Abstract
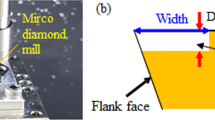
This paper presents a study of tool life, process forces and surface integrity. The focus is on the continuous turning of biocompatible cobalt chromium using ceramic cutting inserts and different cooling systems. The goal when using cooling lubricants with tungsten carbide tools is on the one hand to extend tool life time and on the other hand to achieve a better surface quality on the workpiece. When using ceramic cutting tool materials usually cooling lubricants are dispensable. The heating of the component and thus the reduction in strength is desired, since the ceramic cutting materials withstand higher temperatures. Tool life of ceramic cutting materials without cooling lubricants is often rather low. Therefore, cooling lubricants should help to extend the tool life. It will also be investigated how the different cooling systems affect the surface integrity of the workpiece. The investigations were performed under constant cutting parameters.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Temenoff JS, Mikos Antonios G (2008) Biomaterials: the intersection of biology and materials science. Pearson/Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River
Denkena B, Tönshoff HK (2011) Spanen. 3. Springer, Heidelberg. S. 168, 217. 978-3-642-19771-0
Prilukova Y (2010) Hartdrehen mit beschichteten Schneidkeramiken unter extremen Zerspanbedingungen. Shaker, Aachen
Kollenberg W (Hrsg.) (2009) Technische Keramik. Grundlagen, Werkstoffe, Verfahrenstechnik. s.l.: Vulkan-Verlag GmbH
Brandt G (1999) Ceramic cutting tools, state of the art and development trends. Mater Technol 14:17–22
Chaika D (2013) Einsatz von armierten Keramiken beim Spanen. Dr.-Ing. Diss. OvGU Magdeburg
Oettel H, Schumann H (2011) Metallografie. Mit einer Einführung in die Keramografie. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH-Verl. 15. Auflage
Milošev I (2012) CoCrMo alloy for biomedical applications. In: Djokić SS (Hg.): Biomedical applications, Bd. 55. Boston, Boston: Springer US (Modern Aspects of Electrochemistry), pp 1–72
Davis JR (2000) ASM specialty handbook; nickel, cobalt, and their alloys. ASM International, Materials Park
Karpuschewski B et al (2013) CoCr is not the same: CoCr-blanks for dental machining. In: Schuh G, Neugebauer R, Uhlmann E (Hg.) Future trends in production engineering. Springer, Berlin, S. 261–274
Wintermantel E (2009) Medizintechnik: life science engineering; Interdisziplinarität, Biokompatibilität, Technologien, Implantate, Diagnostik, Werkstoffe, Zertifizierung. Berlin, Heidelberg : Springer Berlin Heidelberg; 5. Auflage
Weinert K et al (2004) Dry machining and minimum quantity lubrication. Ann CIRP 53(2):511–537
DIN ISO 1832 (2005) Wendeschneidplatten für Zerspanwerkzeuge—Bezeichnungen. s.l.: Beuth Verlag, November
ISO 5832-4 (1996) Implants for surgery—Metallic materials—Part 4: Cobalt-chromium-molybdenum casting alloy
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karpuschewski, B., Pieper, HJ. & Döring, J. Impact of the cooling system on the cutting of medical cobalt chromium with ceramic cutting inserts. Prod. Eng. Res. Devel. 8, 613–618 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11740-014-0559-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11740-014-0559-6