Abstract
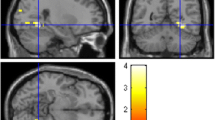
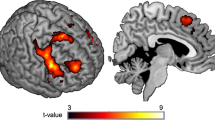
The ability to suppress responses that are inappropriate, as well as the mechanisms monitoring the accuracy of actions in order to compensate for errors, is central to human behavior. Neural alterations that prevent stopping an inaccurate response, combined with a decreased ability of error monitoring, are considered to be prominent features of alcohol abuse. Moreover, (i) alterations of these processes have been reported in heavy social drinkers (i.e. young healthy individuals who do not yet exhibit a state of alcohol dependence); and (ii) through longitudinal studies, these alterations have been shown to underlie subsequent disinhibition that may lead to future alcohol use disorders. In the present functional magnetic resonance imaging study, using a contextual Go/No-Go task, we investigated whether different neural networks subtended correct inhibitions and monitoring mechanisms of failed inhibitory trials in light versus heavy social drinkers. We show that, although successful inhibition did not lead to significant changes, neural networks involved in error monitoring are different in light versus heavy drinkers. Thus, while light drinkers exhibited activations in their right inferior frontal, right middle cingulate and left superior temporal areas; heavy drinkers exhibited activations in their right cerebellum, left caudate nucleus, left superior occipital region, and left amygdala. These data are functionally interpreted as reflecting a “visually-driven emotional strategy” vs. an “executive-based” neural response to errors in heavy and light drinkers, respectively. Such a difference is interpreted as a key-factor that may subtend the transition from a controlled social heavy consumption to a state of clinical alcohol dependence.



Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
06 December 2016
An erratum to this article has been published.
References
Albert, J., Lopez-Martın, S., & Carretié, L. (2010). Emotional context modulates response inhibition: neural and behavioral data. NeuroImage, 49, 914–921.
Aron, A. (2011). From reactive to proactive and selective control: developing a richer model for stopping inappropriate responses. Biological Psychiatry, 69, 55–68.
Aron, A., Robbins, T., & Poldrack, R. (2004). Inhibition and the right inferior frontal cortex. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 8, 170–177.
Babor, T., & Higgins-Biddle, J. (2001). Brief intervention for hazardous and harmful drinking: A manual for use in primary care. Department of Blood Safety and Clinical Technology: World Health Organization.
Babor, T., Campbell, R., Room, R., & Saunders, J. (1994). Lexicon of alcohol and drug terms. Geneva: World Health Organization.
Bari, A., & Robbins, T. (2013). Inhibition and impulsivity: behavioral and neural basis of response control. Progress in Neurobiology, 108, 44–79.
Bartholow, B., Henry, E., & Lust, S. (2007). Effects of alcohol sensitivity on P3 event-related potential reactivity to alcohol cues. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors, 21, 555–563.
Bartholow, B., Lust, S., & Tragesser, S. (2010). Specificity of P3 event-related potential reactivity to alcohol cues in individuals low in alcohol sensitivity. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors, 24, 220–228.
Beck, A. T., & Steer, R. A. (1987). Beck depression inventory manual (1st ed.). San Antonio: Psychological Corporation.
Behrmann, M., Geng, J. J., & Shomstein, S. (2004). Parietal cortex and attention. Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 14(2), 212–217.
Boehler, C. N., Appelbaum, L. G., Krebs, R. M., Hopf, J. M., & Woldorff, M. G. (2010). Pinning down response inhibition in the brain—conjunction analyses of the stop-signal task. NeuroImage, 52(4), 1621–1632.
Boly, M., Coleman, M. R., Davis, M. H., Hampshire, A., Bor, D., Moonen, G., et al. (2007). When thoughts become action: an fMRI paradigm to study volitional brain activity in non-communicative brain injured patients. NeuroImage, 36(3), 979–992.
Bonomo, Y. A., Bowes, G., Coffey, C., Carlin, J. B., & Patton, G. C. (2004). Teenage drinking and the onset of alcohol dependence: a cohort study over seven years. Addiction, 99, 1520–1528.
Botvinick, M. M., Cohen, J. D., & Carter, C. S. (2004). Conflict monitoring and anterior cingulate cortex: an update. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 8(12), 539–546.
Bradley, K. A., Bush, K. R., Epler, A. J., Dobie, D. J., Davis et al. (2003). Two brief alcohol-screening tests from the alcohol use disorders identification test (AUDIT): validation in a female veterans affairs patient population. Archives of Internal Medicine, 163(7), 821–829.
Braver, T. S., Barch, D. M., Gray, J. R., Molfese, D. L., & Snyder, A. (2001). Anterior cingulate cortex and response conflict: effects of frequency, inhibition and errors. Cerebral Cortex, 11(9), 825–836.
Bush, K., Kivlahan, D. R., McDonell, M. B., Fihn, S. D., & Bradley, K. A. (1998). The AUDIT alcohol consumption questions (AUDIT-C): an effective brief screening test for problem drinking. Archives of internal medicine, 158(16), 1789–1795.
Button, K. S., Ioannidis, J. P., Mokrysz, C., Nosek, B. A., Flint, J., et al. (2013). Power failure: why small sample size undermines the reliability of neuroscience. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 14(5), 365–376.
Cai, W., & Leung, H. C. (2011). Rule-guided executive control of response inhibition: functional topography of the inferior frontal cortex. PloS One, 6(6), e20840.
Campanella, S., Peigneux, P., Petit, G., Lallemand, F., Saeremans, M., Noël, X., et al. (2013). Increased cortical activity in binge drinkers during working memory task: a preliminary assessment through a functional magnetic resonance imaging study. PloS One, 8(4), e62260.
Campbell, A. M. G., Evans, M., Thomson, J. L. G., & Williams, M. J. (1971). Cerebral atrophy in young cannabis smokers. Lancet, 298, 1219–1224.
Cardenas, V. A., Studholme, C., Gazdzinski, S., Durazzo, T. C., & Meyerhoff, D. J. (2007). Deformation-based morphometry of brain changes in alcohol dependence and abstinence. NeuroImage, 34(3), 879–887.
Carretié, L., Hinojosa, J. A., Albert, J., & Mercado, F. (2006). Neural response to sustained affective visual stimulation using an indirect task. Experimental Brain Research, 174, 630–637.
Chambers, C., Garavan, H., & Bellgrove, M. (2009). Insights into the neural basis of response inhibition from cognitive and clinical neuroscience. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 33, 631–646.
Chassin, L., Pitts, S. C., & Prost, J. (2002). Binge drinking trajectories from adolescence to emerging adulthood in a high-risk sample: predictors and substance abuse outcomes. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 70(1), 67–78.
Choudhury, S., Blakemore, S. J., & Charman, T. (2006). Social cognitive development during adolescence. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 1(3), 165–174.
Cirilli, L., de Timary, P., Lefèvre, P., & Missal, M. (2011). Individual differences in impulsivity predict anticipatory eye movements. Plos One, 10, e26699.
Cox, W. M., Yeates, G. N., & Regan, C. M. (1999). Effects of alcohol cues on cognitive processing in heavy and light drinkers. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 55, 85–89.
Crego, A., Holguín, S. R., Parada, M., Mota, N., Corral, M., & Cadaveira, F. (2009). Binge drinking affects attentional and visual working memory processing in young university students. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research, 33, 1870–1879.
Crego, A., Rodriguez-Holguín, S., Parada, M., Mota, N., Corral, M., & Cadaveira, F. (2010). Reduced anterior prefrontal cortex activation in young binge drinkers during a visual working memory task. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 109, 45–56.
Crego, A., Cadaveira, F., Parada, M., Corral, M., Caamaño-Isorna, F., & Rodriguez-Holguín, S. (2012). Increased amplitude of P3 event-related potential in young binge drinkers. Alcohol, 46, 415–425.
Crews, F. T., Buckley, T., Dodd, P. R., Ende, G., Foley, H., Harper, C., et al. (2005). Alcoholic neurobiology: changes in dependence and recovery. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research, 29, 1504–1513.
Criaud, M., & Boulinguez, P. (2013). Have we been asking the right questions when assessing response inhibition in go/no-go tasks with fMRI? A meta-analysis and critical review. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 37(1), 11–23.
De Zubicaray, G. I., Andrew, C., Zelaya, F. O., Williams, S. C. R., & Dumanoir, C. (2000). Motor response suppression and the prepotent tendency to respond: a parametric fMRI study. Neuropsychologia, 38(9), 1280–1291.
Dhar, M., Wiersema, J. R., & Pourtois, G. (2011). Cascade of neural events leading from error commission to subsequent awareness revealed using EEG source imaging. PloS One, 6(5), e19578.
Easdon, C., Izenberg, A., Armilio, M. L., Yu, H., & Alain, C. (2005). Alcohol consumption impairs stimulus-and error-related processing during a go/no-go task. Cognitive Brain Research, 25(3), 873–883.
Ehlers, C. L., Phillips, E., Finnerman, G., Gilder, D., Lau, P., & Criado, J. (2007). P3 components and adolescent binge drinking in Southwest California Indians. Neurotoxicology and Teratology, 29, 153–163.
Ernst, M., Bolla, K., Mouratidis, M., Contoreggi, C., Matochik, J. A., Kurian, et al. (2002). Decision-making in a risk-taking task: a PET study. Neuropsychopharmacology 26, 682–691.
Ersche, K. D., Jones, P. S., Williams, G. B., Turton, A. J., Robbins, T. W., & Bullmore, E. T. (2012). Abnormal brain structure implicated in stimulant drug addiction. Science, 335(6068), 601–604.
Etkin, A., Egner, T., Peraza, D. M., Kandel, E. R., & Hirsch, J. (2006). Resolving emotional conflict: a role for the rostral anterior cingulate cortex in modulating activity in the amygdala. Neuron, 51(6), 871–882.
Field, M., Kiernan, A., Eastwood, B., & Child, R. (2008). Rapid approach responses to alcohol cues in heavy drinkers. Journal of Behavior Therapy and Experimental Psychiatry, 39, 209–218.
Friston, K. (2003). Introduction: Experimental design and statistical parametric mapping. In R. Frackowiak, K. Friston, C. Frith, R. Dolan, C. Price, S. Zeki, J. Ashburner, & W. Penny (Eds.), Human brain function. London: Academic Press.
Friston, K. J., Fletcher, P., Josephs, O., Holmes, A., Rugg, M. D., & Turner, R. (1998). Event-related fMRI: characterizing differential responses. Neuro Image, 7(1), 30–40.
Friston, K. J., Stephan, K. E., Lund, T. E., Morcom, A., & Kiebel, S. (2005). Mixed-effects and fMRI studies. Neuro Image, 24(1), 244–252.
Garavan, H., & Stout, J. C. (2005). Neurocognitive insights into substance abuse. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 9(4), 195–201.
Garavan, H., Ross, T. J., Kaufman, J., & Stein, E. A. (2003). A midline dissociation between error-processing and response-conflict monitoring. NeuroImage, 20(2), 1132–1139.
Goldstein, R. Z., & Volkow, N. D. (2011). Dysfunction of the prefrontal cortex in addiction: neuroimaging findings and clinical implications. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 12(11), 652–669.
Goldstein, R. Z., Volkow, N. D., Wang, G. J., Fowler, J. S., & Rajaram, S. (2001). Addiction changes orbitofrontal gyrus function: involvement in response inhibition. Neuroreport, 12(11), 2595.
Goldstein, R. Z., Bechara, A., Garavan, H., Childress, A. R., Paulus, M. P., & Volkow, N. D. (2009). The neurocircuitry of impaired insight in drug addiction. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 13(9), 372–380.
Greeley, J. D., Swift, W., Prescott, J., & Heather, N. (1993). Reactivity to alcohol-related cues in heavy and light drinkers. Journal of Studies on Alcohol, 54, 359–368.
Hall, G. H. (1970). Effects of nicotine and tobacco smoke on the electrical activity of the cerebral cortex and olfactory bulb. British Journal Pharmacology, 38, 271–286.
Henges, A. L., & Marczinski, C. A. (2012). Impulsivity and alcohol consumption in young social drinkers. Addictive Behaviors, 37(2), 217–220.
Hermens, D. F., Lagopoulos, J., Tobias-Webb, J., De Regt, T., Dore, G., et al. (2013). Pathways to alcohol-induced brain impairment in young people: a review. Cortex, 49(1), 3–17.
Herrmann, M. J., Weijers, H. G., Wiesbeck, G. A., Böning, J., & Fallgatter, A. J. (2001). Alcohol cue-reactivity in heavy and light social drinkers as revealed by event-related potentials. Alcohol and Alcoholism, 36, 588–593.
Holmes, A., Poline, J. B., & Friston, K. (1997). Characterizing brain images with the general linear model. In R. Frackowiak, K. Friston, C. Frith, R. Dolan, & J. C. Mazziotta (Eds.), Human brain function (pp. 59–84). farde London: Academic Press.
Houben, K., Havermans, R. C., Nederkoorn, C., & Jansen, A. (2012). Beer à no-go: learning to stop responding to alcohol cues reduces alcohol intake via reduced affective associations rather than increased response inhibition. Addiction, 107(7), 1280–1287.
Jacques, P. L. S., Dolcos, F., & Cabeza, R. (2009). Effects of aging on functional connectivity of the amygdala for subsequent memory of negative pictures a network analysis of functional magnetic resonance imaging data. Psychological Science, 20(1), 74–84.
Jonker, T., Seli, P., Cheyne, J., & Smilek, D. (2013). Performance reactivity in a continuous-performance task: implications for understanding post-error behavior. Consciousness and Cognition, 22, 1468–1476.
Leroux, G., Joliot, M., Dubal, S., Mazoyer, B., Tzourio-Mazoyer, N., & Houdé, O. (2006). Cognitive inhibition of number/length interference in a Piaget-like task in young adults: evidence from ERPs and fMRI. Human Brain Mapping, 27(6), 498–509.
Li, C. S., Luo, X., Yan, P., Bergquist, K., & Sinha, R. (2009). Altered impulse control in alcohol dependence: neural measures of stop signal performance. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research, 33, 740–750.
Liebowitz, M. R. (1987). Social phobia (pp. 141–173). Karger Publishers.
López-Caneda, E., Cadaveira, F., Crego, A., Gómez-Suárez, A., Corral, M., et al. (2012). Hyperactivation of right inferior frontal cortex in young binge drinkers during response inhibition: a follow-up study. Addiction, 107, 1796–1808.
Luijten, M., Machielsen, M. W., Veltman, D. J., Hester, R., Haan, L. D., Franken, I. H. (2014). Systematic review of ERP and fMRI studies investigating inhibitory control and error processing in people with substance dependence and behavioural addictions.
Mahmood, O. M., Goldenberg, D., Thayer, R., Migliorini, R., Simmons, A. N., & Tapert, S. F. (2013). Adolescents' fMRI activation to a response inhibition task predicts future substance use. Addictive Behaviors, 38(1), 1435–1441.
Mainz, V., Drüke, B., Boeker, M., Kessel, R., Gauggel, S., & Forkmann, T. (2012). Influence of cue exposure on inhibitory control and brain activation in patients with alcohol dependence. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 6, 1–13.
Massat, I., Slama, H., Kavec, M., Linotte, S., Mary, A., Baleriaux, D., et al. (2012). Working memory-related functional brain patterns in never medicated children with ADHD. PloS One, 7(11), e49392.
Maurage, P., Pesenti, M., Philippot, P., Joassin, F., & Campanella, S. (2009). Latent deleterious effects of binge drinking over a short period of time revealed only by electrophysiological measures. Journal of Psychiatry & Neuroscience, 34, 111–118.
Maurage, P., Joassin, F., Speth, A., Modave, J., Philippot, P., et al. (2012). Cerebral effects of binge drinking: respective influences of global alcohol intake and consumption pattern. Clinical Neurophysiology, 123, 892–901.
McGue M (1994) Genes, environment, and the etiology of alcoholism. In: Zucker R, Boyd G, Howard J, editors. The Development of Alcohol Problems: Exploring the Biopsychosocial Matrix of Risk (NIAAA Research Monograph No. 26). US Government Printing Office; Washington, DC: pp 1–40.
McKenzie, M., Jorm, A. F., Romaniuk, H., Olsson, C. A., & Patton, G. C. (2011). Association of adolescent symptoms of depression and anxiety with alcohol use disorders in young adulthood: findings from the Victorian adolescent health cohort study. The Medical Journal of Australia, 195, 27–30.
Menon, V., Adleman, N. E., White, C. D., Glover, G. H., & Reiss, A. L. (2001). Error-related brain activation during a go/NoGo response inhibition task. Human Brain Mapping, 12(3), 131–143.
Meyer, C., Rumpf, H. J., Hapke, U., Dilling, H., & John, U. (2000). Prevalence of alcohol consumption, abuse and dependence in a country with high per capita consumption: findings from the German TACOS study. Transitions in alcohol consumption and smoking. Social Psychiatry and Psychiatric Epidemiology, 35(12), 539–547.
Murphy, E. R., Foss-Feig, J., Kenworthy, L., Gaillard, W. D., & Vaidya, C. J. (2012). Atypical functional connectivity of the amygdala in childhood autism spectrum disorders during spontaneous attention to eye-gaze. Autism research and treatment, 2012.
Nederkoorn, C., Baltus, M., Guerrieri, R., & Wiers, R. W. (2009). Heavy drinking is associated with deficient response inhibition in women but not in men. Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior, 93(3), 331–336.
Nee, D. E., Kastner, S., & Brown, J. W. (2011). Functional heterogeneity of conflict, error, task-switching, and unexpectedness effects within medial prefrontal cortex. NeuroImage, 54(1), 528–540.
Nicolas, J. M., Estruch, R., Salamero, M., Orteu, N., Fernandez-Sola, J., et al. (1997). Brain impairment in well-nourished chronic alcoholics is related to ethanol intake. Annals of Neurology, 41, 590–598.
Noël, X., Van der Linden, M., d’Acremont, M., Colmant, M., Hanak, C., et al. (2005). Cognitive biases toward alcohol-related words and executive deficits in polysubstance abusers with alcoholism. Addiction, 100(9), 1302–1309.
Norberg, M. N., Oliver, J., Alperstein, D. M., Zvolensky, M. J., & Norton, A. R. (2011). Adverse consequences of student drinking: the role of sex, social anxiety, drinking motives. Addictive Behaviors, 36, 821–828.
Norman, A. L., Pulido, C., Squeglia, L. M., Spadoni, A. D., Paulus, M. P., & Tapert, S. F. (2011). Neural activation during inhibition predicts initiation of substance use in adolescence. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 119(3), 216–223.
Oldfield, R. C. (1971). The assessment and analysis of handedness: the Edinburgh inventory. Neuropsychologia, 9, 97–113.
Pani, P., Menghini, D., Napolitano, C., et al. (2013). Proactive and reactive control of movement are differently affected in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder children. Research in Developmental Disabilities, 34, 3104–3111.
Peigneux, P., Orban, P., Balteau, E., Degueldre, C., Luxen, A., Laureys, S., et al. (2006). Offline persistence of memory-related cerebral activity during active wakefulness. PLoS Biology, 4, e100.
Penny, W., & Holmes, A. (2003). Random-effect analysis. In R. Frackowiak, K. Friston, C. Frith, R. Dolan, C. Price, S. Zeki, J. Ashburner, & W. Penny (Eds.), Human brain function. London: Academic Press.
Petit, G., Kornreich, C., Noël, X., Verbanck, P., & Campanella, S. (2012). Alcohol-related context modulates performance of social drinkers in a visual go/no-go task: a preliminary assessment of event-related potentials. Plos One, 7(5), e37466.
Petit, G., Cimochowska, A., Kornreich, C., Hanak, C., Verbanck, P., & Campanella, S. (2014a). Neurophysiological correlates of response inhibition predict relapse in detoxified alcoholic patients: some preliminary evidence from event-related potentials. Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment, 10, 1025–1037.
Petit, G., Maurage, P., Kornreich, C., Verbanck, P., & Campanella, S. (2014b). Binge drinking in adolescents: a review of neurophysiological and neuroimaging research. Alcohol and Alcoholism, 49(2), 198–206.
Pfefferbaum, A., Lim, K.O., Zipursky, R.B., Mathalon, D.H., Rosenbloom, et al. (1992). Brain gray and white matter volume loss accelerates with aging in chronic alcoholics: a quantitative MRI study. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research 16 (6), 1078–1089.
Pfefferbaum, A., Desmond, J. E., Galloway, C., Menon, V., Glover, G. H., et al. (2001). Reorganization of frontal systems used by alcoholics for spatial working memory: an fMRI study. Neuro Image, 14, 7–20.
Picard, N., & Strick, P. L. (1996). Motor areas of the medial wall: a review of their location and functional activation. Cerebral Cortex, 6(3), 342–353.
Ray Li, C., Huang, C., Constable, T., & Sinha, R. (2006). Gender differences in the neural correlates of response inhibition during a stop signal task. Neuro Image, 32, 1918–1929.
Ridderinkhof, K. R., de Vlugt, Y., Bramlage, A., Spaan, M., Elton, M., et al. (2002). Alcohol consumption impairs detection of performance errors in mediofrontal cortex. Science, 298, 2209–2211.
Robinson, J. (2013). Edinburgh Handedness Inventory. In Encyclopedia of Autism Spectrum Disorders (pp. 1051–1054). New York: Springer.
Rogers, R. D., & Robbins, T. W. (2001). Investigating the neurocognitive deficits associated with chronic drug misuse. Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 11(2), 250–257.
Rubia, K., Smith, A. B., Brammer, M. J., & Taylor, E. (2003). Right inferior prefrontal cortex mediates response inhibition while mesial prefrontal cortex is responsible for error detection. NeuroImage, 20(1), 351–358.
Rubia, K., Smith, A. B., Brammer, M. J., Toone, B., & Taylor, E. (2005). Abnormal brain activation during inhibition and error detection in medication-naive adolescents with ADHD. American Journal of Psychiatry, 162(6), 1067–1075.
Rubia, K., Smith, A. B., Taylor, E., & Brammer, M. (2007). Linear age-correlated functional development of right inferior fronto-striato-cerebellar networks during response inhibition and anterior cingulate during error-related processes. Human Brain Mapping, 28(11), 1163–1177.
Saunders, J. B., Aasland, O. G., Babor, T. F., de la Fuente, J. R., & Grant, M. (1993). Development of the alcohol use disorders identification test (AUDIT): WHO collaborative project on early detection of persons with harmful alcohol consumption--II. Addiction, 88, 791–804.
Schilbach, L., Hoffstaedter, F., Müller, V., Cieslik, E. C., Goya-Maldonado, R., Trost, S., et al. (2016). Transdiagnostic commonalities and differences in resting state functional connectivity of the default mode network in schizophrenia and major depression. Neuro Image: Clinical, 10, 326–335.
Schuckit, M. A., & Gold, E. O. (1988). A simultaneous evaluation of multiple markers of ethanol/placebo challenges in sons of alcoholics and controls. Archives of General Psychiatry, 45, 211–216.
Schuckit, M. A., Tapert, S., Matthews, S. C., Paulus, M. P., Tolentino, N. J., et al. (2012). fMRI differences between subjects with low and high responses to alcohol during a stop signal task. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research, 36(1), 130–140.
Schweinsburg, A. D., Paulus, M. P., Barlett, V. C., Killeen, L. A., Caldwell, L. C., Pulido, C., et al. (2004). An FMRI study of response inhibition in youths with a family history of alcoholism. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1021(1), 391–394.
Schweinsburg, A. D., McQueeny, T., Nagel, B. J., Eyler, L. T., & Tapert, S. F. (2010). A preliminary study of functional magnetic resonance imaging response during verbal encoding among adolescent binge drinkers. Alcohol, 44, 111–117.
Schweinsburg, A. D., Schweinsburg, B. C., Nagel, B. J., Eyler, L. T., & Tapert, S. F. (2011). Neural correlates of verbal learning in adolescent alcohol and marijuana users. Addiction, 106, 564–573.
Smith, L. A., & Foxcroft, D. R. (2009). The effect of alcohol advertising, marketing and portrayal on drinking behaviour in young people: systematic review of prospective cohort studies. BMC Public Health, 9, 51.
Smith, J. L., & Mattick, R. P. (2013). Evidence of deficits in behavioural inhibition and performance monitoring in young female heavy drinkers. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 133(2), 398–404.
Spielberger, C. D. (1983). Manual for the state-trait anxiety inventory (STAI). Palo Alto: Consulting Psychologists Press.
Squeglia, L. M., Schweinsburg, A. D., Pulido, C., & Tapert, S. F. (2011). Adolescent binge drinking linked to abnormal spatial working memory brain activation: differential gender effects. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research, 35, 1831–1841.
Squeglia, L. M., Pulido, C., Wetherill, R. R., Jacobus, J., Brown, G. G., & Tapert, S. F. (2012). Brain response to working memory over three years of adolescence: influence of initiating heavy drinking. Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs, 73(5), 749–760.
Stacy, A. W., & Wiers, R. W. (2010). Implicit cognition and addiction: a tool for explaining paradoxical behavior. Annual Review of Clinical Psychology, 6, 551–575.
Stevens, A. A., Skudlarski, P., Gatenby, J. C., & Gore, J. C. (2000). Event-related fMRI of auditory and visual oddball tasks. Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 18(5), 495–502.
Strange, B. A., Hurlemann, R., Duggins, A., Heinze, H. J., & Dolan, R. J. (2005). Dissociating intentional learning from relative novelty responses in the medial temporal lobe. NeuroImage, 25(1), 51–62.
Swick, D., Ashley, V., & Turken, U. (2008). Left inferior frontal gyrus is critical for response inhibition. BMC Neuroscience, 9(1), 1.
Taylor, K. S., Seminowicz, D. A., & Davis, K. D. (2009). Two systems of resting state connectivity between the insula and cingulate cortex. Human Brain Mapping, 30(9), 2731–2745.
Tolentino, N. J., Wierenga, C. E., Hall, S., Tapert, S. F., Paulus, M. P., et al. (2011). Alcohol effects on cerebral blood flow in subjects with low and high responses to alcohol. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research, 35(6), 1034–1040.
Verbruggen, F., & Logan, G. D. (2008). Response inhibition in the stop-signal paradigm. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 12(11), 418–424.
Verbruggen, F., & Logan, G. (2009). Automaticity of cognitive control: goal priming in response-inhibition paradigms. Journal of Experimental Psychology, 35(5), 1381–1388.
Verbruggen, F., Adams, R., & Chambers, C. (2012). Proactive motor control reduces monetary risk taking in gambling. Psychological Science, 23, 805–815.
Viner, R. M., & Taylor, B. (2007). Adult outcomes of binge drinking in adolescence: findings from a UK national birth cohort. Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health, 61(10), 902–907.
Vocat, R., Pourtois, G., & Vuilleumier, P. (2008). Unavoidable errors: a spatio-temporal analysis of time-course and neural sources of evoked potentials associated with error processing in a speeded task. Neuropsychologia, 46(10), 2545–2555.
Volkow, N. D., Fowler, J. S., Wang, G. J., & Swanson, J. M. (2004). Dopamine in drug abuse and addiction: results from imaging studies and treatment implications. Molecular Psychiatry, 9(6), 557–569.
Watanabe, J., Sugiura, M., Sato, K., Sato, Y., Maeda, Y., Matsue, Y., et al. (2002). The human prefrontal and parietal association cortices are involved in NO-GO performances: an event-related fMRI study. NeuroImage, 17(3), 1207–1216.
Wetherill, R. R., Squeglia, L. M., Yang, T. T., & Tapert, S. F. (2013). A longitudinal examination of adolescent response inhibition: neural differences before and after the initiation of heavy drinking. Psychopharmacology, 230(4), 663–671.
Whiteside, S. P., & Lynam, D. R. (2003). Understanding the role of impulsivity and externalizing psychopathology in alcohol abuse: application of the UPPS impulsive behavior scale. Experimental and Clinical Psychopharmacology, 11, 210–217.
Worsley, K. J. (1996). A unified statistical approach for determining significant signals in images of cerebral activation. Human Brain Mapping, 4, 58–73.
Xiao, L., Bechara, A., Gong, Q., Huang, X., Li, X., Xue, G., et al. (2013). Abnormal affective decision making revealed in adolescent binge drinkers using a functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors, 27(2), 443.
Acknowledgments
Salvatore Campanella is Research Associate at the Fund of Scientific Research (FRS-FNRS, Belgium). Mathieu Bourguignon benefits of a research grant from the FRIA (FRS-FNRS, Belgium). Xavier De Tiège is “Postdoctorate Clinical Master Specialist” at the Fund of Scientific Research (FRS-FNRS, Belgium).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure
This study was financially supported by the Fund of Scientific Research (Research Grant J.0009.13, FRS-FNRS, Belgium).
Conflict of interest
The authors have no competing financial interest, potential conflict of interest, or financial relationship with commercial entities to report.
Funding
They are funded by the Belgian Fund for Scientific Research (F.N.R.S., Belgium), but this fund did not exert any editorial direction or censorship on any part of this article.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
The original version of this article was revised: There are errors in the name of two authors. Xavier Detiège should be changed to Xavier De Tiège, where De Tiège is the last name, and Carbia Sinde should be captured as the last name for Carina Carbia Sinde.
An erratum to this article is available at https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-016-9664-9.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Campanella, S., Absil, J., Carbia Sinde, C. et al. Neural correlates of correct and failed response inhibition in heavy versus light social drinkers: an fMRI study during a go/no-go task by healthy participants. Brain Imaging and Behavior 11, 1796–1811 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-016-9654-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-016-9654-y