Abstract
Background
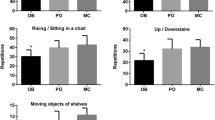
Obese and post-bariatric surgery (BS) subjects often present limitations in physical functioning (PF). The Glittre ADL-test is a simple and useful way to evaluate this outcome. It includes functional activities such as rising from a chair, lifting, carrying weights, and bending over and was never studied in the obese population. This study aimed to determine the validity and reproducibility of the Glittre ADL-test to evaluate PF in obese, post-BS, and healthy control subjects.
Methods
Twenty-one post-BS patients (3–4 years post-surgery) (16 women, 41 ± 11 years, BMI = 28 ± 4 kg m−2) (group PO); 21 obese individuals (16 women, 44 ± 9 years, BMI = 44 ± 6 kg.m−2) (group OB) and 21 control individuals matched to PO (16 women, 42 ± 12 years old, BMI = 27 ± 6 kg m−2) (group MC) were included. For the reproducibility analysis, the Glittre ADL-test was performed twice, with a 30-min interval. As criterion methods for the validation, subjects performed two walking tests and answered a health status questionnaire (SF-36).
Results
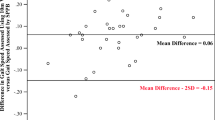
High intraclass correlation (OB: r = 0.91 and PO: r = 0.89; MC: r = 0.86; P < 0.0001 for all) and good Bland–Altman agreement between the two tests were found in all groups. However, learning effect ranged between 8.8 and 11.8 % and significant test–retest differences occurred. The test was valid for all groups (moderate-to-high significant correlations with the criterion methods).
Conclusions
Glittre ADL-test is valid and reproducible to evaluate PF of obese, post-BS, and healthy control subjects. However, due to the large learning effect, two tests are required for accurate assessment.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Josbeno DA, Jakicic JM, Hergenroeder A, et al. Physical activity and physical function changes in obese individuals after gastric bypass surgery. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2010;6:361–6.
de Souza SA, Faintuch J, Valezi AC, et al. Gait cinematic analysis in morbidly obese patients. Obes Surg. 2005;15:1238–42.
Dechman G, Scherer SA. Outcome measures in cardiopulmonary physical therapy: focus on the Glittre ADL-test for people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Cardiopulm Phys Ther J. 2008;19:115–8.
Skumlien S, Hagelund T, Bjortuft O, et al. A field test of functional status as performance of activities of daily living in COPD patients. Respir Med. 2006;100:316–23.
SAGES. Guideline for clinical application of laparoscopic bariatric surgery. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2009;5:387–405.
Ciconelli RM, Ferraz MB, Santos W, et al. Tradução para a língua portuguesa e validação do questionário genérico de avaliação de qualidade de vida Medical Outcomes Study 36-item Short Form Health Survey SF-36 (Brasil SF-36). Rev Bras Reumatol. 1999;39(3):143–50.
Beriault K, Carpentier AC, Gagnon C, et al. Reproducibility of the 6-minute walk test in obese adults. Int J Sports Med. 2009;30:725–7.
Jurgensen SP, Trimer R, Dourado VZ, et al. Shuttle walking test in obese women: test-retest reliability and concurrent validity with peak oxygen uptake. Clin Physiol Funct Imaging. 2015;35:120–6.
Larsson UE, Reynisdottir S. The six-minute walk test in outpatients with obesity: reproducibility and known group validity. Physiother Res Int. 2008;13:84–93.
Jose A, Dal CS. Reproducibility of the six-minute walk test and Glittre ADL-test in patients hospitalized for acute and exacerbated chronic lung disease. Braz J Phys Ther. 2015;19:235–42.
Holland AE, Spruit MA, Troosters T, et al. An official European Respiratory Society/American Thoracic Society technical standard: field walking tests in chronic respiratory disease. Eur Respir J. 2014;44:1428–46.
Acknowledgments
FP is a researcher supported by CNPq (National Council for Scientific and Technological Development), Brazil.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Statement of Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Statement of Human and Animal rights
The study was approved by the institutional Ethics Committee.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Monteiro, F., Ponce, D.A.N., Silva, H. et al. Validity and Reproducibility of the Glittre ADL-Test in Obese and Post-Bariatric Surgery Patients. OBES SURG 27, 110–114 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-016-2244-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-016-2244-7