Abstract
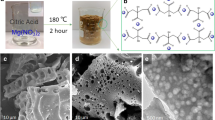
A porous Pb foam was fabricated electrochemically at a copper substrate and then used as the cathode for the electroreduction of CO2. The surface morphology and composition of the porous Pb electrode was characterized by scanning electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, transmission electron microscopy and selected area electron diffraction. The honeycomb-like porous structure was composed of needle-like Pb deposits. Cyclic voltammetry studies demonstrated that the porous Pb electrode had better electrocatalytic performance for the formation of formic acid from CO2 compared with a Pb plate electrode. The increase in current density was due to the large surface area of the porous Pb electrode, which provides more active sites on the electrode surface. The improved formic acid selectivity was due to the morphology of the roughened surface, which contains significantly more low-coordination sites which are more active for CO2 reduction. The highest current efficiency for formic acid was 96.8% at −1.7 V versus saturated calomel electrode at 5 °C. This porous Pb electrode with good catalytic abilities represents a new 3D porous material with applications for the electroreduction of CO2.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Enthaler S, von Langermann J, Schmidt T. Carbon dioxide and formic acid—the couple for environmental-friendly hydrogen storage. Energy & Environmental Science, 2011, 3(9): 1207–1217
Todoroki M, Hara K, Kudo A, Sakata T. Electrochemical reduction of high pressure CO2 at Pb, Hg and In electrodes in an aqueous KHCO3 solution. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 1995, 394(1–2): 199–203
Köleli F, Atilan T, Palamut N, Gizir A M, Aydin R, Hamann C H. Electrochemical reduction of CO2 at Pb- and Sn-electrodes in a fixed-bed reactor in aqueous K2CO3 and KHCO3 media. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 2003, 33(5): 447–450
Machunda R L, Ju H, Lee J. Electrocatalytic reduction of CO2 gas at Sn based gas diffusion electrode. Current Applied Physics, 2011, 11(4): 986–988
Hara K, Kudo A, Sakata T, Hiramoto M, Watanabe M, Sakata T. Electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide under high pressure on various electrodes in an aqueous electrolyte. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 1995, 391(1–2): 141–147
Hara K, Kudo A, Sakata T, Hiramoto M, Watanabe M, Sakata T. Carbon dioxide reduction at low temperature on various metal electrodes. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry and Interfacial Electrochemistry, 1989, 260(2): 441–445
Tang W, Peterson A A, Varela A S, Jovanov Z P, Bech L, DurandW J, Dahl S, Nørskovb J K, Chorkendorff I. The importance of surface morphology in controlling the selectivity of polycrystalline copper for CO2 electroreduction. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2012, 14(1): 76–81
Innocent B, Liaigre D, Pasquier D, Ropital F, Léger J M, Kokoh K B. Electro-reduction of carbon dioxide to formate on lead electrode in aqueous medium. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 2009, 39(2): 227–232
Kwon Y, Lee J. Formic acid from carbon dioxide on nanolayered electrocatalyst. Electrocatalysis, 2010, 1(2–3): 108–115
Machunda R L, Lee J G, Lee J. Microstructural surface changes of electrodeposited Pb on gas diffusion electrode during electroreduction of gas-phase CO2. Surface and Interface Analysis, 2010, 42(6–7): 564–567
Köleli F, Balun D. Reduction of CO2 under high pressure and high temperature on Pb-granule electrodes in a fixed-bed reactor in aqueous medium. Applied Catalysis A, General, 2004, 274(1–2): 237–242
Rolison D R, Long J W, Lytle J C, Fischer A E, Rhodes C P, McEvoy T M, Bourg M E, Lubers A M. Multifunctional 3D nanoarchitectures for energy storage and conversion. Chemical Society Reviews, 2009, 38(1): 226–252
Kang B, Ceder G. Battery materials for ultrafast charging and discharging. Nature, 2009, 458(7235): 190–193
Berube V, Radtke G, Dresselhaus M, Chen G. Size effects on the hydrogen storage properties of nanostructured metal hydrides: A review. International Journal of Energy Research, 2007, 31(6–7): 637–663
Nishizawa M, Menon V P, Martin C R. Metal nanotubule membranes with electrochemically switchable ion-transport selectivity. Science, 1995, 268(5211): 700–702
Lee J, Sohn K, Hyeon T. Fabrication of novel mesocellular carbon foams with uniform ultralarge mesopores. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2001, 123(21): 5146–5147
Shin H C, Dong J, Liu M. Nanoporous structures prepared by an electrochemical deposition process. Advanced Materials, 2003, 15(19): 1610–1614
Shin H C, Liu M. Copper foam structures with highly porous nanostructured walls. Chemistry of Materials, 2004, 16(25): 5460–5464
Li Y, Jia W Z, Song Y Y, Xia X H. Superhydrophobicity of 3D porous copper films prepared using the hydrogen bubble dynamic template. Chemistry of Materials, 2007, 19(25): 5758–5764
Nam D H, Kim R H, Han D W, Kwon H S. Electrochemical performances of Sn anode electrodeposited on porous Cu foam for Li-ion batteries. Electrochimica Acta, 2012, 66: 126–132
Cherevko S, Chung C H. Impact of key deposition parameters on the morphology of silver foams prepared by dynamic hydrogen template deposition. Electrochimica Acta, 2010, 55(22): 6383–6390
Xing X L, Cherevko S, Chung C H. Porous Pd films as effective ethanol oxidation electrocatalysts in alkaline medium. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2011, 126(1–2): 36–40
Cherevko S, Chung C H. Direct electrodeposition of nanoporous gold with controlled multimodal pore size distribution. Electrochemistry Communications, 2011, 13(1): 16–19
Shin H C, Liu M. Three-dimensional porous copper-tin alloy electrodes for rechargeable lithium batteries. Advanced Functional Materials, 2005, 15(4): 582–586
Ni Y H, Zhang Y M, Hong J M. Hierarchical Pb microstructures: A facile electrochemical synthesis, shape evolution and influencing factors. CrystEngComm, 2011, 13(3): 934–940
Nam D H, Kim R H, Han D W, Kim J H, Kwon H S. Effects of (NH4)2SO4 and BTA on the nanostructure of copper foam prepared by electrodeposition. Electrochimica Acta, 2011, 56(22): 9397–9405
Hori Y. Electrochemical CO2 reduction on metal electrodes. New York: Springer, 2008, 89–189
Kaneco S, Hiei N, Xing Y, Katsumata H, Ohnishi H, Suzuki T, Ohta K. Electrochemical conversion of carbon dioxide to methane in aqueous NaHCO3solution at less than 273 K. Electrochimica Acta, 2002, 48(1): 51–55
Kaneco S, Iiba K, Ohta K, Mizuno T, Saji A. Electrochemical reduction of CO2 on Au in KOH + methanol at low temperature. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 1998, 441(1–2): 215–220
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Wang, H., Han, Z. et al. Electrodeposited porous Pb electrode with improved electrocatalytic performance for the electroreduction of CO2 to formic acid. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 9, 57–63 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11705-014-1444-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11705-014-1444-8