Abstract
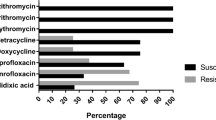
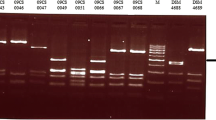
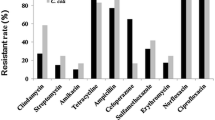
The objective of the current study was to investigate mutations in the gyrA and 23S rRNA gene fragments the high level ciprofloxacin resistant (HL-CipR) Campylobacter isolates (C. jejuni n = 6 and and C. coli n = 9) obtained from chicken meat samples, in Turkey. PCR-based restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) was used to characterize these isolates. In addition, the presence of several virulence traits among these isolates was also examined. Of the 15 HL-CipR Campylobacter strains, there were eight unique RFLP banding patterns. All HL-CipR Campylobacter strains had mutations in codon 86 (Thr-86 to Ile) in the gyrA gene. Four C. jejuni isolates had missense mutation of Asp-203 to Ser, whereas one C. jejuni strain also presented a change at Ala-40 to Ser. A2075G substitution in the 23S rRNA gene was identified in five isolates (C. coli n = 3 and C. jejuni n = 2), whereas none of the isolates had A2074G substitution. The tetO gene conferring resistance to tetracycline were observed among five Campylobacter isolates. Of Campylobacter strains, 13 (86.6 %) were found to be positive for one or more virulence factors, the cdt genes being the most detected. The results of the current study extends the current knowledge about molecular mechanisms for erythromycin and ciprofloxacin resistance as well as virulence traits by investigation of HL-CipR Campylobacter isolates from chicken meat sold in Turkey.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
EFSA (European Food Safety Authority) and ECDC (European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control), J. EFSA 12, 3547 (2014)
G.M. Ruiz-Palacios, Clin. Infect. Dis. 44, 701–703 (2007)
J.P. Butzler, Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 10, 868–876 (2004)
M.C. Peterson, West. J. Med. 161, 148–152 (1994)
R.A. Batchelor, B.M. Pearson, L.M. Friis, P. Guerry, J.M. Wells, Microbiology 150, 3507–3517 (2004)
M.E. Konkel, J.E. Christensen, A.S. Dhillon, A.B. Lane, R. Hare-Sanford, D.M. Schaberg, C.L. Larson, Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 7, 2297–2305 (2007)
M. Lehtopolku, U.M. Nakari, P. Kotilainen, P. Huovinen, A. Siitonen, A.J. Hakanen, Antimicrob. Agent. Chemother. 54, 1232–1236 (2010)
K. Wieczorek, J. Osek, Biomed Res. Int. (2013). doi:10.1155/2013/340605
P.N. Gaunt, L.J.V. Piddock, J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 37, 747–757 (1996)
L.J.V. Piddock, J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 36, 891–898 (1995)
S. Payot, J.M. Bolla, D. Corcoran, S. Fanning, F. Megraud, Q. Zhang, Microb. Infect. 8, 1967–1971 (2006)
D. Bolton, A. Patriarchi, A. Fox, S. Fanning, Food Control 30, 222–226 (2013)
D. Corcoran, T. Quinn, L. Cotter, S. Fanning, FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 253, 39–46 (2005)
G. Zirnstein, Y. Li, B. Swamınathan, F. Angulo, J. Clin. Microbiol. 37(10), 3276–3280 (1999)
R. Alonso, E. Mateo, E. Churruca, I. Martinez, C. Girbau, A. Ferna´ndez-Astorga, J. Microbiol. Meth. 63, 99–103 (2005)
M.R. Khanna, S.P. Bhavsar, B.P. Kapadnis, Lett. Appl. Microbiol 43, 84–90 (2006)
D.D. Bang, E.M. Nielsen, F. Scheutz, K. Pedersen, K. Handberg, M. Madsen, J. Appl. Microbiol. 94, 1003–1014 (2003)
S. Datta, H. Niwa, K. Itoh, J. Med. Microbiol. 52, 345–348 (2003)
D.J. Bacon, R.A. Alm, D.H. Burr, L. Hu, D.J. Kopecko, C.P. Ewing, T.J. Trust, P. Guerry, Infect. Immun. 68, 4384–4390 (2000)
L. Moran, C. Kelly, M. Cormican, S. McGettrick, R.H. Madden, Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 52, 614–618 (2011)
G. Wang, C.G. Clark, T.M. Taylor, C. Pucknell, C. Barton, L. Price, D.L. Woodward, F.G. Rodgerst, J. Clin. Microbiol. 40, 4744–4747 (2002)
I. Nachamkin, K. Bohachick, C.M. Patton, J. Clin. Microbiol. 31, 1531–1536 (1993)
CLSI, Approv. Guidel. M45-A, 26 (2008)
E. Sifré, B.A. Salha, A. Ducournaua, P. Floch, H. Chardon, F. Mégraud, P. Lehours, J. Microbiol. Meth. 119, 206–213 (2015)
D. Corcoran, T. Quinn, L. Cotter, S. Fanning, Int. J. Antimicrob. Agent 27, 40–45 (2006)
A. Pratt, V. Korolik, J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 55, 452–460 (2005)
S. Savaşan, A. Çiftçi, K.S. Diker, J. Turk, Vet. Anim. Sci. 28, 391–397 (2004)
S. Kittl, G. Heckel, B. M. Korczak, P. Kuhnert, Source attribution of human Campylobacter isolates by MLST and Fla-typing and association of genotypes with quinolone resistance. Plos One, 8, (2013). doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0081796
B.M. Korczak, M. Zurfluh, S. Emler, J. Kuhn-Oertli, P. Kuhnert, J. Clin. Microbiol. 47, 1996–2007 (2009)
L. Petersen, S.L.W. On, Lett. Appl. Microbiol 31, 14–19 (2000)
H.B. Ertaş, B. Çetinkaya, A. Muz, H. Öngör, Int. J. Food Microbiol. 94, 203–209 (2004)
K. Wieczorek, J. Osek, Food Microbiol. 49, 161–165 (2015)
J. Zhou, M. Zhang, W. Yang, Y. Fang, G. Wang, F. Hou, Int. J. Infect. Dis. 42, 28–33 (2016)
T. Nakajima, A. Tazumi, S. Nakanishi, J. Xu, L. Han, N. Misawa, J.E. Moore, B.C. Millar, M. Matsuda, Ann. Microbiol. 62, 1495–1500 (2012)
N.M. Iovine, Virulence 4(3), 230–240 (2013)
S.S. Qin, C.M. Wu, Y. Wang, B. Jeon, Z.Q. Shen, Y. Wang, Q. Zhang, J.Z. Shen, Int. J. Food Microbiol. 146, 94–98 (2011)
B.S. Frasao, V. Medeiros, A.V. Barbosa, W.S. Aguiar, F.F. Santos, D.L.C. Abreu, M.M. Clementino, M.H.C. Aquino, Ciência Rural, 45, 2013–2018 (2015)
T. Kayman, S. Abay, H. Hızlısoy, Mikrobiyol. Bul. 47, 230–239 (2013)
K. Wieczorek, E. Denis, O. Lynch, J. Osek, Food Microbiol. 34, 130–136 (2013)
M. N. Acik, M. Karahan, H. Ongor, B. Cetinkaya, Foodborne Pathog. Dis. (2013). doi:10.1089/fpd.2012.1447
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Mustafa Kemal University Scientific Research Fund (Project Number: BAP-10380).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kurekci, C., Pehlivanlar Önen, S. Characteristics of ciprofloxacin resistant Campylobacter spp. isolated from chicken meat in Turkey. Food Measure 11, 586–591 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-016-9426-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-016-9426-9