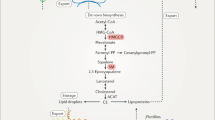
Abstract
A non-deterministic finite automaton is designed to observe the cholesterol metabolism with the states of acceptance and rejection. The acceptance state of the automaton depicts the normal level of metabolism and production of good cholesterol as an end product. The rejection state of this machine shows the inhibition of enzymatic activity in cholesterol synthesis and removal of free fatty acids. The deficiency in human cholesterol metabolism pathway results in abnormal accumulation of cholesterol in plasma, arterial tissues leading to diseases such as hypercholesterolemia, atherosclerosis respectively and formation of gallstones. The designed machine can be used to monitor the cholesterol metabolism at molecular level through regulation of enzymes involved in the biosynthesis and metabolism of cholesterol for the treatment of diseases incident due to the respective metabolic disorder. In addition, an algorithm for this machine has been developed to compare the programmed string with the given string. This study demonstrates the construction of a machine that is used for the development of molecular targeted therapy for the disorders in cholesterol metabolism.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali RMM, Gurusamy PD, Ramachandran S (2014) Computational regulatory model for detoxification of ammonia from urea cycle in liver. Turk J Biol. doi:10.3906/biy-1401-50
Banerji A (2013) An attempt to construct a (general) mathematical framework to model biological “context-dependence”. Syst Synth Biol 7:221–227
Banerji A (2014) A probabilistic model to describe the dual phenomena of biochemical pathway damage and biochemical pathway repair. arXiv:1404.0701 [q-bio.OT]
Benenson Y, Paz-Elizur T, Adar R, Keinan E, Livneh Z, Shapiro E (2001) Programmable and autonomous computing machine made of biomolecules. Nature 414:430–434
Bennion LJ, Grundy SM (1975) Effects of obesity and caloric intake on biliary lipid metabolism in man. J Clin Invest 56:996–1011
Blakes J, Twycross J, Romero-Campero FJ, Krasnogor N (2011) The Infobiotics Workbench: an integrated in silico modelling platform for Systems and Synthetic Biology. Bioinformatics 27:3323–3324
Denning PJ (2005) Is computer science science? Commun ACM 48:27–31
Dhar PK, Giuliani A (2010) Laws of biology: why so few? Syst Synth Biol 4:7–13
Dietschy JMI, Gamel WG (1971) Cholesterol synthesis in the intestine of man: regional differences and control mechanisms. J Clin Invest 50:872–880
Grundy SM (1978) Cholesterol metabolism in man (Medical progress). West J Med 128:13–25
Herman GE (2003) Disorders of cholesterol biosynthesis: prototypic metabolic malformation syndromes. Hum Mol Genet 12:R75–R88
Hopcroft JE, Ullman JD (1979) Introduction to automata theory, languages, and computation. Addison-Wesley, Boston
Houten SM, Wanders RJ, Waterham HR (2000) Biochemical and genetic aspects of mevalonate kinase and its deficiency. Biochim Biophys Acta 1529:19–32
Kari L (1997) DNA computing: the arrival of biological mathematics. Math Intell 19:9–22
Kelley RI, Herman GE (2001) Inborn errors of sterol biosynthesis. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet 2:299–341
Marguet P, Balagadde F, Tan C, You L (2007) Biology by design: reduction and synthesis of cellular components and behaviour. J R Soc Interface 4:607–623
Mead JR, Ramji DP (2002) The pivotal role of lipoprotein lipase in atherosclerosis. Cardiovasc Res 55:261–269
Muhammad MR, Devi GP, Selvakumar R (2013) A computational model for monitoring glycolysis process in cancer cells. J Bioinf Intell Control 2:300–304
Nowak R, Plucienniczak A (2008) Finite state automata built on DNA. Biocybern Biomed Eng 28:3–19
Pandit J, Danley DE, Schulte GK, Mazzalupo S, Pauly TA, Hayward CM, Hamanaka ES, Thompson JF, Harwood HJ Jr (2000) Crystal structure of human squalene synthase: a key enzyme in cholesterol biosynthesis. J Biol Chem 275:30610–30617
Priami C (2009) Algorithmic systems biology. Commun ACM 52:80–88
Selvakumar R, Muhammad MR, Devi GP (2013) Computational model for the extraction of human erythropoietin. Int J ChemTech Res 5:2623–2629
Waterham HR (2002) Inherited disorders of cholesterol biosynthesis. Clin Genet 61:393–403
Acknowledgments
Thanks to Ms. M. Faleela Farzana for supporting the algorithm part.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Selvakumar, R., Rashith Muhammad, M. & Poornima Devi, G. Computational model for monitoring cholesterol metabolism. Syst Synth Biol 8, 307–311 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11693-014-9152-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11693-014-9152-8