Abstract
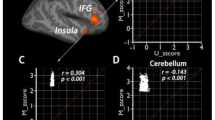
The significance of why a similar set of brain regions are associated with the default mode network and value-related neural processes remains to be clarified. Here, we examined i) whether brain regions exhibiting willingness-to-pay (WTP) task-related activity are intrinsically connected when the brain is at rest, ii) whether these regions overlap spatially with the default mode network, and iii) whether individual differences in choice behavior during the WTP task are reflected in functional brain connectivity at rest. Blood-oxygen-level dependent (BOLD) signal was measured by functional magnetic resonance imaging while subjects performed the WTP task and at rest with eyes open. Brain regions that tracked the value of bids during the WTP task were used as seed regions in an analysis of functional connectivity in the resting state data. The seed in the ventromedial prefrontal cortex was functionally connected to core regions of the WTP task-related network. Brain regions within the WTP task-related network, namely the ventral precuneus, ventromedial prefrontal and posterior cingulate cortex overlapped spatially with publically available maps of the default mode network. Also, those individuals with higher functional connectivity during rest between the ventromedial prefrontal cortex and the ventral striatum showed greater preference consistency during the WTP task. Thus, WTP task-related regions are an intrinsic network of the brain that corresponds spatially with the default mode network, and individual differences in functional connectivity within the WTP network at rest may reveal a priori biases in choice behavior.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antrobus, J. S., Singer, J. L., & Greenberg, S. (1966). Studies in the stream of consciousness: experimental enhancement and suppression of spontaneous cognitive processes. Perceptual and Motor Skills, 23, 399–417.
Baldassarre, A., Lewis, C. M., Committeri, G., Snyder, A. Z., Romani, G. L., & Corbetta, M. (2012). Individual variability in functional connectivity predicts performance of a perceptual task. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 109, 3516–3521.
Becker, G. M., DeGroot, M. H., & Marschak, J. (1964). Measuring utility by a single-response sequential method. Behavioral Science, 9, 226–232.
Berridge, K. C., Robinson, T. E., & Aldridge, J. W. (2009). Dissecting components of reward: ‘liking’, ‘wanting’, and learning. Current Opinion in Pharmacology, 9, 65–73.
Bouret, S., & Richmond, B. J. (2010). Ventromedial and orbital prefrontal neurons differentially encode internally and externally driven motivational values in monkeys. Journal of Neuroscience, 30, 8591–8601.
Buckner, R. L., Andrews-Hanna, J. R., & Schacter, D. L. (2008). The brain’s default network: anatomy, function, and relevance to disease. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1124, 1–38.
Chib, V. S., Rangel, A., Shimojo, S., & O’Doherty, J. P. (2009). Evidence for a common representation of decision values for dissimilar goods in human ventromedial prefrontal cortex. Journal of Neuroscience, 29, 12315–12320.
Clithero, J. A., & Rangel, A. (2012) Reliable features of the network involved in the neural computation of subjective value. In: Neuroeconomics 10th Annual Meeting Miami, USA.
Clithero, J. A., & Rangel, A. (2013) Informatic parcellation of the network involved in the computation of subjective value. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci.
Coste, C. P., Sadaghiani, S., Friston, K. J., & Kleinschmidt, A. (2011). Ongoing brain activity fluctuations directly account for intertrial and indirectly for intersubject variability in Stroop task performance. Cerebral Cortex, 21, 2612–2619.
Cox, R. W. (1996). AFNI: software for analysis and visualization of functional magnetic resonance neuroimages. Computers and Biomedical Research, 29, 162–173.
Damoiseaux, J. S., & Greicius, M. D. (2009). Greater than the sum of its parts: a review of studies combining structural connectivity and resting-state functional connectivity. Brain Structure and Function, 213, 525–533.
Dillon, D. G., Rosso, I. M., Pechtel, P., Killgore, W. D., Rauch, S. L., & Pizzagalli, D. A. (2014). Peril and pleasure: an rdoc-inspired examination of threat responses and reward processing in anxiety and depression. Depression and Anxiety, 31, 233–249.
Erk, S., Spitzer, M., Wunderlich, A. P., Galley, L., & Walter, H. (2002). Cultural objects modulate reward circuitry. Neuroreport, 13, 2499–2503.
Fellows, L. K., & Farah, M. J. (2007). The role of ventromedial prefrontal cortex in decision making: judgment under uncertainty or judgment per se? Cerebral Cortex, 17, 2669–2674.
Fox, M. D., Snyder, A. Z., Vincent, J. L., Corbetta, M., Van Essen, D. C., & Raichle, M. E. (2005). The human brain is intrinsically organized into dynamic, anticorrelated functional networks. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 102, 9673–9678.
Fransson, P. (2006). How default is the default mode of brain function? Further evidence from intrinsic BOLD signal fluctuations. Neuropsychologia, 44, 2836–2845.
Greicius, M. D., Krasnow, B., Reiss, A. L., & Menon, V. (2003). Functional connectivity in the resting brain: a network analysis of the default mode hypothesis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 100, 253–258.
Gusnard, D. A., & Raichle, M. E. (2001). Searching for a baseline: functional imaging and the resting human brain. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 2, 685–694.
Hare, T. A., Camerer, C. F., Knoepfle, D. T., & Rangel, A. (2010). Value computations in ventral medial prefrontal cortex during charitable decision making incorporate input from regions involved in social cognition. Journal of Neuroscience, 30, 583–590.
Hare, T. A., Malmaud, J., & Rangel, A. (2011). Focusing attention on the health aspects of foods changes value signals in vmPFC and improves dietary choice. Journal of Neuroscience, 31, 11077–11087.
Harmelech, T., & Malach, R. (2013). Neurocognitive biases and the patterns of spontaneous correlations in the human cortex. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 17, 606–615.
Janowski, V., Camerer, C., & Rangel, A. (2013). Empathic choice involves vmPFC value signals that are modulated by social processing implemented in IPL. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 8, 201–208.
Jo, H. J., Saad, Z. S., Simmons, W. K., Milbury, L. A., & Cox, R. W. (2010). Mapping sources of correlation in resting state FMRI, with artifact detection and removal. NeuroImage, 52, 571–582.
Kang, M. J., Rangel, A., Camus, M., & Camerer, C. F. (2011). Hypothetical and real choice differentially activate common valuation areas. Journal of Neuroscience, 31, 461–468.
Koyama, M. S., Di Martino, A., Zuo, X. N., Kelly, C., Mennes, M., Jutagir, D. R., Castellanos, F. X., & Milham, M. P. (2011). Resting-state functional connectivity indexes reading competence in children and adults. Journal of Neuroscience, 31, 8617–8624.
Leathers, M. L., & Olson, C. R. (2012). In monkeys making value-based decisions, LIP neurons encode cue salience and not action value. Science, 338, 132–135.
Lee, L., Amir, O., & Ariely, D. (2009). In search of homo economicus: cognitive noise and the role of emotion in preference consistency. J Cons Res, 36, 173–187.
Liljeholm, M., Wang, S., Zhang, J., & O’Doherty, J. P. (2013). Neural correlates of the divergence of instrumental probability distributions. Journal of Neuroscience, 33, 12519–12527.
Mackey, S., & Paulus, M. (2013). Are there volumetric brain differences associated with the use of cocaine and amphetamine-type stimulants? Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 37, 300–316.
Mackey, S., & Petrides, M. (2014) Architecture and morphology of the human ventromedial prefrontal cortex. European Journal of Neuroscience, 40, 2777–2796.
Margulies, D. S., Vincent, J. L., Kelly, C., Lohmann, G., Uddin, L. Q., Biswal, B. B., Villringer, A., Castellanos, F. X., Milham, M. P., & Petrides, M. (2009). Precuneus shares intrinsic functional architecture in humans and monkeys. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 106, 20069–20074.
Mars, R. B., Jbabdi, S., Sallet, J., O’Reilly, J. X., Croxson, P. L., Olivier, E., Noonan, M. P., Bergmann, C., Mitchell, A. S., Baxter, M. G., Behrens, T. E., Johansen-Berg, H., Tomassini, V., Miller, K. L., & Rushworth, M. F. (2011). Diffusion-weighted imaging tractography-based parcellation of the human parietal cortex and comparison with human and macaque resting-state functional connectivity. Journal of Neuroscience, 31, 4087–4100.
Mason, M. F., Norton, M. I., Van Horn, J. D., Wegner, D. M., Grafton, S. T., & Macrae, C. N. (2007). Wandering minds: the default network and stimulus-independent thought. Science, 315, 393–395.
Mayberg, H. S., Lozano, A. M., Voon, V., McNeely, H. E., Seminowicz, D., Hamani, C., Schwalb, J. M., & Kennedy, S. H. (2005). Deep brain stimulation for treatment-resistant depression. Neuron, 45, 651–660.
McClure, S. M., Li, J., Tomlin, D., Cypert, K. S., Montague, L. M., & Montague, P. R. (2004). Neural correlates of behavioral preference for culturally familiar drinks. Neuron, 44, 379–387.
Mevorach, C., Humphreys, G. W., & Shalev, L. (2006). Opposite biases in salience-based selection for the left and right posterior parietal cortex. Nature Neuroscience, 9, 740–742.
Ochsner, K., & Gross, J. (2005) The cognitive control of emotion. TRENDS in Cognitive Sciences, 9, 242–249.
Olafsson, V., Guo, J., Wong, C. W., Kundu, P., Inati, S., Luh, W.-M., Roopchansingh, V., Brenowitz, N., Bandettini, P., Wong, E, Liu, T. (2012). High spatial and temporal resolution fcMRI with BOLD selectivity using multiecho simultaneous multislice EPI. In: Proceedings of the 20th ISMRM, p 2068.
Paulus, M. P., & Frank, L. R. (2003). Ventromedial prefrontal cortex activation is critical for preference judgments. Neuroreport, 14, 1311–1315.
Paulus, M. P., Tapert, S. F., & Schulteis, G. (2009). The role of interoception and alliesthesia in addiction. Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior, 94, 1–7.
Plassmann, H., O’Doherty, J., & Rangel, A. (2007). Orbitofrontal cortex encodes willingness to pay in everyday economic transactions. Journal of Neuroscience, 27, 9984–9988.
Plassmann, H., O’Doherty, J. P., & Rangel, A. (2010). Appetitive and aversive goal values are encoded in the medial orbitofrontal cortex at the time of decision making. Journal of Neuroscience, 30, 10799–10808.
Singer, J. L., & Antrobus, J. S. (1963). A factor-analytic study of daydreaming and conceptually-related cognitive and personality variables. Perceptual and Motor Skills, 17, 187–209.
Smith, S. M., Fox, P. T., Miller, K. L., Glahn, D. C., Fox, P. M., Mackay, C. E., Filippini, N., Watkins, K. E., Toro, R., Laird, A. R., & Beckmann, C. F. (2009). Correspondence of the brain’s functional architecture during activation and rest. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 106, 13040–13045.
Uddin, L. Q. (2013). Complex relationships between structural and functional brain connectivity. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 17, 600–602.
Uddin, L. Q., Kelly, A. M., Biswal, B. B., Xavier Castellanos, F., & Milham, M. P. (2009). Functional connectivity of default mode network components: correlation, anticorrelation, and causality. Human Brain Mapping, 30, 625–637.
Verdejo-Garcia, A., & Bechara, A. (2009). A somatic marker theory of addiction. Neuropharmacology, 56(Suppl 1), 48–62.
Vincent, J. L., Patel, G. H., Fox, M. D., Snyder, A. Z., Baker, J. T., Van Essen, D. C., Zempel, J. M., Snyder, L. H., Corbetta, M., & Raichle, M. E. (2007). Intrinsic functional architecture in the anaesthetized monkey brain. Nature, 447, 83–86.
Zhang, S., & Li, C. S. (2012). Functional connectivity mapping of the human precuneus by resting state fMRI. NeuroImage, 59, 3548–3562.
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by a grants received from the National Institute on Drug Abuse: R01 DA027797 & P20 DA027843.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 365 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mackey, S., Olafsson, V., Aupperle, R.L. et al. Greater preference consistency during the Willingness-to-Pay task is related to higher resting state connectivity between the ventromedial prefrontal cortex and the ventral striatum. Brain Imaging and Behavior 10, 730–738 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-015-9435-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-015-9435-z