Abstract
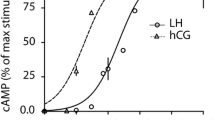
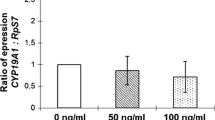
It has previously been shown that Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hCG) can stimulate steroidogenesis in Leydig cells. In the present study, the mechanisms of hCG-stimulated steroidogenesis in Leydig cells of immaturated pigs were investigated. It was found that both hCG and 8-Br-cAMP could enhance the expression level of both the Steroidogenic acute regulatory protein (StAR) and mRNA, and increase the activity of extracellular signal-regulated kinase1/2 (ERK1/2) significantly depending on stimulating time. However, the effect of 8-Br-cAMP was more significant than that of hCG. While appending the inhibitor of Protein Kinase A (PKA) to Leydig cells in culture, the expression level of StAR protein, mRNA and the activity of ERK1/2 began to drop significantly, but the level of StAR mRNA could still be detectable. While appending the inhibitor of MAPK (PD98059), the expression level of StAR protein and mRNA declined significantly. These results infer that at the beginning of hCG stimulation, hCG increases the level of StAR protein by cAMP-PKA. With prolonged stimulating time, hCG increases the level of StAR protein through cAMP-PKA-ERK1/2.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Clark B J, Stocco D M (1997). Steroidogenic acute regulatory protein: The StAR still shines brightly. Mol Cell Endocrinol, 134: 1–8
Cooke B A (1999). Signal transduction involving cyclic AMP-dependent and cyclic AMP-independent mechanisms in the control of steroidogenesis. Mol Cell Endocrinol, 151(1): 25–35
Dewi D A, Abayasekara D R E, Wheeler-Jones C P D (2001). Requirement for ERK1/2 activation in the regulation of progesterone production in human granulosa-lutein cells is stimulus specific. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 86: 375–380
Irina P A, Zhao D, Dale B H, Hales K H, Jefcoate C R (2001). Mitochondrial processing of newly synthesized steroidogenic acute regulatory protein (StAR), but not total StAR, mediates cholesterol transfer to cytochrome P450 side chain cleavage enzyme in adrenal cells. J Biol Chem, 276(49): 46583–46596
Mauduit C, Gasnier F, Rey C, Chauvin M A, Stocco D M, Louisot P, Benahmed M (1998). Tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibits Leydig cell steroidogenesis through a decrease in steroidogenic acute regulatory protein expression. Endocrinol, 139(6): 2863–2868
Moore R K, Otsuka F, Shimasaki S (2001). Role of ERK1/2 in the differential synthesis of progesterone and estradiol by granulosa cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 289(4): 796–800
Reinhart A J, Williams S C, Stocco D M (1999). Transcriptional regulation of the StAR gene. Mol Cell Endocrinol, 151(1): 161–169
Seger R, Hanoch T, Rosenberg R, Dantes A, Merz W E, Strauss J F (2001). The ERK signaling cascade inhibits gonadotropin-stimulated steroidogenesis. J Biol Chem, 276(17): 13957–13964
Stocco D M (1997). A StAR search: implications in controlling steroidogenesis. Biol Reprod, 56: 328–336
Tajima K, Dantes A, Yao Z, Sorokina K, Kotsuji F, Seger R, Amsterdam A (2003). Down-regulation of steroidogenic response to gonadotropins in human and rat preovulatory granulosa cells involves mitogen-activated protein kinase activation and modulation of DAX-1 and steroidogenic factor-1. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 88(5): 2288–2299
Tremblay J J, Viger R S (2001). GATA factors differentially activate multiple gonadal promoters through conserved GATA regulatory elements. Endocrinol, 142(3): 977–986
Wang X Z, Pan H M, Sun Y, Wu J Y, Zhang J H (2005). HCG acutely regulating testosterone’s biosynthesis through increasing the expressing of StAR protein. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 36(8): 789–793 (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2006, 37(11): 1154–1159 [译自: 畜牧兽医学报]
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Sun, Y., Wu, J. et al. Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) regulates the expression of Steroidogenic acute regulatory protein (StAR) via the ERK1/2 pathway. Front. Agric. China 1, 334–338 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11703-007-0056-1
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11703-007-0056-1