Abstract
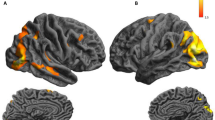
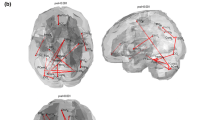
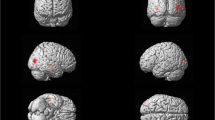
In order to identify the cortical changes in patients with Sialidosis type 1, diffusion tensor imaging and resting state fMRI were acquired from 11 patients and 11 sex/age matched normal controls after clinical evaluations. The neuroimages from each participant were normalized and parcellated according to the Automatic Anatomical Labeling. Both the mean diffusivity and the corresponding functional connectivity were calculated from each cortical region. The white matter tract integrity was examined. The difference between patients and controls was examined using Student’s t-test and between patients with either homozygous or heterozygous mutations by Mann–Whitney U test, both at a threshold of 0.05. Increased mean diffusivity throughout the brain can be noticed in the patients, together with a compromised white matter tracts integrity. The most severely affected cortical regions are in the occipital lobe. Decreased functional connectivity was from the temporal and occipital lobes to the hippocampus and parahippocampus. In contrast, connectivity from thalamus was enhanced. Diffused cortical atrophy with posterior focal lesions was noticed. We concluded that MRI observed functional changes in the posterior cortical pathways in the patients with Sialidosis. The observation might be related to the cortical blindness due to an altered neural network and a compromised visual pathway in the patients.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander, A. L., Lee, J. E., Lazar, M., & Field, A. S. (2007). Diffusion tensor imaging of the brain. Neurotherapeutics, 4(3), 316–329.
Amano, N., Yokoi, S., Akagi, M., Sakai, M., Yagishita, S., & Nakata, K. (1983). Neuropathological findings of an autopsy case of adult beta-galactosidase and neuraminidase deficiency. Acta Neuropathologica, 61(3–4), 283–290.
Basser, P. J., & Pierpaoli, C. (1996). Microstructural and physiological features of tissues elucidated by quantitative-diffusion-tensor MRI. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Series B, 111(3), 209–219.
Bejjani, B. P., Arnulf, I., Vidailhet, M., Pidoux, B., Damier, P., Papadopoulos, S., et al. (2000). Irregular jerky tremor, myoclonus, and thalamus: a study using low-frequency stimulation. Movement Disorders: Official Journal of the Movement Disorder Society, 15(5), 919–924.
Biswal, B. B., Mennes, M., Zuo, X. N., Gohel, S., Kelly, C., Smith, S. M., et al. (2010). Toward discovery science of human brain function. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 107(10), 4734–4739.
Bullmore, E. T., Suckling, J., Overmeyer, S., Rabe-Hesketh, S., Taylor, E., & Brammer, M. J. (1999). Global, voxel, and cluster tests, by theory and permutation, for a difference between two groups of structural MR images of the brain. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 18(1), 32–42.
Chang, C. C., Chang, W. N., Lui, C. C., Huang, S. H., Lee, C. C., Chen, C., et al. (2011). Clinical significance of the pallidoreticular pathway in patients with carbon monoxide intoxication. Brain, 134(Pt 12), 3632–3646.
Chao-Gan, Y., & Yu-Feng, Z. (2010). DPARSF: a MATLAB toolbox for "pipeline" data analysis of resting-state fMRI. Frontiers in Systems Neuroscience, 413.
Cook, P. A., Bai, Y., Nedjati-Gilani, S., Seunarine, K. K., Hall, M. G., Parker, G. J., Camino, D. C. Alexander (2006) Open-Source Diffusion-MRI Reconstruction and Processing. In 14th scientific meeting of the international society for magnetic resonance in medicine, (pp. 2759) Seattle.
Corbetta, M., & Shulman, G. L. (1998). Human cortical mechanisms of visual attention during orienting and search. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological Sciences, 353(1373), 1353–1362.
Ganos, C., Kassavetis, P., Erro, R., Edwards, M. J., Rothwell, J., & Bhatia, K. P. (2014). The role of the cerebellum in the pathogenesis of cortical myoclonus. Movement Disorders: Official Journal of the Movement Disorder Society, 29(4), 437–443.
Gauthier, I., Tarr, M. J., Anderson, A. W., Skudlarski, P., & Gore, J. C. (1999). Activation of the middle fusiform 'face area' increases with expertise in recognizing novel objects. Nature Neuroscience, 2(6), 568–573.
Greicius, M. D., Srivastava, G., Reiss, A. L., & Menon, V. (2004). Default-mode network activity distinguishes Alzheimer's disease from healthy aging: evidence from functional MRI. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 101(13), 4637–4642.
Heywood, C. A., Gadotti, A., & Cowey, A. (1992). Cortical area V4 and its role in the perception of color. The Journal of Neuroscience, 12(10), 4056–4065.
Huang, Y. Z., Lai, S. C., Lu, C. S., Weng, Y. H., Chuang, W. L., & Chen, R. S. (2008). Abnormal cortical excitability with preserved brainstem and spinal reflexes in sialidosis type I. Clinical Neurophysiology: Official Journal of the International Federation of Clinical Neurophysiology, 119(5), 1042–1050.
Lai, S. C., Chen, R. S., Wu Chou, Y. H., Chang, H. C., Kao, L. Y., Huang, Y. Z., et al. (2009). A longitudinal study of Taiwanese sialidosis type 1: an insight into the concept of cherry-red spot myoclonus syndrome. European Journal of Neurology: The Official Journal of the European Federation of Neurological Societies, 16(8), 912–919.
Nemanic, S., Alvarado, M. C., & Bachevalier, J. (2004). The hippocampal/parahippocampal regions and recognition memory: insights from visual paired comparison versus object-delayed nonmatching in monkeys. The Journal of Neuroscience, 24(8), 2013–2026.
Nichols, T. E., & Holmes, A. P. (2002). Nonparametric permutation tests for functional neuroimaging: a primer with examples. Human Brain Mapping, 15(1), 1–25.
Palmeri, S., Villanova, M., Malandrini, A., van Diggelen, O. P., Huijmans, J. G., Ceuterick, C., et al. (2000). Type I sialidosis: a clinical, biochemical and neuroradiological study. European Neurology, 43(2), 88–94.
Parise, M., Kubo, T. T., Doring, T. M., Tukamoto, G., Vincent, M., & Gasparetto, E. L. (2014). Cuneus and fusiform cortices thickness is reduced in trigeminal neuralgia. The Journal of Headache and Pain, 15, 17.
Pattison, S., Pankarican, M., Rupar, C. A., Graham, F. L., & Igdoura, S. A. (2004). Five novel mutations in the lysosomal sialidase gene (NEU1) in type II sialidosis patients and assessment of their impact on enzyme activity and intracellular targeting using adenovirus-mediated expression. Human Mutation, 23(1), 32–39.
Pierpaoli, C., & Basser, P. J. (1996). Toward a quantitative assessment of diffusion anisotropy. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 36(6), 893–906.
Sekijima, Y., Nakamura, K., Kishida, D., Narita, A., Adachi, K., Ohno, K., et al. (2013). Clinical and serial MRI findings of a sialidosis type I patient with a novel missense mutation in the NEU1 gene. Internal Medicine, 52(1), 119–124.
Seyrantepe, V., Poupetova, H., Froissart, R., Zabot, M. T., Maire, I., & Pshezhetsky, A. V. (2003). Molecular pathology of NEU1 gene in sialidosis. Human Mutation, 22(5), 343–352.
Slotnick, S. D., & White, R. C. (2013). The fusiform face area responds equivalently to faces and abstract shapes in the left and central visual fields. NeuroImage, 83, 408–417.
Smith, S. M., Jenkinson, M., Johansen-Berg, H., Rueckert, D., Nichols, T. E., Mackay, C. E., et al. (2006). Tract-based spatial statistics: voxelwise analysis of multi-subject diffusion data. NeuroImage, 31(4), 1487–1505.
Song, X. W., Dong, Z. Y., Long, X. Y., Li, S. F., Zuo, X. N., Zhu, C. Z., et al. (2011). REST: a toolkit for resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging data processing. PloS One, 6(9), e25031.
Traff, J., Petrovic, P., & Ingvar, M. (2000). Thalamic activation in photic myoclonus. Acta Neurologica Scandinavica, 101(5), 339–343.
van den Heuvel, M. P., & Hulshoff Pol, H. E. (2010). Exploring the brain network: a review on resting-state fMRI functional connectivity. European Neuropsychopharmacology: the Journal of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology, 20(8), 519–534.
Ventre-Dominey, J., Bailly, A., Lavenne, F., Lebars, D., Mollion, H., Costes, N., et al. (2005). Double dissociation in neural correlates of visual working memory: a PET study. Brain Research. Cognitive Brain Research, 25(3), 747–759.
Wakana, S., Jiang, H., Nagae-Poetscher, L. M., van Zijl, P. C., & Mori, S. (2004). Fiber tract-based atlas of human white matter anatomy. Radiology, 230(1), 77–87.
Wang, J., Wai, Y., Weng, Y., Ng, K., Huang, Y. Z., Ying, L., et al. (2009). Functional MRI in the assessment of cortical activation during gait-related imaginary tasks. Journal of Neural Transmission, 116(9), 1087–1092.
Wang, J. J., Lin, W. Y., Lu, C. S., Weng, Y. H., Ng, S. H., Wang, C. H., et al. (2011). Parkinson disease: diagnostic utility of diffusion kurtosis imaging. Radiology, 261(1), 210–217.
Acknowledgments
The imaging facility was supported by the Center for Advanced Molecular Imaging and Translation, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital and Medical Imaging Research Center, Institute for Radiological Research of Chang Gung University /Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Linkou. The patients were referred by Neuroscience Research Center of Chang Gung Memorial Hospital. The authors would like to thank Healthy Aging Research Center, Chang Gung University for additional support. The funding source had no involvement in the collection, analysis and interpretation data; in the writing of the report; and in the decision to submit the paper for publication.
Author contribution statement
Chin-Song Lu: substantial contributions to conception and design; drafting the article or revising it critically for important intellectual content;
Shu-Hang Ng:
Szu-Chia Lai:
Ling-Yuh Kao: analysis and interpretation of data;
Laura Liu:
Wey-Yil Lin:
Yi-Ming Wu: analysis and interpretation of data;
Yao-Liang Chen:
Jiun-Jie Wang: substantial contributions to conception and design; drafting the article; revising it critically for important intellectual content; final approval of the version to be published.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Fundings
This work was supported by grants from the Ministry of Science and Technology Taiwan (MOST103-2325-B-182-001), the Ministry of Education Taiwan (EMRPD1D0951 and EMRPD1E1731) and Chang-Gung University/Chang-Gung Memorial Hospital (CMRPD1C0293, CMRPD3D0012, CIRPD1E0061, BMRP655, CMRPD1B0331 and CMRPD1B0332).
Additional information
Chin-Song Lu and Shu-Hang Ng these two authors contributed equally
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, CS., Ng, SH., Lai, SC. et al. Cortical damage in the posterior visual pathway in patients with sialidosis type 1. Brain Imaging and Behavior 11, 214–223 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-016-9517-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-016-9517-6