Abstract
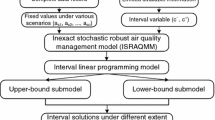
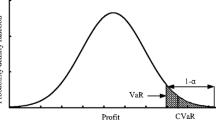
In this study, interval-parameter programming, two-stage stochastic programming (TSP), and conditional value-at-risk (CVaR) were incorporated into a general optimization framework, leading to an interval-parameter CVaR-based two-stage programming (ICTP) method. The ICTP method had several advantages: (i) its objective function simultaneously took expected cost and risk cost into consideration, and also used discrete random variables and discrete intervals to reflect uncertain properties; (ii) it quantitatively evaluated the right tail of distributions of random variables which could better calculate the risk of violated environmental standards; (iii) it was useful for helping decision makers to analyze the trade-offs between cost and risk; and (iv) it was effective to penalize the second-stage costs, as well as to capture the notion of risk in stochastic programming. The developed model was applied to sulfur dioxide abatement in an air quality management system. The results indicated that the ICTP method could be used for generating a series of air quality management schemes under different risk-aversion levels, for identifying desired air quality management strategies for decision makers, and for considering a proper balance between system economy and environmental quality.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed S (2004). Mean-risk objectives in stochastic programming. Technical report, Georgia Institute of Technology, available at www.optimization-online.org
An H, Eheart J W (2007). A screening technique for joint chance-constrained programming for air-quality management. Oper Res, 55(4): 792–798
Athanasiadis I N, Mitkas P A (2007). Knowledge discovery for operational decision support in air quality management. Journal of Environmental Informatics, 9(2): 100–107
Birbil S I, Frenk J, Kaynar B, Noyan N (2009). Risk measures and their applications in asset management. In: Gregoriou G N, ed. The VaR Implementation Handbook. New York: The McGraw-Hill Companies, 311–337
Birge J R, Louveaux F V (1988). A multicut algorithm for two-stage stochastic linear programs. Eur J Oper Res, 34(3): 384–392
Byun D W, Kim S T, Chen F Y, Kim S B, Cuclis A, Moon N K (2003). Information infrastructure for air quality modeling and analysis: application to the houston-galveston ozone non-attainment area. Journal of Environmental Informatics, 2(2): 38–57
Cai Y P, Huang G H, Tan Q, Yang Z F (2011a). An integrated approach for climate-change impact analysis and adaptation planning under multi-level uncertainties. Part I: methodology. Renewable & Sustainable Energy Reviews, 15: 2779–2790
Cai Y P, Huang G H, Tan Q, Liu L (2011b). An integrated approach for climate-change impact analysis and adaptation planning under multilevel uncertainties. Part II. case study. Renewable & Sustainable Energy Reviews, 15: 3051–3073
Chen C, Huang G H, Li Y, Li M (2013a). Model of risk analysis on site selection of biomass power plant based on stochastic robust interval method. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 29(20): 206–213
Chen C, Huang G H, Li Y P, Zhou Y (2013b). A robust risk analysis method for water resources allocation under uncertainty. Stochastic Environ Res Risk Assess, 27(3): 713–723
Dai C, Li Y, Huang G (2012). An interval-parameter chance-constrained dynamic programming approach for capacity planning under uncertainty. Resour Conserv Recycling, 62: 37–50
Dentcheva D, Ruszczynski A (2006). Portfolio optimization with stochastic dominance constraints. J Bank Finance, 30(2): 433–451
Dong C, Huang G H, Cai Y P, Liu Y (2012). An inexact optimization modeling approach for supporting energy systems planning and air pollution mitigation in Beijing City. Energy, 37(1): 673–688
Fábián C I (2008). Handling CVaR objectives and constraints in two-stage stochastic models. Eur J Oper Res, 191(3): 888–911
Haurie A, Kübler J, Clappier A, Van Den Bergh H (2004). A metamodeling approach for integrated assessment of air quality policies. Environ Model Assess, 9(1): 1–12
Hsu C P, Huang CW, Paul Chiou WJ P (2012). Effectiveness of copulaextreme value theory in estimating value-at-risk: empirical evidence from Asian emerging markets. Rev Quant Finance Account, 39(4): 447–468
Huang G, Loucks D (2000). An inexact two-stage stochastic programming model for water resources management under uncertainty. Civ Eng Environ Syst, 17(2): 95–118
Huang G H, Baetz B W, Patry G G (1994). Grey dynamic programming for waste-management planning under uncertainty. J Urban Plann Dev, 120(3): 132–156
Huang G H, Chang N B (2003). Perspectives of environmental informatics and systems analysis. J Environ Inform, 1(1): 1–6
Inuiguchi M, Sakawa M (1998). Robust optimization under softness in a fuzzy linear programming problem. Int J Approx Reason, 18(1–2): 21–34
Lejano R P, Ayala P M, Gonzales E A (1997). RESEARCH: optimizing the mix of strategies for control of vehicular emissions. Environ Manage, 21(1): 79–87
Li Y, Huang G, Nie X, Nie S (2008). An inexact fuzzy-robust two-stage programming model for managing sulfur dioxide abatement under uncertainty. Environ Model Assess, 13(1): 77–91
Li Y, Huang G H, Veawab A, Nie X, Liu L (2006). Two-stage fuzzy-stochastic robust programming: a hybrid model for regional air quality management. J Air Waste Manag Assoc, 56(8): 1070–1082
Lim C, Sherali H D, Uryasev S (2010). Portfolio optimization by minimizing conditional value-at-risk via nondifferentiable optimization. Comput Optim Appl, 46(3): 391–415
Liu L, Huang G, Liu Y, Fuller G, Zeng G (2003). A fuzzy-stochastic robust programming model for regional air quality management under uncertainty. Eng Optim, 35(2): 177–199
Liu Y, Zou R, Guo H (2011). Risk explicit interval linear programming model for uncertainty-based nutrient-reduction optimization for the Lake Qionghai Watershed. J Water Resour Plann Manage, 137(1), 83–91
Lv Y, Huang G H, Li Y P, Yang Z F, Sun W (2011). A two-stage inexact joint-probabilistic programming method for air quality management under uncertainty. J Environ Manage, 92(3): 813–826
Ma X, Zhang F (2002). A genetic algorithm based stochastic programming model for air quality management. J Environ Sci (China), 14(3): 367–374
Marti K, Ploöchinger E (1990). Optimal step sizes in semi-stochastic approximation procedures. I. Optimization, 21(1): 123–153
Miller N, Ruszczynski A (2008). Risk-adjusted probability measures in portfolio optimization with coherent measures of risk. Eur J Oper Res, 191(1): 193–206
Noyan N (2012). Risk-averse two-stage stochastic programming with an application to disaster management. Comput Oper Res, 39(3): 541–559
Rockafellar R T, Uryasev S (2000). Optimization of conditional valueatrisk. Journal of Risk, 2: 21–42
Ruszczyński A (1993). Parallel decomposition of multistage stochastic programming problems. Math Program, 58(1–3): 201–228
Schultz R (2011). Risk aversion in two-stage stochastic integer programming. Stochastic Programming: 165–187
Schultz R, Tiedemann S (2006). Conditional value-at-risk in stochastic programs with mixed-integer recourse. Math Program, 105(2–3): 365–386
Seifi A, Hipel K (2001). Interior-point method for reservoir operation with stochastic inflows. J Water Resour Plan Manage, 127(1): 48–57
Shao L G, Qin X S, Xu Y (2011). A conditional value-at-risk based inexact water allocation model. Water Resour Manage, 25(9): 2125–2145
Tan Q, Huang G H, Wu C Z, Cai Y P (2011). IF-EM: an interval-parameter fuzzy linear programming model for environment-oriented evacuation planning under uncertainty. J Adv Transport, 45(4): 286–303
Tong X J, Qi L Q, Wu F, Zhou H (2010). A smoothing method for solving portfolio optimization with CVaR and applications in allocation of generation asset. Appl Math Comput, 216(6): 1723–1740
Turner D B (1970). Workbook of atmospheric dispersion estimates. Washington D C: Office of Air Programs, Publication No. AP-26, U. S. Environmental Protection Agency
Wang L, Milford J B (2001). Reliability of optimal control strategies for photochemical air pollution. Environ Sci Technol, 35(6): 1173–1180
Zolezzi T (2001). Well-posedness and optimization under perturbations. Ann Oper Res, 101(1/4): 351–361
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dai, C., Sun, W., Tan, Q. et al. Risk management for sulfur dioxide abatement under multiple uncertainties. Front. Earth Sci. 10, 87–107 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11707-015-0495-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11707-015-0495-6