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells, J. Biol. Chem. 272, 32240–32246.
Oh, K.B., Miyazawa, H., Naito, T., and Matsuoka, H. (2001) Purification and Characterization of an Autoregulatory Substance Capable of Regulating the Morphological Transition in Candida albicans, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 4664–4668.
Kim, S., Kim, E., Shin, D.S., Kang, H., and Oh, K.B. (2002) Evaluation of Morphogenic Regulatory Activity of Farnesoic Acid and Its Derivatives Against Candida albicans Dimorphism, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 12, 895–898.
Hornby, J.M., Jensen, E.C., Lisec, A.D., Tasto, J.J., Jahnke, B., Shoemaker, R., Dussault, P., and Nickerson, K.W. (2001) Quorum Sensing in the Dimorphic Fungus Candida albicans is Mediated by Farnesol, Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 67, 2982–2992.
Hornby, J.M., Kebaara, B.W., and Nickerson, K.W. (2003) Farnesol Biosynthesis in Candida albicans: Cellular Response to Sterol Inhibition by Zaragozic Acid B, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 47, 2366–2369.
Ramage, G., Saville, S.P., Wickes, B.L., and Lopez-Ribot, J.L. (2002) Inhibition of Candida albicans Biofilm Formation by Farnesol, a Quorum-Sensing Molecule, Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 68, 5459–5463.
Koga, T., Kawada, H., Utsui, Y., Domon, H., Ishii, C., and Yasuda, H. (1996) In-vitro and in-vivo Antibacterial Activity of Plaunotol, a Cytoprotective Antiulcer Agent, Against Heli-cobacter pylori, J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 37, 919–929.
Rasoamiaranjanahary, L., Marston, A., Guilet, D., Schenk, K., Randimbivolona, F., and Hostettmann, K. (2003) Antifungal Diterpenes from Hypoestes serpens (Acanthaceae), Phytochemistry 62, 333–337.
Habtemariam, S. (2003) In vitro Antileishmanial Effects of Antibacterial Diterpenes from Two Ethiopian Premna Species: P. schimperi and P. oligotricha, BMC Pharmacol. 3, 6.
Carroll, J., Jonsson, E.N., Ebel, R., Hartman, M.S., Holman, T.R., and Crews, P. (2001) Probing Sponge-Derived Terpenoids for Human 15-Lipoxygenase Inhibitors, J. Org. Chem. 66, 6847–6851.
Klein Gebbinck, E.A., Jansen, B.J., and de Groot, A. (2002) Insect Antifeedant Activity of Clerodane Diterpenes and Related Model Compounds, Phytochemistry 61, 737–770.
Silva, R.M., Santos, F.A., Rao, V.S., Maciel, M.A., and Pinto, A.C. (2001) Blood Glucose- and Triglyceride-Lowering Effect of trans-Dehydrocrotonin, a Diterpene from Croton cajucara Benth., in Rats, Diabetes Obes. Metab. 3, 452–456.
Iwamoto, M., Ohtsu, H., Tokuda, H., Nishino, H., Matsunaga, S., and Tanaka, R. (2001) Anti-tumor Promoting Diterpenes from the Stem Bark of Thuja standishii (Cupressaceae), Bioorg. Med. Chem. 9, 1911–1921.
Ownby, S.E., and Hohl, R.J. (2002) Farnesol and Geranyl-geraniol: Prevention and Reversion of Lovastatin-Induced Effects in NIH3T3 Cells, Lipids 37, 185–192.
Ohnuma, S., Watanabe, M., and Nishino, T. (1996) Identification and Characterization of Geranylgeraniol Kinase and Geranylgeranyl Phosphate Kinase from the Archaebacterium Sulfolobus acidocaldarius, J. Biochem. (Tokyo) 119, 541–547.
Kodaira, Y., Usui, K., Kon, I., and Sagami, H. (2002) Formation of (R)-2,3-Dihydrogeranylgeranoic Acid from Geranylgeraniol in Rat Thymocytes, J. Biochem (Tokyo) 132, 327–334.
Wang, X., Wu, J., Shidoji, Y., Muto, Y., Ohishi, N., Yagi, K., Ikegami, S., Shinki, T., Udagawa, N., Suda, T., and Ishimi, Y. (2002) Effects of Geranylgeranoic Acid in Bone: Induction of Osteoblast Differentiation and Inhibition of Osteoclast Formation, J. Bone Miner. Res. 17, 91–100.
Nishizawa, Y., Tanaka, H., and Kinoshita, K. (1987) Incorporation of Radioactivity into Amino Acids and Fatty Acids After Administration of 14C-Geranylgeranylacetone to Rats, Xenobiotica 17, 469–476.
Nishizawa, Y., Abe, S., Yamada, K., Nakamura, T., Yamatsu, I., and Kinoshita, K. (1987) Identification of Urinary and Microsomal Metabolites of Geranylgeranylacetone in Rats, Xenobiotica 17, 575–584.
Ohizumi, H., Masuda, Y., Nakajo, S., Ohsawa, S., and Nakaya, K. (1995) Geranylgeraniol Is a Potent Inducer of Apoptosis in Tumor Cells, J. Biochem. (Tokyo) 117, 11–13.
Takeda, Y., Nakao, K., Nakata, K., Kawakami, A., Ida, H., Ichikawa, T., Shigeno, M., Kajiya, Y., Hamasaki, K., Kato, Y., and Eguchi, K. (2001) Geranylgeraniol, an Intermediate Product in Mevalonate Pathway, Induces Apoptotic Cell Death in Human Hepatoma Cells: Death Receptor-Independent Activation of Caspase-8 with Down-Regulation of Bcl-xL Expression, Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 92, 918–925.
Shidoji, Y., Nakamura, N., Moriwaki, H., and Muto, Y. (1997) Rapid Loss in the Mitochondrial Membrane Potential During Geranylgeranoic Acid-Induced Apoptosis, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 230, 58–63.
Kotake-Nara, E., Kim, S.J., Kobori, M., Miyashita, K., and Nagao, A. (2002) Acyclo-Retinoic Acid Induces Apoptosis in Human Prostate Cancer Cells, Anticancer Res. 22, 689–695.
Nakajo, S., Okamoto, M., Masuda, Y., Sakai, I., Ohsawa, S., and Nakaya, K. (1996) Geranylgeraniol Causes a Decrease in Levels of Calreticulin and Tyrosine Phosphorylation of a 36-kDa Protein Prior to the Appearance of Apoptotic Features in HL-60 Cells, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 226, 741–745.
Masuda, Y., Nakaya, M., Nakajo, S., and Nakaya, K. (1997) Geranylgeraniol Potently Induces Caspase-3-Like Activity During Apoptosis in Human Leukemia U937 Cells, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 234, 641–645.
Masuda, Y., Nakaya, M., Aiuchi, T., Hashimoto, S., Nakajo, S., and Nakaya, K. (2000) The Mechanism of Geranylgeraniol-Induced Apoptosis Involves Activation, by a Caspase-3-like Protease, of a c-jun N-Terminal Kinase Signaling Cascade and Differs from Mechanisms of Apoptosis Induced by Conventional Chemotherapeutic Drugs, Leuk. Res. 24, 937–950.
Nakamura, N., Shidoji, Y., Moriwaki, H., and Muto, Y. (1996) Apoptosis in Human Hepatoma Cell Line Induced by 4,5-Didehydro Geranylgeranoic Acid (acyclic retinoid) via Down-Regulation of Transforming Growth Factor-α, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 219, 100–104.
Murakami, M., Oketani, K., Fujisaki, H., Wakabayashi, T., and Ohgo, T. (1981) Antiulcer Effect of Geranylgeranylacetone, a New Acyclic Polyisoprenoid, on Experimentally Induced Gastric and Duodenal Ulcers in Rats, Arzneimittelforschung. 31, 799–804.
Terano, A., Hiraishi, H., Ota, S., and Sugimoto, T. (1986) Geranylgeranylacetone, a Novel Anti-ulcer Drug, Stimulates Mucus Synthesis and Secretion in Rat Gastric Cultured Cells, Digestion 33, 206–210.
Yoshimura, N., Suzuki, Y., and Saito, Y. (2002) Suppression of Helicobacter pylori-Induced Interleukin-8 Production in Gastric Cancer Cell Lines by an Anti-ulcer Drug, Geranylgeranylacetone, J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 17, 1153–1160.
Tsutsumi, S, Rokutan, K., Tsuchiya, T., and Mizushima, T. (1999) Geranylgeranylacetone Suppresses Spontaneous Apoptotic DNA Fragmentation in Cultured Guinea Pig Gastric Pit Cells, Biol. Pharm. Bull. 22, 886–887.
Hirakawa, T., Rokutan, K., Nikawa, T., and Kishi, K. (1996) Geranylgeranylacetone Induces Heat Shock Proteins in Cultured Guinea Pig Gastric Mucosal Cells and Rat Gastric Mucosa, Gastroenterology 111, 345–357.
Tsuruma, T., Yagihashi, A., Hirata, K., Araya, J., Katsuramaki, T., Tarumi, K., Yanai, Y., and Watanabe, N. (2000) Induction of Heat Shock Protein-70 (hsp-70) by Intraarterial Administration of Geranylgeranylacetone, Transplant. Proc. 32, 1631–1633.
Fujiki, M., Kobayashi, H., Abe, T., and Ishii, K. (2003) Astroglial Activation Accompanies Heat Shock Protein Upregulation in Rat Brain Following Single Oral Dose of Geranylgeranylacetone, Brain Res. 991, 254–257.
Caprioli, J., Ishii, Y., and Kwong, J.M. (2003) Retinal Ganglion Cell Protection with Geranylgeranylacetone, a Heat Shock Protein Inducer, in a Rat Glaucoma Model, Trans. Am. Ophthalmol. Soc. 101, 39–50.
Fudaba, Y., Ohdan, H., Tashiro, H., Ito, H., Fukuda, Y., Dohi, K., and Asahara, T. (2001) Geranylgeranylacetone, a Heat Shock Protein Inducer, Prevents Primary Graft Nonfunction in Rat Liver Transplantation, Transplantation 72, 184–189.
Yamanaka, K., Takahashi, N., Ooie, T., Kaneda, K., Yoshimatsu, H., and Saikawa, T. (2003) Role of Protein Kinase C in Geranylgeranylacetone-Induced Expression of Heat-Shock Protein 72 and Cardioprotection in the Rat Heart, J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 35, 785–794.
Koga, T., Watanabe, H., Kawada, H., Takahashi, K., Utsui, Y., Domon, H., Ishii, C., Narita, T., and Yasuda, H. (1998) Interactions of Plaunotol with Bacterial Membranes, J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 42, 133–140.
Ushiyama, S., Matsuda, K., Asai, F., and Yamazaki, M. (1987) Stimulation of Prostaglandin Production by (2E, 6Z, 10E)-7-Hydroxymethyl-3,11,15-trimethyl-2,6,10,14-hexadecatetraen-1-ol (plaunotol_, a New Anti-Ulcer Drug, in vitro and in vivo, Biochem. Pharmacol. 36, 369–375.
Chang, J.H., Watanabe, S., Shiratori, K., Moriyoshi, Y., and Takeuchi, T. (1989) Plaunotol Stimulates Endogenous Secretin Release and Exocrine Pancreatic Secretion in Rats, Digestion 44, 142–147.
Okabe, N., Okada, M., Sakai, T., and Kuroiwa, A. (1995) Effect of Plaunotol on Superoxide Production Activity in vivo, Dig. Dis. Sci. 40, 2321–2322.
Murakami, K., Okajima, K., Harada, N., Isobe, H., Liu, W., Johno, M., and Okabe, H. (1999) Plaunotol Prevents Indomethacin-Induced Gastric Mucosal Injury in Rats by Inhibiting Neutrophil Activation, Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 13, 521–530.
Zimmermann, P.R., Chatfield, R.B., Fishman, J., Crutzen, P.J., and Hanst, P.L. (1978) Estimates of the Production of CO and H2 from the Oxidation of Hydrocarbon Emissions from Vegetation, Geophys. Res. Lett. 5, 679–682.
Rontani, J.F., Bonin, P.C., and Volkman, J.K. (1999) Biodegradation of Free Phytol by Bacterial Communities Isolated from Marine Sediments Under Aerobic and Denitrifying Conditions, Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 65, 5484–5492.
Pirnik, M.P., Atlas, R.M., and Bartha, R. (1974) Hydrocarbon Metabolism by Brevibacterium erythrogenes: Normal and Branched Alkanes, J. Bacteriol. 119, 868–878.
Berthou, F., and Friovourt, M.P. (1981) Gas Chromatographic Separation of Diastereomeric Isoprenoids as Molecular Markers of Oil Pollution, J. Chromatogr. A. 219, 393–402.
Harder, J., and Probian, C. (1995) Microbial Degradation of Monoterpenes in the Absence of Molecular Oxygen, Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 61, 3804–3808.
Rontani, J.F., Mouzdahir, A., Michotey, V., and Bonin, P. (2002) Aerobic and Anaerobic Metabolism of Squalene by a Denitrifying Bacterium Isolated from Marine Sediment, Arch. Microbiol. 178, 279–287.
Harder, J., and Probian, C. (1997) Anaerobic Mineralization of Cholesterol by a Novel Type of Denitrifying Bacterium, Arch. Microbiol. 167, 269–274.
Misra, G., Pavlostathis, S.G., Perdue, E.M., and Araujo, R. (1996) Aerobic Biodegradation of Selected Monoterpenes, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 45, 831–838.
Hara, A., Syutsubo, K., and Harayama, S. (2003) Alcanivorax Which Prevails in Oil-Contaminated Seawater Exhibits Broad Substrate Specificity for Alkane Degradation, Environ. Microbiol. 5, 746–753.
Linos, A., Berekaa, M.M., Reichelt, R., Keller, U., Schmitt, J., Flemming, H.C., Kroppenstedt, R.M., and Steinbuchel, A. (2000) Biodegradation of cis-1,4-Polyisoprene Rubbers by Distinct Actinomycetes: Microbial Strategies and Detailed Surface Analysis, Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 66, 1639–1645.
Brown, A.G., Smale, T.C., King, T.J., Hasenkamp, R., and Thompson, R.H. (1976) Crystal and Molecular Structure of Compactin, a New Antifungal Metabolite from Penicillium brevicopactum, J. Chem. Soc. Perkin I, 1165–1170.
Tanzawa, K., and Endo, A. (1979) Kinetic Analysis of the Reaction Catalyzed by Rat-Liver 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-Coenzyme-A Reductase Using Two Specific Inhibitors, Eur. J. Biochem. 98, 195–201.
Kaneko, I., Hazama-Shimada, Y., and Endo, A. (1978) Inhibitory Effects on Lipid Metabolism in Cultured Cells of ML-236B, a Potent Inhibitor of 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutary-Coenzyme-A Reductase, Eur. J. Biochem. 87, 313–321.
Doi, O., and Endo, A. (1978) Specific Inhibition of Desmosterol Synthesis by ML-236B in Mouse LM Cells Grown in Suspension in a Lipid-Free Medium, Jpn. J. Med. Sci. Biol. 31, 225–233.
Tsujita, Y., Kuroda, M., Tanzawa, K., Kitano, N., and Endo, A. (1979) Hypolipidemic Effects in Dogs of ML-236B, a Competitive Inhibitor of 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl Coenzyme A Reductase, Atherosclerosis 32, 307–313.
Kuroda, M., Tsujita, Y., Tanzawa, K., and Endo, A. (1979) Hypolipidemic Effects in Monkeys of ML-236B, a Competitive Inhibitor of 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl Coenzyme A Reductase, Lipids 14, 585–589.
Yamamoto, A., Sudo, H., and Endo, A. (1980) Therapeutic Effects of ML-236B in Primary Hypercholesterolemia, Atherosclerosis 35, 259–266.
Alberts, A.W., Chen, J., Kuron, G., Hunt, V., Huff, J., Hoffman, C., Rothrock, J., Lopez, M., Joshua, H., Harris, E. et al. (1980) Mevinolin: A Highly Potent Competitive Inhibitor of Hydroxymethylglutaryl-Coenzyme A Reductase and a Cholesterol-Lowering Agent, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 77, 3957–3961.
Gunde-Cimerman, N., Plemenitas, A., and Cimerman, A. (1993) Pleurotus Fungi Produce Mevinolin, an Inhibitor of HMG CoA Reductase, FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 113, 333–337.
Gunde-Cimerman, N., Plemenitas, A., and Cimerman, A. (1995) A Hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA Reductase Inhibitor Synthesized by Yeasts, FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 132, 39–43.
Endo, A. (1979) Monacolin K, a New Hypocholesterolemic Agent Produced by a Monascus Species, J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 32, 852–854.
Shindia, A.A. (2000) Studies on Mevinolin Production by Some Fungi, Microbios 102, 53–61.
Topol, E.J. (2004) Intensive Statin Therapy—A Sea Change in Cardiovascular Prevention, New Engl. J. Med. 350, 1562–1564.
Chan, K.K., Oza, A.M., and Siu, L.L. (2003) The Statins as Anticancer Agents, Clin. Cancer Res. 9, 10–19.
Meske, V., Albert, F., Richter, D., Schwarze, J., and Ohm, T.G. (2003) Blockade of HMG-CoA Reductase Activity Causes Changes in Microtubule-Stabilizing Protein Tau via Suppression of Geranylgeranylpyrophosphate Formation: Implications for Alzheimer's Disease, Eur. J. Neurosci. 17, 93–102.
Bauer, D.C., Mundy, G.R., Jamal, S.A., Black, D.M., Cauley, J.A., Ensrud, K.E., van der Klift, M., and Pols, H.A. (2004) Use of Statins and Fracture: Results of 4 Prospective Studies and Cumulative Meta-analysis of Observational Studies and Controlled Trials, Arch. Intern. Med. 164, 146–152.
Spin, J.M., and Vagelos, R.H. (2003) Early Use of Statins in Acute Coronary Syndromes, Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 5, 44–51.
Weis, M., Heeschen, C., Glassford, A.J., and Cooke, J.P. (2002) Statins Have Biphasic Effects on Angiogenesis, Circulation 105, 739–745.
Patel, R., Nagueh, S.F., Tsybouleva, N., Abdellatif, M., Lutucuta, S., Kopelen, H.A., Quinones, M.A., Zoghbi, W.A., Entman, M.L., Robert, R., and Marian, A.J. (2001) Simvastatin Induces Regression of Cardiac Hypertrophy and Fibrosis and Improves Cardiac Function in a Transgenic Rabbit Model of Human Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy, Circulation 104, 317–324.
Blanco-Colio, L.M., Tunon, J., Martin-Ventura, J.L., and Egido, J. (2003) Anti-inflammatory and Immunomodulatory Effects of Statins, Kidney Int. 63, 12–23.
Wolfrum, S., Jensen, K.S., and Liao, J.K. (2003) Endothelium-Dependent Effects of Statins, Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 23, 729–736.
Krysiak, R., Okopien, B., and Herman, Z. (2003) Effects of HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitors on Coagulation and Fibrinolysis Processes, Drugs. 63, 1821–1854.
Fenton, J.W., Jr., and Shen, G.X. (1999) Statins as Cellular Antithrombotics, Haemostasis 29, 166–169.
Staunton, J., and Weissman, K.J. (2001) Polyketide Biosynthesis: A Millennium Review, Nat. Prod. Rep. 18, 380–416.
Abe, Y., Suzuki, T., Ono, C., Iwamoto, K., Hosobuchi, M., and Yoshikawa, H. (2002) Molecular Cloning and Characterization of an ML-236B (compactin) Biosynthetic Gene Cluster in Penicillium citrinum, Mol. Genet. Genomics 267, 636–646.
Hutchinson, C.R., Kennedy, J., Park, C., Kendrew, S., Auclair, K., and Vederas, J. (2000) Aspects of the Biosynthesis of Nonaromatic Fungal Polyketides by Iterative Polyketide Synthases, Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 78, 287–295.
Hajjaj, H., Niederberger, P., and Duboc, P. (2001) Lovastatin Biosynthesis by Aspergillus terreus in a Chemically Defined Medium, Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 67, 2596–2602.
Shindia, A.A. (2001) Some Nutritional Factors Influencing Mevinolin Production by Aspergillus terreus Strain, Folia Microbiol. (Praha) 46, 413–416.
Ikeura, R., Murakawa, S., and Endo, A. (1988) Growth Inhibition of Yeast by Compactin (ML-236B) Analogues, J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 41, 1148–1150.
Bach, T.J., and Lichtenthaler, H.K. (1982) Mevinolin: A Highly Specific Inhibitor of Microsomal 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutary-Coenzyme A Reductase of Radish Plants, Z. Naturforsch. [C] 37, 46–50.
Josekutty, P.C. (1998) Inhibition of Plant Growth by Mevinolin and Reversal of This Inhibition by Isoprenoids, S. Afr. J. Bot. 64, 18–24.
van Beek, E., Pieterman, E., Cohen, L., Lowik, C., and Papapoulos, S. (1999) Farnesyl Pyrophosphate Synthase Is the Molecular Target of Nitrogen-Containing Bisphosphonates, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 264, 108–111.
Keller, R.K., and Fliesler, S.J. (1999) Mechanism of Aminobisphosphonate Action: Characterization of Alendronate Inhibition of the Isoprenoid Pathway, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 266, 560–563.
Bergstrom, J.D., Bostedor, R.G., Masarachia, P.J., Reszka, A.A., and Rodan, G. (2000) Alendronate Is a Specific, Nanomolar Inhibitor of Farnesyl Diphosphate Synthase, Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 373, 231–241.
Luckman, S.P., Hughes, D.E., Coxon, F.P., Graham, R., Russell, G., and Rogers, M.J. (1998) Nitrogen-Containing Bisphosphonates Inhibit the Mevalonate Pathway and Prevent Post-translational Prenylation of GTP-Binding Proteins, Including Ras, J. Bone Miner. Res. 13, 581–589.
Reszka, A.A., Halasy-Nagy, J.M., Masarachia, P.J., and Rodan, G.A. (1999) Bisphosphonates Act Directly on the Osteoclast to Induce Caspase Cleavage of Mst1 Kinase During Apoptosis. A Link Between Inhibition of the Mevalonate Pathway and Regulation of an Apoptosis-Promoting Kinase, J. Biol. Chem. 274, 34967–34973.
Benford, H.L., Frith, J.C., Auriola, S., Monkkonen, J., and Rogers, M.J. (1999) Farnesol and Geranylgeraniol Prevent Activation of Caspases by Aminobisphosphonates: Biochemical Evidence for Two Distinct Pharmacological Classes of Bisphosphonate Drugs, Mol. Pharmacol. 56, 131–140.
Fisher, J.E., Rogers, M.J., Halasy, J.M., Luckman, S.P., Hughes, D.E., Masarachia, P.J., Wesolowski, G., Russell, R.G., Rodan, G.A., and Reszka, A.A. (1999) Alendronate Mechanism of Action: Geranylgeraniol, an Intermediate in the Mevalonate Pathway, Prevents Inhibition of Osteoclast Formation, Bone Resorption, and Kinase Activation in vitro, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96, 133–138.
van beek, E., Lowik, C., van der Pluijm, G., and Papapoulos, S. (1999) The Role of Geranylgeranylation in Bone Resorption and Its Suppression by Bisphosphonates in Fetal Bone Explants in vitro: A Clue to the Mechanism of Action of Nitrogen-Containing Bisphosphonates, J. Bone Miner. Res. 14, 722–729.
Virtanen, S.S., Vaananen, H.K., Harkonen, P.L., and Lakkakorpi, P.T. (2002) Alendronate Inhibits Invasion of PC-3 Prostate Cancer Cells by Affecting the Mevalonate Pathway, Cancer Res. 62, 2708–2714.
Szabo, C.M., Matsumura, Y., Fukura, S., Martin, M.B., Sanders, J.M., Sengupta, S., Cieslak, J.A., Loftus, T.C., Lea, C.R., Lee, H.J., et al. (2002) Inhibition of Geranylgeranyl Diphosphate Synthase by Bisphosphonates and Diphosphates: A Potential Route to New Bone Antiresorption and Antiparasitic Agents, J. Med. Chem. 45, 2185–2196.
Ohashi, K., Osuga, J., Tozawa, R., Kitamine, T., Yagyu, H., Sekiya, M., Tomita, S., Okazaki, H., Tamura, Y., Yahagi, N., et al. (2003) Early Embryonic Lethality Caused by Targeted Disruption of the 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA Reductase Gene, J. Biol. Chem. 278, 42936–42941.
Berger, R., Smit, G.P., Schierbeek, H., Bijsterveld, K., and le Coultre, R. (1985) Mevalonic Aciduria: An Inborn Error of Cholesterol Biosynthesis?, Clin. Chim. Acta 152, 219–222.
Houten, S.M., Frenkel, J., and Waterham, H.R. (2003) Isoprenoid Biosynthesis in Hereditary Periodic Fever Syndromes and Inflammation, Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 60, 1118–1134.
van der Meer, J.W., Vossen, J.M., Radl, J., van Nieuwkoop, J.A., Meyer, C.J., Lobatto, S., and van Furth, R. (1984) Hyperimmunoglobulinaemia D and Periodic Fever: A New Syndrome, Lancet 1, 1087–1090.
Houten, S.M., Romeijn, G.J., Koster, J., Gray, R.G., Darbyshire, P., Smit, G.P., de Klerk, J.B., Duran, M., Gibson, K.M., Wanders, R.J., and Waterham, H.R. (1999) Identification and Characterization of Three Novel Missense Mutations in Mevalonate Kinase cDNA Causing Mevalonic Aciduria, a Disorder of Isoprene Biosynthesis, Hum. Mol. Genet. 8, 1523–1528.
Houten, S.M., Kuis, W., Duran, M., de Koning, T.J., van Royen-Kerkhof, A., Romeijn, G.J., Frenkel, J., Dorland, L., de Barse, M.M., Huijbers, W.A., et al. (1999) Mutations in MVK, Encoding Mevalonate Kinase, Cause Hyperimmunoglobulinaemia D and Periodic Fever Syndrome, Nat. Genet. 22, 175–177.
Houten, S.M., Koster, J., Romeijn, G.J., Frenkel, J., Di Rocco, M., Caruso, U., Landrieu, P., Kelley, R.I., Kuis, W., Poll-The, B.T., et al. (2001) Organization of the Mevalonate Kinase (MVK) Gene and Identification of Novel Mutations Causing Mevalonic Aciduria and Hyperimmunoglobulinaemia D and Periodic Fever Syndrome, Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 9, 253–259.
Hinson, D.D., Ross, R.M., Krisans, S., Shaw, J.L., Kozich, V., Rolland, M.O., Divry, P., Mancini, J., Hoffmann, G.F., and Gibson, K.M. (1999) Identification of a Mutation Cluster in Mevalonate Kinase Deficiency, Including a New Mutation in a Patient of Mennonite Ancestry, Am. J. Hum. Genet. 65, 327–335.
Hinson, D.D., Chambliss, K.L., Hoffmann, G.F., Krisans, S., Keller, R.K., and Gibson, K.M. (1997) Identification of an Active Site Alanine in Mevalonate Kinase Through Characterization of a Novel Mutation in Mevalonate Kinase Deficiency, J. Biol. Chem. 272, 26756–26760.
Frenkel, J., Houten, S.M., Waterham, H.R., Wanders, R.J., Rijkers, G.T., Duran, M., Kuijpers, T.W., van Luijk, W., Poll-The, B.T., and Kuis, W. (2001) Clinical and Molecular Variability in Childhood Periodic Fever with Hyperimmunoglobulinaemia D, Rheumatology 40, 579–584.
Hoffmann, G.F., Charpentier, C., Mayatepek, E., Mancini, J., Leichsenring, M., Gibson, K.M., Divry, P., Hrebicek, M., Lehnert, W., Sartor, K., et al. (1993) Clinical and Biochemical Phenotype in 11 Patients with Mevalonic Aciduria, Pediatrics 91, 915–921.
Houten, S.M., Frenkel, J., Rijkers, G.T., Wanders, R.J., Kuis, W., and Waterham, H.R. (2002) Temperature Dependence of Mutant Mevalonate Kinase Activity as a Pathogenic Factor in Hyper-IgD and Periodic Fever Syndrome, Hum. Mol. Genet. 11, 3115–3124.
Hoffmann, G., Gibson, K.M., Nyhan, W.L., and Sweetman, L. (1988) Mevalonic Aciduria: Pathobiochemical Effects of Mevalonate Kinase Deficiency on Cholesterol Metabolism in Intact Fibroblasts, J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 11, 229–232.
Gibson, K.M., Hoffmann, G., Schwall, A., Broock, R.L., Aramaki, S., Sweetman, L., Nyhan, W.L., Brandt, I.K., Wappner, R.S., Lehnert, W., and Trefz, F.H. (1990) 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl Coenzyme A Reductase Activity in Cultured Fibroblasts from Patients with Mevalonate Kinase Deficiency: Differential Response to Lipid Supplied by Fetal Bovine Serum in Tissue Culture Medium, J. Lipid Res. 31, 515–521.
Hubner, C., Hoffmann, G.F., Charpentier, C., Gibson, K.M., Finckh, B., Puhl, H., Lehr, H.A., and Kohlschutter, A. (1993) Decreased Plasma Ubiquinone-10 Concentration in Patients with Mevalonate Kinase Deficiency, Pediatr. Res. 34, 129–133.
Hoffmann, G.F., Wiesmann, U.N., Brendel, S., Keller, R.K., and Gibson, K.M. (1997) Regulatory Adaption of Isoprenoid Biosynthesis and the LDL Receptor Pathway in Fibroblasts from Patients with Mevalonate Kinase Deficiency, Pediatr. Res. 41, 541–546.
Houten, S.M., Schneiders, M.S., Wanders, R.J., and Waterham, H.R. (2003) Regulation of Isoprenoid/Cholesterol Biosynthesis in Cells from Mevalonate Kinase-Deficient Patients, J. Biol. Chem. 278, 5736–5743.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Holstein, S.A., Hohl, R.J. Isoprenoids: Remarkable diversity of form and function. Lipids 39, 293–309 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-004-1233-3
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-004-1233-3