Abstract
Approximately 30 % of Americans suffer from chronic pain disorders, such as fibromyalgia (FM), which can cause debilitating pain. Many pain-killing drugs prescribed for chronic pain disorders are highly addictive, have limited clinical efficacy, and do not treat the cognitive symptoms reported by many patients. The neurobiological substrates of chronic pain are largely unknown, but evidence points to altered dopaminergic transmission in aberrant pain perception. We sought to characterize the dopamine (DA) system in individuals with FM. Positron emission tomography (PET) with [18F]fallypride (FAL) was used to assess changes in DA during a working memory challenge relative to a baseline task, and to test for associations between baseline D2/D3 availability and experimental pain measures. Twelve female subjects with FM and 11 female controls completed study procedures. Subjects received one FAL PET scan while performing a “2-back” task, and one while performing a “0-back” (attentional control, “baseline”) task. FM subjects had lower baseline FAL binding potential (BP) in several cortical regions relative to controls, including anterior cingulate cortex. In FM subjects, self-reported spontaneous pain negatively correlated with FAL BP in the left orbitofrontal cortex and parahippocampal gyrus. Baseline BP was significantly negatively correlated with experimental pain sensitivity and tolerance in both FM and CON subjects, although spatial patterns of these associations differed between groups. The data suggest that abnormal DA function may be associated with differential processing of pain perception in FM. Further studies are needed to explore the functional significance of DA in nociception and cognitive processing in chronic pain.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aalto, S., Bruck, A., Laine, M., Nagren, K., & Rinne, J. O. (2005). Frontal and temporal dopamine release during working memory and attention tasks in healthy humans: a positron emission tomography study using the high-affinity dopamine D2 receptor ligand [11C]FLB 457. Journal of Neuroscience, 25(10), 2471–2477.
Albrecht, D. S., Kareken, D. A., Christian, B. T., Dzemidzic, M., & Yoder, K. K. (2014). Cortical dopamine release during a behavioral response inhibition task. Synapse, 68(6), 266–274.
Apkarian, A. V., Bushnell, M. C., Treede, R. D., & Zubieta, J. K. (2005). Human brain mechanisms of pain perception and regulation in health and disease. European Journal of Pain, 9(4), 463–484.
Apkarian, A. V., Baliki, M. N., & Geha, P. Y. (2009). Towards a theory of chronic pain. Progress in Neurobiology, 87(2), 81–97.
Asmundson, G. J., & Katz, J. (2009). Understanding the co-occurrence of anxiety disorders and chronic pain: state-of-the-art. Depression and Anxiety, 26(10), 888–901.
Baliki, M. N., Chialvo, D. R., Geha, P. Y., Levy, R. M., Harden, R. N., Parrish, T. B., et al. (2006). Chronic pain and the emotional brain: specific brain activity associated with spontaneous fluctuations of intensity of chronic back pain. Journal of Neuroscience, 26(47), 12165–12173.
Ballantyne, J. C., & Shin, N. S. (2008). Efficacy of opioids for chronic pain: a review of the evidence. The Clinical Journal of Pain, 24(6), 469–478.
Beck, A. T., Ward, C. H., Mendelson, M., Mock, J., & Erbaugh, J. (1961). An inventory for measuring depression. Archives of General Psychiatry, 4, 561–571.
Berryman, C., Stanton, T. R., Jane Bowering, K., Tabor, A., McFarlane, A., & Lorimer Moseley, G. (2013). Evidence for working memory deficits in chronic pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Pain, 154(8), 1181–1196.
Burckhardt, C. S., Clark, S. R., & Bennett, R. M. (1991). The fibromyalgia impact questionnaire: development and validation. The Journal of Rheumatology, 18(5), 728–733.
Cervenka, S., Palhagen, S. E., Comley, R. A., Panagiotidis, G., Cselenyi, Z., Matthews, J. C., et al. (2006). Support for dopaminergic hypoactivity in restless legs syndrome: a PET study on D2-receptor binding. Brain, 129(Pt 8), 2017–2028.
Christian, B. T., Lehrer, D. S., Shi, B., Narayanan, T. K., Strohmeyer, P. S., Buchsbaum, M. S., et al. (2006). Measuring dopamine neuromodulation in the thalamus: using [F-18]fallypride PET to study dopamine release during a spatial attention task. NeuroImage, 31(1), 139–152.
Clauw, D. J. (2009). Fibromyalgia: an overview. The American Journal of Medicine, 122(12 Suppl), S3–S13.
Cleeland, C. S., & Ryan, K. M. (1994). Pain assessment: global use of the brief pain inventory. Annals of the Academy of Medicine, Singapore, 23(2), 129–138.
Costes, N., Merlet, I., Ostrowsky, K., Faillenot, I., Lavenne, F., Zimmer, L., et al. (2005). A 18F-MPPF PET normative database of 5-HT1A receptor binding in men and women over aging. Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 46(12), 1980–1989.
Etkin, A., Egner, T., & Kalisch, R. (2011). Emotional processing in anterior cingulate and medial prefrontal cortex. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 15(2), 85–93.
Fallon, N. (2013). Structural and functional brain alterations in fibromyalgia syndrome patients. University of Liverpool.
Fonville, L., Giampietro, V., Surguladze, S., Williams, S., & Tchanturia, K. (2014). Increased BOLD signal in the fusiform gyrus during implicit emotion processing in anorexia nervosa. Neuroimage: Clinical, 4, 266–273.
Forkmann, K., Wiech, K., Ritter, C., Sommer, T., Rose, M., & Bingel, U. (2013). Pain-specific modulation of hippocampal activity and functional connectivity during visual encoding. The Journal of Neuroscience, 33(6), 2571–2581.
Gao, M., Wang, M., Mock, B. H., Glick-Wilson, B. E., Yoder, K. K., Hutchins, G. D., et al. (2010). An improved synthesis of dopamine D2/D3 receptor radioligands [11C]fallypride and [18F]fallypride. Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 68(6), 1079–1086.
Glass, J. M. (2008). Fibromyalgia and cognition. The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, 69(Suppl 2), 20–24.
Gosselin, N., Samson, S., Adolphs, R., Noulhiane, M., Roy, M., Hasboun, D., et al. (2006). Emotional responses to unpleasant music correlates with damage to the parahippocampal cortex. Brain, 129(Pt 10), 2585–2592.
Grace, G. M., Nielson, W. R., Hopkins, M., & Berg, M. A. (1999). Concentration and memory deficits in patients with fibromyalgia syndrome. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology, 21(4), 477–487.
Gracely, R. H., Petzke, F., Wolf, J. M., & Clauw, D. J. (2002). Functional magnetic resonance imaging evidence of augmented pain processing in fibromyalgia. Arthritis and Rheumatism, 46(5), 1333–1343.
Greicius, M. D., Krasnow, B., Reiss, A. L., & Menon, V. (2003). Functional connectivity in the resting brain: a network analysis of the default mode hypothesis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 100(1), 253–258.
Gronwall, D. (1977). Paced auditory serial-addition task: a measure of recovery from concussion. Perceptual and Motor Skills, 44(2), 367–373.
Gu, X., Hof, P. R., Friston, K. J., & Fan, J. (2013). Anterior insular cortex and emotional awareness. Journal of Comparative Neurology, 521(15), 3371–3388.
Gureje, O. (2007). Psychiatric aspects of pain. Current Opinion in Psychiatry, 20(1), 42–46.
Hagelberg, N., Martikainen, I. K., Mansikka, H., Hinkka, S., Nagren, K., Hietala, J., et al. (2002). Dopamine D2 receptor binding in the human brain is associated with the response to painful stimulation and pain modulatory capacity. Pain, 99(1–2), 273–279.
Hagelberg, N., Forssell, H., Aalto, S., Rinne, J. O., Scheinin, H., Taiminen, T., et al. (2003a). Altered dopamine D2 receptor binding in atypical facial pain. Pain, 106(1–2), 43–48.
Hagelberg, N., Forssell, H., Rinne, J. O., Scheinin, H., Taiminen, T., Aalto, S., et al. (2003b). Striatal dopamine D1 and D2 receptors in burning mouth syndrome. Pain, 101(1–2), 149–154.
Harry, B., Williams, M. A., Davis, C., & Kim, J. (2013). Emotional expressions evoke a differential response in the fusiform face area. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 7, 692.
Innis, R. B., Cunningham, V. J., Delforge, J., Fujita, M., Gjedde, A., Gunn, R. N., et al. (2007). Consensus nomenclature for in vivo imaging of reversibly binding radioligands. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism, 27(9), 1533–1539.
Jensen, K. B., Loitoile, R., Kosek, E., Petzke, F., Carville, S., Fransson, P., et al. (2012). Patients with fibromyalgia display less functional connectivity in the brain’s pain inhibitory network. Molecular Pain, 8, 32.
Johannes, C. B., Le, T. K., Zhou, X., Johnston, J. A., & Dworkin, R. H. (2010). The prevalence of chronic pain in United States adults: results of an Internet-based survey. The Journal of Pain, 11(11), 1230–1239.
Johnson, A. L., Storzbach, D., Binder, L. M., Barkhuizen, A., Kent Anger, W., Salinsky, M. C., et al. (2010). MMPI-2 profiles: fibromyalgia patients compared to epileptic and non-epileptic seizure patients. The Clinical Neuropsychologist, 24(2), 220–234.
Kanwisher, N., McDermott, J., & Chun, M. M. (1997). The fusiform face area: a module in human extrastriate cortex specialized for face perception. Journal of Neuroscience, 17(11), 4302–4311.
Kim, J., Loggia, M. L., Cahalan, C. M., Harris, R. E., Beissner, F., Garcia, R. G., et al. (2015). The somatosensory link in fibromyalgia: functional connectivity of the primary somatosensory cortex is altered by sustained pain and is associated with clinical/autonomic dysfunction. Arthritis and Rheumatology, 67(5), 1395–1405.
Kodama, T., Hikosaka, K., Honda, Y., Kojima, T., & Watanabe, M. (2014). Higher dopamine release induced by less rather than more preferred reward during a working memory task in the primate prefrontal cortex. Behavioural Brain Research, 266, 104–107.
Kuijpers, T., van Middelkoop, M., Rubinstein, S., Ostelo, R., Verhagen, A., Koes, B., et al. (2011). A systematic review on the effectiveness of pharmacological interventions for chronic non-specific low-back pain. European Spine Journal, 20(1), 40–50.
Lamm, C., Decety, J., & Singer, T. (2011). Meta-analytic evidence for common and distinct neural networks associated with directly experienced pain and empathy for pain. NeuroImage, 54(3), 2492–2502.
Landro, N. I., Stiles, T. C., & Sletvold, H. (1997). Memory functioning in patients with primary fibromyalgia and major depression and healthy controls. Journal of Psychosomatic Research, 42(3), 297–306.
Logan, J., Fowler, J. S., Volkow, N. D., Wang, G. J., Ding, Y. S., & Alexoff, D. L. (1996). Distribution volume ratios without blood sampling from graphical analysis of PET data. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism, 16(5), 834–840.
Loggia, M. L., Berna, C., Kim, J., Cahalan, C. M., Gollub, R. L., Wasan, A. D., et al. (2014). Disrupted brain circuitry for pain-related reward/punishment in fibromyalgia. Arthritis and Rheumatology, 66(1), 203–212.
Luerding, R., Weigand, T., Bogdahn, U., & Schmidt-Wilcke, T. (2008). Working memory performance is correlated with local brain morphology in the medial frontal and anterior cingulate cortex in fibromyalgia patients: structural correlates of pain-cognition interaction. Brain, 131(Pt 12), 3222–3231.
Martikainen, I. K., Hagelberg, N., Mansikka, H., Hietala, J., Nagren, K., Scheinin, H., et al. (2005). Association of striatal dopamine D2/D3 receptor binding potential with pain but not tactile sensitivity or placebo analgesia. Neuroscience Letters, 376(3), 149–153.
Martikainen, I. K., Nuechterlein, E. B., Pecina, M., Love, T. M., Cummiford, C. M., Green, C. R., et al. (2015). Chronic back pain is associated with alterations in dopamine neurotransmission in the ventral striatum. Journal of Neuroscience, 35(27), 9957–9965.
McCracken, L. M., & Iverson, G. L. (2001). Predicting complaints of impaired cognitive functioning in patients with chronic pain. Journal of Pain and Symptom Management, 21(5), 392–396.
McDonald, B. C., Conroy, S. K., Ahles, T. A., West, J. D., & Saykin, A. J. (2012). Alterations in brain activation during working memory processing associated with breast cancer and treatment: a prospective functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 30(20), 2500–2508.
Melzack, R. (1987). The short-form McGill pain questionnaire. Pain, 30(2), 191–197.
Mutso, A. A., Radzicki, D., Baliki, M. N., Huang, L., Banisadr, G., Centeno, M. V., et al. (2012). Abnormalities in hippocampal functioning with persistent pain. Journal of Neuroscience, 32(17), 5747–5756.
Nieoullon, A. (2002). Dopamine and the regulation of cognition and attention. Progress in Neurobiology, 67(1), 53–83.
Oldfield, R. C. (1971). The assessment and analysis of handedness: the Edinburgh inventory. Neuropsychologia, 9(1), 97–113.
Olson, I. R., Plotzker, A., & Ezzyat, Y. (2007). The Enigmatic temporal pole: a review of findings on social and emotional processing. Brain, 130(Pt 7), 1718–1731.
Pertovaara, A., Martikainen, I. K., Hagelberg, N., Mansikka, H., Nagren, K., Hietala, J., et al. (2004). Striatal dopamine D2/D3 receptor availability correlates with individual response characteristics to pain. The European Journal of Neuroscience, 20(6), 1587–1592.
Picard, F., Bruel, D., Servent, D., Saba, W., Fruchart-Gaillard, C., Schollhorn-Peyronneau, M. A., et al. (2006). Alteration of the in vivo nicotinic receptor density in ADNFLE patients: a PET study. Brain, 129(Pt 8), 2047–2060.
Ploghaus, A., Narain, C., Beckmann, C. F., Clare, S., Bantick, S., Wise, R., et al. (2001). Exacerbation of pain by anxiety is associated with activity in a hippocampal network. The Journal of Neuroscience, 21(24), 9896–9903.
Pomerleau, C. S., Carton, S. M., Lutzke, M. L., Flessland, K. A., & Pomerleau, O. F. (1994). Reliability of the fagerstrom tolerance questionnaire and the fagerstrom test for nicotine dependence. Addictive Behaviors, 19(1), 33–39.
Scott, D. J., Heitzeg, M. M., Koeppe, R. A., Stohler, C. S., & Zubieta, J. K. (2006). Variations in the human pain stress experience mediated by ventral and dorsal basal ganglia dopamine activity. Journal of Neuroscience, 26(42), 10789–10795.
Seeley, W. W., Menon, V., Schatzberg, A. F., Keller, J., Glover, G. H., Kenna, H., et al. (2007). Dissociable intrinsic connectivity networks for salience processing and executive control. Journal of Neuroscience, 27(9), 2349–2356.
Seo, J., Kim, S. H., Kim, Y. T., Song, H. J., Lee, J. J., Han, S. W., et al. (2012). Working memory impairment in fibromyalgia patients associated with altered frontoparietal memory network. PloS One, 7(6), e37808.
Seymour, B., & McClure, S. M. (2008). Anchors, scales and the relative coding of value in the brain. Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 18(2), 173–178.
Singer, T., Seymour, B., O’Doherty, J., Kaube, H., Dolan, R. J., & Frith, C. D. (2004). Empathy for pain involves the affective but not sensory components of pain. Science, 303(5661), 1157–1162.
Sobell, M. B., Sobell, L. C., Klajner, F., Pavan, D., & Basian, E. (1986). The reliability of a timeline method for assessing normal drinker college students’ recent drinking history: utility for alcohol research. Addictive Behaviors, 11(2), 149–161.
Spielberger, C. D. (1983). Manual for the State-Trait Anxiety Inventory (STAI). Palo Alta: Consulting Psychologists Press.
Stancak, A., Ward, H., & Fallon, N. (2013). Modulation of pain by emotional sounds: a laser‐evoked potential study. European Journal of Pain, 17(3), 324–335.
Suhr, J. A. (2003). Neuropsychological impairment in fibromyalgia: relation to depression, fatigue, and pain. Journal of Psychosomatic Research, 55(4), 321–329.
Tracey, I. (2008). Imaging pain. British Journal of Anaesthesia, 101(1), 32–39.
van Middendorp, H., Lumley, M. A., Moerbeek, M., Jacobs, J. W., Bijlsma, J. W., & Geenen, R. (2010). Effects of anger and anger regulation styles on pain in daily life of women with fibromyalgia: a diary study. European Journal of Pain, 14(2), 176–182.
Watson, D., Clark, L. A., & Tellegen, A. (1988). Development and validation of brief measures of positive and negative affect: the PANAS scales. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 54(6), 1063–1070.
Wechsler, D. (1997). Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (3rd ed.). San Antonio: The Pscyhological Corporation.
Williams, D. A., Clauw, D. J., & Glass, J. M. (2011). Perceived cognitive dysfunction in fibromyalgia syndrome. Journal of Musculoskeletal Pain, 19(2), 66–75.
Winston, J. S., Vlaev, I., Seymour, B., Chater, N., & Dolan, R. J. (2014). Relative valuation of pain in human orbitofrontal cortex. Journal of Neuroscience, 34(44), 14526–14535.
Wolfe, F., Smythe, H. A., Yunus, M. B., Bennett, R. M., Bombardier, C., Goldenberg, D. L., et al. (1990). The American College of Rheumatology 1990 criteria for the classification of fibromyalgia. Arthritis & Rheumatism, 33(2), 160–172.
Wood, P. B., Schweinhardt, P., Jaeger, E., Dagher, A., Hakyemez, H., Rabiner, E. A., et al. (2007). Fibromyalgia patients show an abnormal dopamine response to pain. The European Journal of Neuroscience, 25(12), 3576–3582.
Wood, P. B., Glabus, M. F., Simpson, R., & Patterson, J. C., 2nd. (2009). Changes in gray matter density in fibromyalgia: correlation with dopamine metabolism. The Journal of Pain, 10(6), 609–618.
Ziolko, S. K., Weissfeld, L. A., Klunk, W. E., Mathis, C. A., Hoge, J. A., Lopresti, B. J., et al. (2006). Evaluation of voxel-based methods for the statistical analysis of PIB PET amyloid imaging studies in Alzheimer’s disease. NeuroImage, 33(1), 94–102.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by R03DA024774 (KKY). The authors thank Christine Herring, Lauren Federici, and James Walters for assistance with data collection; Kevin Perry for acquisition of PET data; Michele Beal and Courtney Robbins for assistance with MR scanning; and Dr. Bruce Mock, Dr. Clive Brown-Proctor, Dr. Qi-Huang Zheng, Barbara Glick-Wilson, and Brandon Steele for [18F]fallypride synthesis. Dr. Brenna McDonald provided consultation for scoring and interpretation of the neuropsychological assessments and working memory task.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This study was supported by the National Institute on Drug Abuse R03DA024774 (KKY).
Conflict of interest
D.S. Albrecht, P.J. MacKie, D.A. Kareken, G.D. Hutchins, E.J. Chumin, B.T. Christian, and K.K. Yoder declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Informed consent
All study procedures were approved by the Indiana University Institutional Review Board, and as such, were in accordance with the ethical standards of the Belmont Report (1974; National Commission for the Protection of Human Subjects of Biomedical and Behavioral Research). Written informed consent was obtained from all patients prior to participation in the study.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Online Resource 1
Timeline of a scan day. N-back represents either 0-back or 2-back. (PDF 74 kb)
Online Resource 2
Cognitive Task Performance. All variables are presented as average ± s.d. The range of possible scores are displayed to the right of the variable, if available. FM: fibromyalgia; CON: control; PASAT: Paced Auditory Serial Addition Task; WAIS: Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale. * indicates significant group differences at p < 0.05 (PDF 63 kb)
Online Resource 3
Group Differences in baseline FAL BP. BLBP values are presented as mean ± s.d. MNI: Montreal Neurological Institute; FM: fibromyalgia; CON: control; diff: difference; ACC: anterior cingulate cortex. (PDF 54 kb)
Online Resource 4
Baseline scan pain is negatively correlated with FAL BLBP in FM subjects. OFC: orbitofrontal cortex. (PDF 52 kb)
Online Resource 5
Baseline FAL BP is negatively correlated with average pain sensitivity in FM and CON groups. FM: fibromyalgia; CON: control; SFG: superior frontal gyrus; OFC: orbitofrontal cortex; ACC: anterior cingulate cortex. (PDF 63 kb)
Online Resource 6
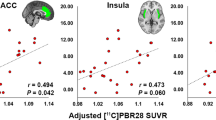
Baseline FAL BP is negatively correlated with average pain tolerance in FM and CON groups. FM: fibromyalgia; CON: control; ACC: anterior cingulate cortex; DCA: dorsal caudate; IFG: inferior frontal gyrus; SFG: superior frontal gyrus; SMA: supplementary motor area; MTG: middle temporal gyrus; MFG: middle frontral gyrus (PDF 81 kb)
Online Resource 7
Extracted FAL BLBP from clusters where experimental pain tolerance was significantly negatively correlated with FAL BLBP in FM left dorsal caudate (L-DCA, top) and CON right thalamus (R-thalamus, bottom). (PDF 169 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Albrecht, D.S., MacKie, P.J., Kareken, D.A. et al. Differential dopamine function in fibromyalgia. Brain Imaging and Behavior 10, 829–839 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-015-9459-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-015-9459-4