Abstract
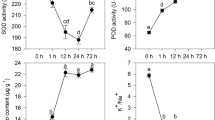
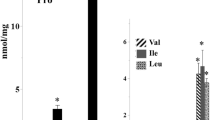
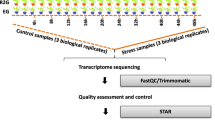
Waterlogging stress lowers yields in sesame (Sesamum indicum L.). A major component of waterlogging stress is the lack of oxygen available to submerged tissues. Although the morphology and physiology of plants grown under anaerobic conditions have been studied in detail, limited work has been done to elucidate adaptations at the molecular level. To gain comprehensive insight into how sesame responds to hypoxia at the genome level, we performed gene expression profiling at two time points during a 36-h period following hypoxic treatment using a whole-genome RNA-Seq analysis. We identified sets of significantly positively and negatively expressed genes (induced and repressed, respectively) in response to hypoxia with distinct temporal profiles. The genes that were affected were associated with glycolysis, nitrogen metabolism, starch and sucrose metabolism and plant hormone signal transduction and indicated the upregulation of particular pathways (glycolysis/glycogenesis) in the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes. Moreover, significant changes in the expression of genes were found for pathways, including flavone and flavonol biosynthesis, steroid biosynthesis, photosynthesis, cysteine and methionine metabolism, glutathione metabolism, as well as phenylpropanoid biosynthesis, spliceosome, circadian rhythm. This study helps in elucidating the molecular mechanisms of waterlogging tolerance and provides a basis for the genetic engineering of sesame.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashri A (2010) Sesame breeding. In: Janick J (ed) Plant breeding reviews, vol 16. Wiley, Oxford. doi:10.1002/9780470650110.ch5
Bailey-Serres J, Voesenek LA (2008) Flooding stress: acclimations and genetic diversity. Annu Rev Plant Biol 59:313–339. doi:10.1146/annurev.arplant.59.032607.092752
Banti V, Mafessoni F, Loreti E, Alpi A, Perata P (2010) The heat-inducible transcription factor HsfA2 enhances anoxia tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 152(3):1471–1483. doi:10.1104/pp.109.149815
Bedigian D, Harlan J (1986) Evidence for cultivation of sesame in the ancient world. Econ Bot 40(2):137–154. doi:10.1007/bf02859136
Benjamini BY, Yekutieli D (2001) The control of the false discovery rate in multiple testing under dependency. Ann Stat 29(4):1165–1188. doi:10.1214/aos/1013699998
Branco-Price C, Kawaguchi R, Ferreira RB, Bailey-Serres J (2005) Genome-wide analysis of transcript abundance and translation in Arabidopsis seedlings subjected to oxygen deprivation. Ann Bot 96(4):647–660. doi:10.1093/aob/mci217
Christianson JA, Llewellyn DJ, Dennis ES, Wilson IW (2010) Global gene expression responses to waterlogging in roots and leaves of cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Plant Cell Physiol 51(1):21–37. doi:10.1093/pcp/pcp163
Drew MC (1997) Oxygen deficiency and root metabolism: injury and acclimation under hypoxia and anoxia. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 48:223–250. doi:10.1146/annurev.arplant.48.1.223
Du H, Zhang Z, Li J (2010) Isolation and functional characterization of a waterlogging-induced promoter from maize. Plant Cell Rep 29(11):1269–1275. doi:10.1007/s00299-010-0913-x
Hegedus Z, Zakrzewska A, Agoston VC, Ordas A, Racz P, Mink M, Spaink HP, Meijer AH (2009) Deep sequencing of the zebrafish transcriptome response to mycobacterium infection. Mol Immunol 46(15):2918–2930. doi:10.1016/j.molimm.2009.07.002
Hinz M, Wilson IW, Yang J, Buerstenbinder K, Llewellyn D, Dennis ES, Sauter M, Dolferus R (2010) Arabidopsis RAP2.2: an ethylene response transcription factor that is important for hypoxia survival. Plant Physiol 153(2):757–772. doi:10.1104/pp.110.155077
Klok EJ, Wilson IW, Wilson D, Chapman SC, Ewing RM, Somerville SC, Peacock WJ, Dolferus R, Dennis ES (2002) Expression profile analysis of the low-oxygen response in Arabidopsis root cultures. Plant Cell 14(10):2481–2494. doi:10.1105/tpc.004747
Kreuzwieser J, Hauberg J, Howell KA, Carroll A, Rennenberg H, Millar AH, Whelan J (2009) Differential response of gray poplar leaves and roots underpins stress adaptation during hypoxia. Plant Physiol 149(1):461–473. doi:10.1104/pp.108.125989
Lasanthi-Kudahettige R, Magneschi L, Loreti E, Gonzali S, Licausi F, Novi G, Beretta O, Vitulli F, Alpi A, Perata P (2007) Transcript profiling of the anoxic rice coleoptile. Plant Physiol 144(1):218–231. doi:10.1104/pp.106.093997
Lee JJ, Hassan OS, Gao W, Wei NE, Kohel RJ, Chen XY, Payton P, Sze SH, Stelly DM, Chen ZJ (2006) Developmental and gene expression analyses of a cotton naked seed mutant. Planta 223(3):418–432. doi:10.1007/s00425-005-0098-7
Li R, Yu C, Li Y, Lam TW, Yiu SM, Kristiansen K, Wang J (2009) SOAP2: an improved ultrafast tool for short read alignment. Bioinformatics 25(15):1966–1967. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btp336
Liu J, Tu L, Xu R, Zheng Y (1993) The relationship between the waterlogging resistance and the genotypes and the vigor of root system in sesame (Sesamum indicum L.). Acta Agric Bor Sin 8(3):82–86 (in Chinese)
Liu F, VanToai T, Moy LP, Bock G, Linford LD, Quackenbush J (2005) Global transcription profiling reveals comprehensive insights into hypoxic response in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 137(3):1115–1129. doi:10.1104/pp.104.055475
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT method. Methods 25(4):402–408. doi:10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Loreti E, Poggi A, Novi G, Alpi A, Perata P (2005) A genome-wide analysis of the effects of sucrose on gene expression in Arabidopsis seedlings under anoxia. Plant Physiol 137(3):1130–1138. doi:10.1104/pp.104.057299
Morrissy AS, Morin RD, Delaney A, Zeng T, McDonald H, Jones S, Zhao Y, Hirst M, Marra MA (2009) Next-generation tag sequencing for cancer gene expression profiling. Genome Res 19(10):1825–1835. doi:10.1101/gr.094482.109
Mortazavi A, Williams BA, McCue K, Schaeffer L, Wold B (2008) Mapping and quantifying mammalian transcriptomes by RNA-Seq. Nat Methods 5(7):621–628. doi:10.1038/nmeth.1226
Noctor G, Dutilleul C, De Paepe R, Foyer CH (2004) Use of mitochondrial electron transport mutants to evaluate the effects of redox state on photosynthesis, stress tolerance and the integration of carbon/nitrogen metabolism. J Exp Bot 55(394):49–57. doi:10.1093/jxb/erh021
Quesada A, Gomez-Garcia I, Fernandez E (2000) Involvement of chloroplast and mitochondria redox valves in nitrate assimilation. Trends Plant Sci 5(11):463–464
Saldanha AJ (2004) Java Treeview-extensible visualization of microarray data. Bioinformatics 20(17):3246–3248. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/bth349
Snowden RED, Wheeler BD (1993) Iron toxicity to fen plant species. J Ecol 81(1):35–46
Soomro AW, Waring SA (1987) Effect of temporary flooding on cotton growth and nitrogen nutrition in soils with different organic-matter levels. Aust J Agric Res 38(1):91–99. doi:10.1071/AR9870091
Sun J, Zhang XR, Zhang YX, Wang LH, Huang B (2009) Effects of waterlogging on leaf protective enzyme activities and seed yield of sesame at different growth stages. Chin J Appl Environ Biol 15(6):790–795. doi:10.3724/SP.J.1145.2009.00790
Sun J, Zhang XR, Zhang YX, Wang LH, Li DH (2010) Evaluation of yield characteristics and waterlogging tolerance of sesame germplasm with different plant types after waterlogging. J Plant Genet Resour 11(2):139–146. doi:CNKI:SUN:ZWYC.0.2010-02-006
Wang WQ, Zheng YZ, Mei HX, Zhang JS, Zhang FS (2004) Anaerobic inducible expression of xyloglucan endotransglycosylase (XET) gene in sesame and w heat roots. J Agric Biotechol 12(3):258–263 (in Chinese)
Wang LH, Lv ZP, Zhang YX, Li DH, Lv HX, Zhang XY, Zhang XR (2010) Isolating waterlogging tolerance related genes from sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) by suppression subtractive hybridization. Chin J Oil Crop Sci 32(4):485–490 (in Chinese)
Wei WL, Qi XQ, Wang LH, Zhang YX, Hua W, Li DH, Lv HX, Zhang XR (2011) Characterization of the sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) global transcriptome using Illumina paired-end sequencing and development of EST-SSR markers. BMC Genomics 12:451
Wu Y, Machado AC, White RG, Llewellyn DJ, Dennis ES (2006) Expression profiling identifies genes expressed early during lint fibre initiation in cotton. Plant Cell Physiol 47(1):107–127. doi:10.1093/pcp/pci228
Yang E, Maguire T, Yarmush ML, Berthiaume F, Androulakis IP (2007) Bioinformatics analysis of the early inflammatory response in a rat thermal injury model. BMC Bioinform 8:10. doi:10.1186/1471-2105-8-10
Yang CY, Hsu FC, Li JP, Wang NN, Shih MC (2011) The AP2/ERF transcription factor AtERF73/HRE1 modulates ethylene responses during hypoxia in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 156(1):202–212. doi:10.1104/pp.111.172486
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 31101182), China Agriculture Research System (no. CARS-15), and the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program) (no. 2011CB109304).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by S. Abe.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, L., Zhang, Y., Qi, X. et al. Global gene expression responses to waterlogging in roots of sesame (Sesamum indicum L.). Acta Physiol Plant 34, 2241–2249 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-012-1024-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-012-1024-9