Abstract
Background
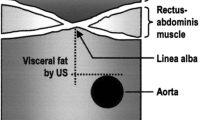
Architecture of abdominal fat above and below Scarpa’s fascia is morphologically different. Little information is available about the relative distribution patterns of deep and superficial fat layers in massive weight loss (MWL) patients. This study aimed to evaluate the relative distribution patterns of deep and superficial abdominal fat layers in two groups of MWL patients presenting for abdominoplasty: (1) MWL via nutritional management and (2) MWL via bariatric surgery.
Methods
All MWL patients with stable body weight for a minimum of 24 months presenting for abdominal body contouring at Lausanne University Hospital, Department of Plastic Surgery between July 2008 and June 2009 were included. Patients with preexisting metabolic diseases were excluded. Patients with nutritional deficiencies were deferred until corrected.
Results
Nineteen consecutive patients were included in the study, 7 post-bariatric patients and 12 patients after dietary-induced weight loss (5 were males and 14 were females; average age 45.5 years, range 36–64 years), with an average weight loss of 48 kg (57 kg post-bariatric, 28 kg dietary induced) and a mean body mass index of 29.2 kg/m2 (range 24.0–40.7) at the time of abdominoplasty. Morphologic evaluation yielded a relative distribution of deep to superficial fat layers of 42 to 58 % in the post-bariatric group versus 31 to 69 % (p < 0.05) in the nutritionally induced group.
Conclusions
These data show that the morphologic distribution patterns of deep and superficial abdominal fat layers differ with regards to mode of weight loss.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abu-Hijleh MF, Roshier AL, Al Shboul Q, et al. The membranous layer of superficial fascia: evidence for its widespread distribution in the body. Surg Radiol Anat. 2006;28:606–19.
Lancerotto L, Stecco C, Macchi V, et al. Layers of the abdominal wall: anatomical investigation of subcutaneous tissue and superficial fascia. Surg Radiol Anat. 2011;33(10):835–42.
Chopra J, Rani A, Rani A, et al. Re-evaluation of superficial fascia of anterior abdominal wall: a computed tomographic study. Surg Radiol Anat. 2011;33(10):843–9.
Illouz YG. Body contouring by lipolysis: a 5-year experience with over 3000 cases. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1983;72:591–7.
Lee Y, Hong JJ, Bang C. Dual-plane lipoplasty for the superficial and deep layers. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1999;104:1877–84.
Gradmark AM, Rydh A, Renstrom F, et al. Computed tomography-based validation of abdominal adiposity measurements from ultrasonography, dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry and anthropometry. Br J Nutr. 2010;104:582–8.
Gasperoni C, Salgarello M. Rationale of subdermal superficial liposuction related to the anatomy of subcutaneous fat and the superficial fascial system. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 1995;19:13–20.
Rieger U, Scheufler O, Schmid D, et al. Six treatment principles of the basle pressure sore concept. Handchir Mikrochir Plast Chir. 2007;39:206–14.
Pitanguy I, Mayer B, Labrakis G. Abdominoplasty—personal surgical guidelines. Zentralbl Chir. 1988;113:765–71.
Kohli S, Sniderman AD, Tchernof A, et al. Ethnic-specific differences in abdominal subcutaneous adipose tissue compartments. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2010;18:2177–83.
Kalbermatten DF, Schaakxs D, Kingham PJ, et al. Neurotrophic activity of human adipose stem cells isolated from deep and superficial layers of abdominal fat. Cell Tissue Res. 2011;344:251–60.
Monzon JR, Basile R, Heneghan S, et al. Lipolysis in adipocytes isolated from deep and superficial subcutaneous adipose tissue. Obes Res. 2002;10:266–9.
Walker GE, Verti B, Marzullo P, et al. Deep subcutaneous adipose tissue: a distinct abdominal adipose depot. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2007;15:1933–43.
Kelley DE, Thaete FL, Troost F, et al. Subdivisions of subcutaneous abdominal adipose tissue and insulin resistance. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2000;278:E941–8.
Walker GE, Marzullo P, Verti B, et al. Subcutaneous abdominal adipose tissue subcompartments: potential role in rosiglitazone effects. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2008;16:1983–91.
Ybarra J, Blanco-Vaca F, Fernandez S, et al. The effects of liposuction removal of subcutaneous abdominal fat on lipid metabolism are independent of insulin sensitivity in normal-overweight individuals. Obes Surg. 2008;18:408–14.
Narsete T, Narsete M, Buckspan R, et al. Large-volume liposuction and prevention of type 2 diabetes: a preliminary report. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2011;36(2):438–42.
He Q, Engelson ES, Kotler DP. A comparison of abdominal subcutaneous adipose tissue pattern in obese and lean HIV-infected women. J Nutr. 2005;135:53–7.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rieger, U.M., Raschke, G.F. & Kalbermatten, D.F. Deep and Superficial Fat Ratio in Dietary and Surgically Induced Weight Loss Patients. OBES SURG 22, 1617–1622 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-012-0717-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-012-0717-x