Abstract
Objective
To observe the clinical effect of acupuncture on chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and the improvements of patients’ pulmonary ventilation function and 6-minute walk test (6-MWT) distance.
Methods
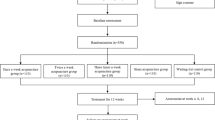
A total of 80 COPD patients [grade 3-4 in Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD), qi deficiency of the lung and kidney in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) pattern] were randomly allocated into a treatment group (n=40) and a control group (n=40). Salmeterol Xinafoate and Fluticasone Propionate powder (Seretide, 50 μg/250 μg) for inhalation was used for basic treatment in both groups (once in the morning and once in the evening). Patients in the treatment group received acupuncture at Feishu (BL 13), Shenshu (BL 23), Qihai (CV 6), Guanyuan (CV 4), Dingchuan (EX-B 1), Danzhong (CV 17) and Zusanli (ST 36) twice a week for 3 months. After 3 months of treatment, clinical effects, lung ventilation functions and 6-MWT distance were observed and compared in the two groups.
Results
After 3 months of treatment, the total effective rate was 95.0% in the treatment group, versus 80.0% in the control group, showing a statistical difference (P<0.05); the phlegm expectoration, dyspnea and shortness of breath were more significantly improved in the treatment group than those in the control group (P<0.01, P<0.05); and the 6-MWT distance and forced expiratory volume in 1 second percentage of predicted value (FEV1%) were more significantly improved in the treatment group than those in the control group (P<0.05, P<0.01).
Conclusion
Seretide inhaler combined with acupuncture can improve signs and symptoms in COPD patients, increase the 6-MWT distance, improve FEV1% and obtain better results than Seretide alone.
摘要
目的
观察针刺治疗慢性阻塞性肺疾病(chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, COPD)的临床疗效及对患者肺通气功能、6 分钟步行测试(6-minute walk test, 6-MWT)距离的影响。
方法
共纳入80 例COPD 患者(肺功能GOLD 3-4 级, 中医辨证为肺肾气虚证), 按就诊顺序随机分为治疗组与对照组, 每组40 例。两组均以沙美特罗替卡松粉吸入剂(舒利迭, 50 μg/250 μg, 早晚各一次吸入)作为基础治疗。治疗组在此基础上加用针刺肺俞、肾俞、气海、关元、定喘、膻中、足三里, 每星期2 次, 连续治疗3 个月后观察两组治疗临床疗效及肺通气功能、6-MWT距离等指标变化。
结果
治疗3 个月后, 治疗组总有效率为95.0%, 对照组为80.0%, 两组差异有统计学意义(P<0.05); 治疗组咯痰、喘息、气短积分改善优于对照组且有统计学差异(P<0.01, P<0.05); 治疗组6-MWT 距离和第一秒用力呼气容积占预计值比值(forced expiratory volume in 1 second percentage of predicted value, FEV1%)增加优于对照组且有统计学差异(P<0.05, P<0.01)。
结论
舒利迭加用针刺疗法能改善COPD 患者临床症状及体征, 增加6-MWT 距离, 提高FEV1%, 其疗效优于单用舒利迭。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ministry of Health of the People’s Republic of China. 2007 China Health Statistical Yearbook. Beijing: Peking Union Medical College Press, 2007.
Barnes PJ. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. N Engl J Med, 2000, 343(4): 269–280.
Vestbo J, Hurd SS, Agustí AG, Jones PW, Vogelmeier C, Anzueto A, Barnes PJ, Fabbri LM, Martinez FJ, Nishimura M, Stockley RA, Sin DD, Rodriguez-Roisin R. Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: GOLD executive summary. Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 2013, 187(4): 347–365.
The State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Traditional Chinese Medicine Diagnostic and Therapeutic Protocols for 105 Diseases in 24 Disciplines. Beijing: Division of Medical Administration, State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2011: 103–104.
State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Criteria of Diagnosis and Therapeutic Effects of Diseases and Syndromes in Traditional Chinese Medicine. Beijing: China Medical Science Press, 2002: 54–58.
Group of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, Chinese Thoracic Society. COPD diagnosis and treatment guidelines (2013 revised edition). Zhongguo Yixue Qianyan Zazhi: Electronic Version, 2014, 6(2): 67–80.
Chen YH, Wang C. GOLD global strategy for diagnosis, management and prevention of COPD. Zhongguo Yixue Qianyan Zazhi: Electronic Version, 2015, 7(2): 34–39.
Mahler DA, Wells CK. Evaluation of clinical methods for rating dyspnea. Chest, 1988, 93(3): 580–586.
Jones PW, Harding G, Berry P, Wiklund I, Chen WH, Kline Leidy N. Development and first validation of the COPD assessment test. Eur Respir J, 2009, 34(3): 648–654.
Chai JJ, Liu T, Cai BQ. Evaluation of clinical significance of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease assessment test. Chin J Tuberc Respir Dis, 2011, 34(4): 256–258.
Rabe KF, Wedzicha JA. Controversies in treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Lancet, 2011, 378(9795): 1038–1047.
American Thoracic Society Committee on Proficiency Standards for Clinical Pulmonary Function Laboratories. ATS statement: guidelines for the six-minute walk test. Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 2002, 166(1): 111–117.
Liu LY, Zou ZW, Li ZJ. Research advance on spleen/kidney-tonifying method for chronic obstructive lung disease. Jilin Yixue, 2011, 32(23): 3–6.
Tian ZJ, Xu YM, Li YQ. TCM pathogenesis of chronic obstructive lung disease. Hubei Zhongyi Xueyuan Xuebao, 2001, 3(1): 29-30.
Xu D, Gao Z, Jing J, Yang CH, Li Z, Liao CY, Li FS. 410 cases of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease syndromes distribution in Xinjiang. Zhongguo Shiyan Fangjixue Zazhi, 2012, 18(3): 45–47.
Chen XJ, Zhang BL. Chinese Internal Medicine. Shanghai Scientific & Technical Publishers, 2004: 64.
Luo Q, Wang LS, Wu Z, Zhang ZP, Wang Y, Peng L. Observations on the efficacy of moxibustion and acupuncture point injection as main treatment for stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Shanghai Zhenjiu Zazhi, 2012, 31(12): 871–873.
Shi MY, Shu ZT, Zhang W, Tian J. Effect of rapid point pressure on therapeutic efficacy and pulmonary function in patients with chronic persistent bronchial asthma. J Acupunct Tuina Sci, 2015, 13(1): 36–43.
Liu XH, Liu Q. Effect of earth-supporting and metal-generating therapy for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease during remission stage. Xin Zhongyi, 2002, 34(10): 18–19.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Lj., Shi, My., Song, Xm. et al. Clinical effect observation on acupuncture for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J. Acupunct. Tuina. Sci. 13, 306–311 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11726-015-0872-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11726-015-0872-4
Keywords
- Acupuncture Therapy
- Pulmonary Disease
- Chronic Obstructive
- Respiratory Function Tests
- Heart Function Tests