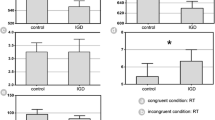
Abstract
Internet Gaming Disorder (IGD) among adolescents has become an important public concern and gained more and more attention internationally. Recent studies focused on IGD and revealed brain abnormalities in the IGD group, especially the prefrontal cortex (PFC). However, the role of PFC-striatal circuits in pathology of IGD remains unknown. Twenty-five adolescents with IGD and 21 age- and gender-matched healthy controls were recruited in our study. Voxel-based morphometric (VBM) and functional connectivity analysis were employed to investigate the abnormal structural and resting-state properties of several frontal regions in individuals with online gaming addiction. Relative to healthy comparison subjects, IGD subjects showed significant decreased gray matter volume in PFC regions including the bilateral dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC), orbitofrontal cortex (OFC), anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) and the right supplementary motor area (SMA) after controlling for age and gender effects. We chose these regions as the seeding areas for the resting-state analysis and found that IGD subjects showed decreased functional connectivity between several cortical regions and our seeds, including the insula, and temporal and occipital cortices. Moreover, significant decreased functional connectivity between some important subcortical regions, i.e., dorsal striatum, pallidum, and thalamus, and our seeds were found in the IGD group and some of those changes were associated with the severity of IGD. Our results revealed the involvement of several PFC regions and related PFC-striatal circuits in the process of IGD and suggested IGD may share similar neural mechanisms with substance dependence at the circuit level.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barke, A., Nyenhuis, N., & Kröner-Herwig, B. (2012). The German version of the internet addiction test: a validation study. Cyberpsychology, Behavior and Social Networking, 15(10), 534–542.
Blasi, G., Goldberg, T. E., Weickert, T., Das, S., Kohn, P., Zoltick, B., et al. (2006). Brain regions underlying response inhibition and interference monitoring and suppression. European Journal of Neuroscience, 23(6), 1658–1664.
Bonnelle, V., Ham, T. E., Leech, R., Kinnunen, K. M., Mehta, M. A., Greenwood, R. J., et al. (2012). Salience network integrity predicts default mode network function after traumatic brain injury. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 109(12), 4690–4695.
Bremer, J. (2005). The internet and children: advantages and disadvantages. Child and Adolescent Psychiatric Clinics of North America, 14(3), 405.
Brier, M. R., Thomas, J. B., Snyder, A. Z., Benzinger, T. L., Zhang, D., Raichle, M. E., et al. (2012). Loss of intranetwork and internetwork resting state functional connections with Alzheimer’s disease progression. The Journal of Neuroscience, 32(26), 8890–8899.
Bunge, S. A., Ochsner, K. N., Desmond, J. E., Glover, G. H., & Gabrieli, J. D. (2001). Prefrontal regions involved in keeping information in and out of mind. Brain, 124(10), 2074–2086.
Cao, H., Sun, Y., Wan, Y., Hao, J., & Tao, F. (2011). Problematic internet use in Chinese adolescents and its relation to psychosomatic symptoms and life satisfaction. BMC Public Health, 11(1), 802.
Crockford, D. N., Goodyear, B., Edwards, J., Quickfall, J., & El-Guebaly, N. (2005). Cue-induced brain activity in pathological gamblers. Biological Psychiatry, 58(10), 787–795.
Dimitri, C., Megan, M., Lauren, J., Mon, M., & Chuan, Z. (2011) Problematic internet usage in US college students: a pilot study. BMC Medicine, 9.
Dong, G., Lu, Q., Zhou, H., & Zhao, X. (2010). Impulse inhibition in people with Internet addiction disorder: electrophysiological evidence from a Go/NoGo study. Neuroscience Letters, 485(2), 138–142.
Durkee, T., Kaess, M., Carli, V., Parzer, P., Wasserman, C., Floderus, B., et al. (2012). Prevalence of pathological internet use among adolescents in Europe: demographic and social factors. Addiction, 107(12), 2210–2222.
Everitt, B. J., & Robbins, T. W. (2005). Neural systems of reinforcement for drug addiction: from actions to habits to compulsion. Nature Neuroscience, 8(11), 1481–1489.
Feil, J., Sheppard, D., Fitzgerald, P. B., Yücel, M., Lubman, D. I., & Bradshaw, J. L. (2010). Addiction, compulsive drug seeking, and the role of frontostriatal mechanisms in regulating inhibitory control. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 35(2), 248–275.
Forman, S. D., Dougherty, G. G., Casey, B., Siegle, G. J., Braver, T. S., Barch, D. M., et al. (2004). Opiate addicts lack error-dependent activation of rostral anterior cingulate. Biological Psychiatry, 55(5), 531–537.
Fox, M. D., & Raichle, M. E. (2007). Spontaneous fluctuations in brain activity observed with functional magnetic resonance imaging. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 8(9), 700–711.
Goldstein, R. Z., & Volkow, N. D. (2002). Drug addiction and its underlying neurobiological basis: neuroimaging evidence for the involvement of the frontal cortex. American Journal of Psychiatry, 159(10), 1642–1652.
Goldstein, R. Z., & Volkow, N. D. (2011). Dysfunction of the prefrontal cortex in addiction: neuroimaging findings and clinical implications. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 12(11), 652–669.
Grant, J. E., Potenza, M. N., Weinstein, A., & Gorelick, D. A. (2010). Introduction to behavioral addictions. The American Journal of Drug and Alcohol Abuse, 36(5), 233–241.
Hanlon, C. A., Wesley, M. J., Stapleton, J. R., Laurienti, P. J., & Porrino, L. J. (2011). The association between frontal–striatal connectivity and sensorimotor control in cocaine users. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 115(3), 240–243.
Hong, L. E., Gu, H., Yang, Y., Ross, T. J., Salmeron, B. J., Buchholz, B., et al. (2009). Association of nicotine addiction and nicotine’s actions with separate cingulate cortex functional circuits. Archives of General Psychiatry, 66(4), 431–441.
Hong, S.-B., Zalesky, A., Cocchi, L., Fornito, A., Choi, E.-J., Kim, H.-H., et al. (2013). Decreased functional brain connectivity in adolescents with internet addiction. PLoS ONE, 8(2), e57831.
Horn, N., Dolan, M., Elliott, R., Deakin, J., & Woodruff, P. (2003). Response inhibition and impulsivity: an fMRI study. Neuropsychologia, 41(14), 1959–1966.
Jelenchick, L. A., Becker, T., & Moreno, M. A. (2012). Assessing the psychometric properties of the Internet Addiction Test (IAT) in US college students. Psychiatry Research, 196(2–3), 296–301.
Jin, C., Yuan, K., Zhao, L., Zhao, L., Yu, D., Deneen, K. M., et al. (2013). Structural and functional abnormalities in migraine patients without aura. NMR in Biomedicine, 26(1), 58–64.
Kalivas, P. W., & Volkow, N. D. (2005). The neural basis of addiction: a pathology of motivation and choice. American Journal of Psychiatry, 162(8), 1403–1413.
Kim, S. H., Baik, S.-H., Park, C. S., Kim, S. J., Choi, S. W., & Kim, S. E. (2011). Reduced striatal dopamine D2 receptors in people with Internet addiction. NeuroReport, 22(8), 407.
Ko, C. H., Liu, G. C., Yen, J. Y., Chen, C. Y., Yen, C. F., & Chen, C. S. (2011). Brain correlates of craving for online gaming under cue exposure in subjects with Internet gaming addiction and in remitted subjects. Addiction Biology, 18(3), 559–569.
Ko, C.-H., Liu, G.-C., Yen, J.-Y., Yen, C.-F., Chen, C.-S., & Lin, W.-C. (2012). The brain activations for both cue-induced gaming urge and smoking craving among subjects comorbid with Internet gaming addiction and nicotine dependence. Journal of Psychiatric Research, 47(4), 486–493.
Kober, H., Mende-Siedlecki, P., Kross, E. F., Weber, J., Mischel, W., Hart, C. L., et al. (2010). Prefrontal–striatal pathway underlies cognitive regulation of craving. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 107(33), 14811–14816.
Lin, F., Zhou, Y., Du, Y., Qin, L., Zhao, Z., Xu, J., et al. (2012). Abnormal white matter integrity in adolescents with Internet Addiction Disorder: a tract-based spatial statistics study. PLoS ONE, 7(1), e30253.
Liston, C., Watts, R., Tottenham, N., Davidson, M. C., Niogi, S., Ulug, A. M., et al. (2006). Frontostriatal microstructure modulates efficient recruitment of cognitive control. Cerebral Cortex, 16(4), 553–560.
Meda, S. A., Gill, A., Stevens, M. C., Lorenzoni, R. P., Glahn, D. C., Calhoun, V. D., et al. (2012). Differences in resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging functional network connectivity between schizophrenia and psychotic bipolar probands and their unaffected first-degree relatives. Biological Psychiatry, 71(10), 881–889.
Pine, D., Cohen, P., & Brook, J. (2001). Emotional reactivity and risk for psychopathology among adolescents. CNS Spectrums, 6(1), 27.
Romano, M., Osborne, L. A., Truzoli, R., & Reed, P. (2013). Differential psychological impact of internet exposure on internet addicts. PLoS ONE, 8(2), e55162.
Schoenbaum, G., Roesch, M. R., & Stalnaker, T. A. (2006). Orbitofrontal cortex, decision-making and drug addiction. Trends in Neurosciences, 29(2), 116–124.
Seeley, W. W., Crawford, R. K., Zhou, J., Miller, B. L., & Greicius, M. D. (2009). Neurodegenerative diseases target large-scale human brain networks. Neuron, 62(1), 42.
Silveri, M. M., Tzilos, G. K., Pimentel, P. J., & Yurgelun‐Todd, D. A. (2004). Trajectories of adolescent emotional and cognitive development: effects of sex and risk for drug use. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1021(1), 363–370.
Smith, S. M., Jenkinson, M., Woolrich, M. W., Beckmann, C. F., Behrens, T., Johansen-Berg, H., et al. (2004). Advances in functional and structural MR image analysis and implementation as FSL. NeuroImage, 23, S208.
Steinberg, L. (2005). Cognitive and affective development in adolescence. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 9(2), 69–74.
Tanabe, J., Tregellas, J. R., Dalwani, M., Thompson, L., Owens, E., Crowley, T., et al. (2009). Medial orbitofrontal cortex gray matter is reduced in abstinent substance-dependent individuals. Biological Psychiatry, 65(2), 160–164.
Volkow, N. D., Fowler, J. S., Wang, G. J., Hitzemann, R., Logan, J., Schlyer, D. J., et al. (1993). Decreased dopamine D2 receptor availability is associated with reduced frontal metabolism in cocaine abusers. Synapse, 14(2), 169–177.
Volkow, N. D., Wang, G.-J., Begleiter, H., Porjesz, B., Fowler, J. S., Telang, F., et al. (2006). High levels of dopamine D2 receptors in unaffected members of alcoholic families: possible protective factors. Archives of General Psychiatry, 63(9), 999.
Volkow, N. D., Wang, G.-J., Telang, F., Fowler, J. S., Thanos, P. K., Logan, J., et al. (2008). Low dopamine striatal D2 receptors are associated with prefrontal metabolism in obese subjects: possible contributing factors. NeuroImage, 42(4), 1537–1543.
Volkow, N., Fowler, J., Wang, G., Baler, R., & Telang, F. (2009). Imaging dopamine’s role in drug abuse and addiction. Neuropharmacology, 56, 3–8.
Volkow, N. D., Wang, G.-J., Tomasi, D., & Baler, R. D. (2013). Unbalanced neuronal circuits in addiction. Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 23(4), 639–648.
Winkler, A., Dörsing, B., Rief, W., Shen, Y., & Glombiewski, J. A. (2013). Treatment of internet addiction: a meta-analysis. Clinical Psychology Review, 33(2), 317–329.
Xing, L., Yuan, K., Bi, Y., Yin, J., Cai, C., Feng, D., et al. (2014). Reduced fiber integrity and cognitive control in adolescents with internet gaming disorder. Brain Research, 1586, 109–117.
Xue, T., Yuan, K., Zhao, L., Yu, D., Zhao, L., Dong, T., et al. (2012). Intrinsic brain network abnormalities in migraines without aura revealed in resting-state fMRI. PLoS ONE, 7(12), e52927.
Young, K. S. (1998a). Caught in the net: How to recognize the signs of internet addiction--and a winning strategy for recovery. New York: Wiley.
Young, K. S. (1998b). Internet addiction: the emergence of a new clinical disorder. CyberPsychology & Behavior, 1(3), 237–244.
Yu, D., Yuan, K., Zhao, L., Zhao, L., Dong, M., Liu, P., et al. (2012). Regional homogeneity abnormalities in patients with interictal migraine without aura: a resting‐state study. NMR in Biomedicine, 25(5), 806–812.
Yuan, K., Qin, W., Dong, M., Liu, J., Sun, J., Liu, P., et al. (2010a). Gray matter deficits and resting-state abnormalities in abstinent heroin-dependent individuals. Neuroscience Letters, 482(2), 101–105.
Yuan, K., Qin, W., Liu, J., Guo, Q., Dong, M., Sun, J., et al. (2010b). Altered small-world brain functional networks and duration of heroin use in male abstinent heroin-dependent individuals. Neuroscience Letters, 477(1), 37–42.
Yuan, K., Qin, W., Wang, G., Zeng, F., Zhao, L., Yang, X., et al. (2011). Microstructure abnormalities in adolescents with internet addiction disorder. PLoS ONE, 6(6), e20708.
Yuan, K., Cheng, P., Dong, T., Bi, Y., Xing, L., Yu, D., et al. (2013a). Cortical thickness abnormalities in late adolescence with online gaming addiction. PLoS ONE, 8(1), e53055.
Yuan, K., Jin, C., Cheng, P., Yang, X., Dong, T., Bi, Y., et al. (2013b). Amplitude of low frequency fluctuation abnormalities in adolescents with online gaming addiction. PLoS ONE, 8(11), e78708.
Yuan, K., Qin, W., Yu, D., Bi, Y., Xing, L., Jin, C., et al. (2015). Core brain networks interactions and cognitive control in internet gaming disorder individuals in late adolescence/early adulthood. Brain Structure and Function. doi:10.1007/s00429-014-0982-7.
Zhang, X., Salmeron, B. J., Ross, T. J., Gu, H., Geng, X., Yang, Y., et al. (2011). Anatomical differences and network characteristics underlying smoking cue reactivity. NeuroImage, 54(1), 131–141.
Zhou, Z., Yuan, G., & Yao, J. (2012). Cognitive biases toward internet game-related pictures and executive deficits in individuals with an internet game addiction. PLoS ONE, 7(11), e48961.
Acknowledgments
This paper is supported by the Project for the National Key Basic Research and Development Program (973) under Grant nos. 2014CB543203, 2011CB707700, 2012CB518501, the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant nos. 81401478, 81401488, 81227901, 81271644, 81271546, 81101036, 81101108, 31200837, 81301281, the Natural Science Basic Research Plan in Shaanxi Province of China under Grant no. 2014JQ4118, and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities under the Grant nos. 8002-72125760, 8002-72135767, 8002-72145760, the Natural Science Foundation of Inner Mongolia under Grant no. 2012MS0908. General Financial Grant the China Post- doctoral Science Foundation under Grant no. 2014 M552416. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Chenwang Jin and Ting Zhang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, C., Zhang, T., Cai, C. et al. Abnormal prefrontal cortex resting state functional connectivity and severity of internet gaming disorder. Brain Imaging and Behavior 10, 719–729 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-015-9439-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-015-9439-8