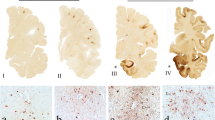
Abstract
Neuroimaging identified abnormalities associated with traumatic brain injury (TBI) are but gross indicators that reflect underlying trauma-induced neuropathology at the cellular level. This review examines how cellular pathology relates to neuroimaging findings with the objective of more closely relating how neuroimaging findings reveal underlying neuropathology. Throughout this review an attempt will be made to relate what is directly known from post-mortem microscopic and gross anatomical studies of TBI of all severity levels to the types of lesions and abnormalities observed in contemporary neuroimaging of TBI, with an emphasis on mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI). However, it is impossible to discuss the neuropathology of mTBI without discussing what occurs with more severe injury and viewing pathological changes on some continuum from the mildest to the most severe. Historical milestones in understanding the neuropathology of mTBI are reviewed along with implications for future directions in the examination of neuroimaging and neuropathological correlates of TBI.




















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agnati, L. F., Genedani, S., et al. (2007). One century of progress in neuroscience founded on Golgi and Cajal’s outstanding experimental and theoretical contributions. Brain Research Reviews, 55(1), 167–189.
Albensi, B. C., Knoblach, S. M., et al. (2000). Diffusion and high resolution MRI of traumatic brain injury in rats: time course and correlation with histology. Experimental Neurology, 162(1), 61–72.
Babikian, T., Freier, M. C., et al. (2006). MR spectroscopy: predicting long-term neuropsychological outcome following pediatric TBI. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging: JMRI, 24(4), 801–811.
Bain, A. C., Raghupathi, R., et al. (2001). Dynamic stretch correlates to both morphological abnormalities and electrophysiological impairment in a model of traumatic axonal injury. Journal of Neurotrauma, 18(5), 499–511.
Barkhoudarian, G., Hovda, D. A., et al. (2011). The molecular pathophysiology of concussive brain injury. Clinics in Sports Medicine, 30(1), 33–48. vii–iii.
Barr, W. B., Prichep, L. S., et al. (2011). Measuring brain electrical activity to track recovery from sport-related concussion. Brain Injury, [BI].
Beauchamp, M. H., Ditchfield, M., et al. (2011). Detecting traumatic brain lesions in children: CT vs conventional MRI vs susceptibility weighted imaging (SWI). Journal of Neurotrauma, 28(6), 915-927
Belanger, H. G., Vanderploeg, R. D., et al. (2007). Recent neuroimaging techniques in mild traumatic brain injury. The Journal of Neuropsychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences, 19(1), 5–20.
Bendlin, B. B., Ries, M. L., et al. (2008). Longitudinal changes in patients with traumatic brain injury assessed with diffusion-tensor and volumetric imaging. NeuroImage, 42(2), 503–514.
Benson, R. R., Meda, S. A., et al. (2007). Global white matter analysis of diffusion tensor images is predictive of injury severity in traumatic brain injury. Journal of Neurotrauma, 24(3), 446–459.
Biasca, N., & Maxwell, W. L. (2007). Minor traumatic brain injury in sports: a review in order to prevent neurological sequelae. Progress in Brain Research, 161, 263–291.
Bigler, E. D. (2007). Anterior and middle cranial fossa in traumatic brain injury: relevant neuroanatomy and neuropathology in the study of neuropsychological outcome. Neuropsychology, 21(5), 515–531.
Bigler, E. D., McCauley, S. R., et al. (2010). The temporal stem in traumatic brain injury: preliminary findings. Brain Imaging and Behavior, 4(3–4), 270–282.
Bigler, E. D., Pertab, J., Merkley, T. L., Newsome, M. R., Scheibel, R. S., Wilde, E. A., et al. (2011). Working memory correlates of brain structure and function in child traumatic brain injury. International Journal of Psychophysiology (in press).
Bigler, E. D. M., & Maxwell, W. L. (2011). Neuroimaging and neuropathology of TBI. NeuroRehabilitation, 28(2), 63–74.
Blankenberg, F. G. (2008). Monitoring of treatment-induced apoptosis in oncology with PET and SPECT. Current Pharmaceutical Design, 14(28), 2974–2982.
Blumbergs, P. C., Scott, G., et al. (1995). Topography of axonal injury as defined by amyloid precursor protein and the sector scoring method in mild and severe closed head injury. Journal of Neurotrauma, 12(4), 565–572.
Bouilleret, V., Cardamone, L., et al. (2009). Progressive brain changes on serial manganese-enhanced MRI following traumatic brain injury in the rat. Journal of Neurotrauma, 26(11), 1999–2013.
Bramlett, H. M., & Dietrich, W. D. (2002). Quantitative structural changes in white and gray matter 1 year following traumatic brain injury in rats. Acta Neuropathologica, 103(6), 607–614.
Brandstack, N., Kurki, T., et al. (2011). Diffusivity of normal-appearing tissue in acute traumatic brain injury. Clinical Neuroradiology, 21(2), 75–82.
Brenner, L. A., Terrio, H., et al. (2010). Neuropsychological test performance in soldiers with blast-related mild TBI. Neuropsychology, 24(2), 160–167.
Budde, M. D., Janes, L., et al. (2011). The contribution of gliosis to diffusion tensor anisotropy and tractography following traumatic brain injury: validation in the rat using Fourier analysis of stained tissue sections. Brain: A Journal of Neurology.
Buki, A., Okonkwo, D. O., et al. (2000). Cytochrome c release and caspase activation in traumatic axonal injury. The Journal of Neuroscience: The Official Journal of the Society for Neuroscience, 20(8), 2825–2834.
Chanraud, S., Pitel, A. L., et al. (2010). Dual tasking and working memory in alcoholism: relation to frontocerebellar circuitry. Neuropsychopharmacology, 35(9), 1868–1878.
Chanraud, S., Zahr, N., et al. (2010). MR diffusion tensor imaging: a window into white matter integrity of the working brain. Neuropsychology Review, 20(2), 209–225.
Chen, J. K., Johnston, K. M., et al. (2008). Neural substrates of symptoms of depression following concussion in male athletes with persisting postconcussion symptoms. Archives of General Psychiatry, 65(1), 81–89.
Clark, R. S. B., Chen, M., et al. (2001). Detection of single- and double-strand DNA breaks after traumatic brain injury in rats: comparison of in situ labeling techniques using DNA polymerase I, the Klenow fragment of DNA polymerase I, and terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase. Journal of Neurotrauma, 18(7), 675–689.
Cloots, R. J., Gervaise, H. M., et al. (2008). Biomechanics of traumatic brain injury: influences of the morphologic heterogeneities of the cerebral cortex. Annals of Biomedical Engineering, 36(7), 1203–1215.
Cloots, R. J., van Dommelen, J. A., et al. (2010). Micromechanics of diffuse axonal injury: influence of axonal orientation and anisotropy. Biomech Model Mechanobiol, 10(3), 413–422.
Cohen, B. A., Inglese, M., et al. (2007). Proton MR spectroscopy and MRI-volumetry in mild traumatic brain injury. AJNR. American Journal of Neuroradiology, 28(5), 907–913.
Colicos, M. A., & Dash, P. K. (1996). Apoptotic morphology of dentate gyrus granule cells following experimental cortical impact injury in rats: possible role in spatial memory deficits. Brain Research, 739(1–2), 120–131.
Collewijn, H., & Van Harreveld, A. (1966). Intracellular recording from cat spinal motoneurones during acute asphyxia. The Journal of Physiology, 185(1), 1–14.
Courville, C. B. (1952). Traumatic alterations in the neurons of the human brain incident to craniocerebral injury; a comparison with Cajal’s observations of experimental animals. Bulletin of the Los Angeles Neurological Society, 17(1–2), 71–93.
Cubon, V. A., Putukian, M., et al. (2011). A diffusion tensor imaging study on the white matter skeleton in individuals with sports-related concussion. Journal of Neurotrauma, 28(2), 189–201.
Davenport, N. D., Lim, K. O., et al. (2011). Diffuse and spatially variable white matter disruptions are associated with blast-related mild traumatic brain injury. Neuroimage. in press
De Beaumont, L., Tremblay, S., et al. (2011). Altered bidirectional plasticity and reduced implicit motor learning in concussed athletes. Cerebral Cortex.
DeKosky, S. T., Ikonomovic, M. D., et al. (2010). Traumatic brain injury–football, warfare, and long-term effects. The New England Journal of Medicine, 363(14), 1293–1296.
Ding, K., Marquez de la Plata, C., et al. (2008). Cerebral atrophy after traumatic white matter injury: correlation with acute neuroimaging and outcome. Journal of Neurotrauma, 25(12), 1433–1440.
Downes, C. E., & Crack, P. J. (2010). Neural injury following stroke: are Toll-like receptors the link between the immune system and the CNS? British Journal of Pharmacology, 160(8), 1872–1888.
Duma, S. M., & Rowson, S. (2009). Every Newton Hertz: a macro to micro approach to investigating brain injury. Conference Proceedings—IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, 2009, 1123–1126.
Elkin, B. S., & Morrison, B., 3rd. (2007). Region-specific tolerance criteria for the living brain. Stapp Car Crash Journal, 51, 127–138.
Ellemberg, D., Henry, L. C., et al. (2009). Advances in sport concussion assessment: from behavioral to brain imaging measures. Journal of Neurotrauma, 26(12), 2365–2382.
Fabricius, M., Fuhr, S., et al. (2006). Cortical spreading depression and peri-infarct depolarization in acutely injured human cerebral cortex. Brain: A Journal of Neurology, 129(Pt 3), 778–790.
Farkas, O., & Povlishock, J. T. (2007). Cellular and subcellular change evoked by diffuse traumatic brain injury: a complex web of change extending far beyond focal damage. Progress in Brain Research, 161, 43–59.
Feng, Y., Abney, T. M., et al. (2010). Relative brain displacement and deformation during constrained mild frontal head impact. Journal of the Royal Society, Interface, 7(53), 1677–1688.
Fuster, J. M. (2009). Cortex and memory: emergence of a new paradigm. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 21(11), 2047–2072.
Gale, S. D., Baxter, L., et al. (2005). Traumatic brain injury and grey matter concentration: a preliminary voxel based morphometry study. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 76(7), 984–988.
Gao, X., & Chen, J. (2011). Mild traumatic brain injury results in extensive neuronal degeneration in the cerebral cortex. Journal of Neuropathology and Experimental Neurology, 70(3), 183–191.
Gasparetto, E. L., Rueda Lopes, F. C., et al. (2011). Diffusion imaging in traumatic brain injury. Neuroimaging Clinics of North America, 21(1), 115–125. viii.
Gavett, B. E., Stern, R. A., et al. (2010). Mild traumatic brain injury: a risk factor for neurodegeneration. Alzheimer’s Research & Therapy, 2(3), 18.
Ge, Y., Patel, M. B., et al. (2009). Assessment of thalamic perfusion in patients with mild traumatic brain injury by true FISP arterial spin labelling MR imaging at 3T. Brain Injury, 23(7), 666–674.
Geary, E. K., Kraus, M. F., et al. (2011). Verbal learning strategy following mild traumatic brain injury. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society: JINS, 1–11.
Ghosh, A., Wilde, E. A., et al. (2009). The relation between Glasgow Coma Scale score and later cerebral atrophy in paediatric traumatic brain injury. Brain Injury, 23(3), 228–233.
Giza, C. C., & Hovda, D. A. (2000). Ionic and metabolic consequences of concussion. In R. C. Cantu & R. I. Cantu (Eds.), Neurologic athletic and spine injuries (pp. 80–100). St. Louis: W.B. Saunders.
Giza, C. C., & Hovda, D. A. (2001). The neurometabolic cascade of concussion. Journal of Athletic Training, 36(3), 228–235.
Gosselin, N., Bottari, C., et al. (2011). Electrophysiology and functional MRI in post-acute mild traumatic brain injury. Journal of Neurotrauma, 28(3), 329–341.
Govind, V., Gold, S., et al. (2010). Whole-brain proton MR spectroscopic imaging of mild-to-moderate traumatic brain injury and correlation with neuropsychological deficits. Journal of Neurotrauma, 27(3), 483–496.
Graham, D. I., & Lantos, P. L. (2002). Greenfield’s Neuropathology (Volume I). London: Arnold Publishing.
Greenberg, G., Mikulis, D. J., et al. (2008). Use of diffusion tensor imaging to examine subacute white matter injury progression in moderate to severe traumatic brain injury. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, 89(12 Suppl), S45–S50.
Greer, J. E., McGinn, M. J., et al. (2011). Diffuse traumatic axonal injury in the mouse induces atrophy, c-Jun activation, and axonal outgrowth in the axotomized neuronal population. The Journal of Neuroscience: The Official Journal of the Society for Neuroscience, 31(13), 5089–5105.
Grossman, E. J., Ge, Y. et al. (2011). Thalamus and cognitive impairment in Mild Traumatic Brain Injury: A Diffusional Kurtosis Imaging Study. Journal of Neurotrauma.
Guskiewicz, K. M., & Mihalik, J. P. (2011). Biomechanics of sport concussion: quest for the elusive injury threshold. Exercise and Sport Sciences Reviews, 39(1), 4–11.
Harrison, L. C., Raunio, M., et al. (2010). MRI texture analysis in multiple sclerosis: toward a clinical analysis protocol. Academic Radiology, 17(6), 696–707.
Hartings, J. A., Watanabe, T., et al. (2011). Spreading depolarizations have prolonged direct current shifts and are associated with poor outcome in brain trauma. Brain: A Journal of Neurology, 134(Pt 5), 1529–1540.
Hasiloglu, Z. I., Albayram, S., et al. (2011). Cerebral microhemorrhages detected by susceptibility-weighted imaging in amateur boxers. AJNR. American Journal of Neuroradiology, 32(1), 99–102.
Helmy, A., Carpenter, K. L., et al. (2010). The cytokine response to human traumatic brain injury: temporal profiles and evidence for cerebral parenchymal production. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism.
Henry, L. C., Tremblay, S., et al. (2010). Neurometabolic changes in the acute phase after sports concussions correlate with symptom severity. Journal of Neurotrauma, 27(1), 65–76.
Hillary, F. G., Medaglia, J. D., et al. (2011). Examining working memory task acquisition in a disrupted neural network. Brain: A Journal of Neurology, 134(Pt 5), 1555–1570.
Holli, K. K., Harrison, L., et al. (2010). Texture analysis of MR images of patients with mild traumatic brain injury. BMC Medical Imaging, 10, 8.
Holli, K. K., Waljas, M., et al. (2010). Mild traumatic brain injury: tissue texture analysis correlated to neuropsychological and DTI findings. Academic Radiology, 17(9), 1096–1102.
Hunter, J. V., Wilde, E. A., et al. (2011). Emerging imaging tools for use with traumatic brain injury research. Journal of Neurotrauma. in press
Inglese, M., Makani, S., et al. (2005). Diffuse axonal injury in mild traumatic brain injury: a diffusion tensor imaging study. Journal of Neurosurgery, 103(2), 298–303.
Inglese, M., Grossman, R. I., et al. (2006). Clinical significance of dilated Virchow-Robin spaces in mild traumatic brain injury. Brain Injury, 20(1), 15–21.
Irimia, A., Chambers, M. C., et al. (2011). Comparison of acute and chronic traumatic brain injury using semi-automatic multimodal segmentation of MR volumes. Journal of Neurotrauma, 28(11), 2287–2306.
Iverson, G. L., Lovell, M. R., et al. (2000). Prevalence of abnormal CT-scans following mild head injury. Brain Injury, 14(12), 1057–1061.
Jafari, S. S., Nielson, M., et al. (1998). Axonal cytoskeletal changes after nondisruptive axonal injury. II. Intermediate sized axons. Journal of Neurotrauma, 15(11), 955–966.
Jander, S., Schroeter, M., et al. (2001). Cortical spreading depression induces proinflammatory cytokine gene expression in the rat brain. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism: Official Journal of the International Society of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism, 21(3), 218–225.
Jantzen, K. J. (2010). Functional magnetic resonance imaging of mild traumatic brain injury. The Journal of Head Trauma Rehabilitation, 25(4), 256–266.
Johnson, B., Zhang, K., et al. (2011). Metabolic alterations in corpus callosum may compromise brain functional connectivity in MTBI patients: an (1)H-MRS study. Neuroscience Letters.
Kerr, J. F. (1971). Shrinkage necrosis: a distinct mode of cellular death. The Journal of Pathology, 105(1), 13–20.
Kilinc, D., Gallo, G., et al. (2009). Mechanical membrane injury induces axonal beading through localized activation of calpain. Experimental Neurology, 219(2), 553–561.
Kilinc, D., Peyrin, J. M., et al. (2011). Wallerian-like degeneration of central neurons after synchronized and geometrically registered mass axotomy in a three-compartmental microfluidic chip. Neurotoxicity Research, 19(1), 149–161.
Kinnunen, K. M., Greenwood, R., et al. (2011). White matter damage and cognitive impairment after traumatic brain injury. Brain: A Journal of Neurology, 134(Pt 2), 449–463.
Konrad, C., Geburek, A. J., et al. (2010). Long-term cognitive and emotional consequences of mild traumatic brain injury. Psychological Medicine, 1–15.
Kraus, M. F., Susmaras, T., et al. (2007). White matter integrity and cognition in chronic traumatic brain injury: a diffusion tensor imaging study. Brain, 130(Pt 10), 2508–2519.
Kuceyeski, A., Maruta, J., et al. (2011). The generation and validation of white matter connectivity importance maps. NeuroImage, 58(1), 109–121.
Kurca, E., Sivak, S., et al. (2006). Impaired cognitive functions in mild traumatic brain injury patients with normal and pathologic magnetic resonance imaging. Neuroradiology, 48(9), 661–669.
Lange, R. T., Iverson, G. L., et al. (2009). Neuropsychological functioning following complicated vs. uncomplicated mild traumatic brain injury. Brain Injury, 23(2), 83–91.
Lange, R. T., Iverson, G. L., et al. (2011). Diffusion tensor imaging findings are not strongly associated with postconcussional disorder 2 months following mild traumatic brain injury. The Journal of Head Trauma Rehabilitation.
LaPlaca, M. C., & Prado, G. R. (2010). Neural mechanobiology and neuronal vulnerability to traumatic loading. Journal of Biomechanics, 43(1), 71–78.
LaPlaca, M. C., Simon, C. M., et al. (2007). CNS injury biomechanics and experimental models. Progress in Brain Research, 161, 13–26.
LaPlaca, M. C., & Meaney, D. F. (2011). Perspectives on the role of bioengineering in neurotrauma research. Journal of Neurotrauma, 28(11), 2201–2202.
Le, T. H., & Gean, A. D. (2009). Neuroimaging of traumatic brain injury. The Mount Sinai Journal of Medicine, 76(2), 145–162.
Levine, B., Kovacevic, N., et al. (2008). The Toronto traumatic brain injury study: injury severity and quantified MRI. Neurology, 70(10), 771–778.
Lewine, J. D., Davis, J. T., et al. (2007). Objective documentation of traumatic brain injury subsequent to mild head trauma: multimodal brain imaging with MEG, SPECT, and MRI. The Journal of Head Trauma Rehabilitation, 22(3), 141–155.
Li, X. Y., & Feng, D. F. (2009). Diffuse axonal injury: novel insights into detection and treatment. Journal of Clinical Neuroscience, 16(5), 614–619.
Li, X., Link, J. M., et al. (2008). Site-specific labeling of annexin V with F-18 for apoptosis imaging. Bioconjugate Chemistry, 19(8), 1684–1688.
Lo, C., Shifteh, K., et al. (2009). Diffusion tensor imaging abnormalities in patients with mild traumatic brain injury and neurocognitive impairment. Journal of Computer Assisted Tomography, 33(2), 293–297.
Lo, T. P., Jr., Cho, K. S., et al. (2009). Systemic hypothermia improves histological and functional outcome after cervical spinal cord contusion in rats. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 514(5), 433–448.
Mac Donald, C. L., Johnson, A. M., et al. (2011). Detection of blast-related traumatic brain injury in U.S. military personnel. The New England Journal of Medicine, 364(22), 2091–2100.
MacKenzie, J. D., Siddiqi, F., et al. (2002). Brain atrophy in mild or moderate traumatic brain injury: a longitudinal quantitative analysis. AJNR. American Journal of Neuroradiology, 23(9), 1509–1515.
Mao, H., Yang, K. H., et al. (2010). Computational neurotrauma-design, simulation, and analysis of controlled cortical impact model. Biomechanics and Modeling in Mechanobiology, 9(6), 763–772.
Marino, S., Ciurleo, R., et al. (2011). 1H-MR spectroscopy in traumatic brain injury. Neurocritical Care, 14(1), 127–133.
Marquez de la Plata, C., Ardelean, A., et al. (2007). Magnetic resonance imaging of diffuse axonal injury: quantitative assessment of white matter lesion volume. Journal of Neurotrauma, 24(4), 591–598.
Maruishi, M., Miyatani, M., et al. (2007). Compensatory cortical activation during performance of an attention task by patients with diffuse axonal injury: a functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 78(2), 168–173.
Maruta, J., Lee, S. W., et al. (2010). A unified science of concussion. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1208, 58–66.
Mathew, P., Graham, D. I., et al. (1994). Focal brain injury: histological evidence of delayed inflammatory response in a new rodent model of focal cortical injury. Acta Neurochirurgica Supplementum (Wien), 60, 428–430.
Maxwell, W. L., & Graham, D. I. (1997). Loss of axonal microtubules and neurofilaments after stretch-injury to guinea pig optic nerve fibers. Journal of Neurotrauma, 14(9), 603–614.
Maxwell, W. L., Hardy, I. G., et al. (1992). Changes in the choroid plexus, responses by intrinsic epiplexus cells and recruitment from monocytes after experimental head acceleration injury in the non-human primate. Acta Neuropathologica, 84(1), 78–84.
Maxwell, W. L., Whitfield, P. C., et al. (1992). The cerebrovascular response to experimental lateral head acceleration. Acta Neuropathologica, 84(3), 289–296.
Maxwell, W. L., Watt, C., et al. (1993). Ultrastructural evidence of axonal shearing as a result of lateral acceleration of the head in non-human primates. Acta Neuropathologica, 86(2), 136–144.
Maxwell, W. L., Bullock, R., et al. (1994). Massive astrocytic swelling in response to extracellular glutamate–a possible mechanism for post-traumatic brain swelling? Acta Neurochirurgica Supplementum, 60, 465–467.
Maxwell, W. L., McCreath, B. J., et al. (1995). Cytochemical evidence for redistribution of membrane pump calcium-ATPase and ecto-Ca-ATPase activity, and calcium influx in myelinated nerve fibres of the optic nerve after stretch injury. Journal of Neurocytology, 24(12), 925–942.
Maxwell, W. L., Povlishock, J. T., et al. (1997). A mechanistic analysis of nondisruptive axonal injury: a review. Journal of Neurotrauma, 14(7), 419–440.
Maxwell, W. L., Domleo, A., et al. (2003). Post-acute alterations in the axonal cytoskeleton after traumatic axonal injury. Journal of Neurotrauma, 20(2), 151–168.
Maxwell, W. L., MacKinnon, M. A., et al. (2006). Thalamic nuclei after human blunt head injury. Journal of Neuropathology and Experimental Neurology, 65(5), 478–488.
Maxwell, W. L., Irvine, A., et al. (1991). Focal axonal injury: the early axonal response to stretch. Journal of Neurocytology, 20(3), 157–164.
Maxwell, W. L., MacKinnon, M. A., et al. (2010). Stereology of cerebral cortex after traumatic brain injury matched to the Glasgow outcome score. Brain: A Journal of Neurology, 133(Pt 1), 139–160.
Mayer, A. R., Ling, J., et al. (2010). A prospective diffusion tensor imaging study in mild traumatic brain injury. Neurology, 74(8), 643–650.
Mayer, A. R., Mannell, M. V., et al. (2011). Functional connectivity in mild traumatic brain injury. Human Brain Mapping.
Mazzeo, A. T., Beat, A., et al. (2009). The role of mitochondrial transition pore, and its modulation, in traumatic brain injury and delayed neurodegeneration after TBI. Experimental Neurology, 218(2), 363–370.
McAllister, T. W., Flashman, L. A., et al. (2006). Mechanisms of working memory dysfunction after mild and moderate TBI: evidence from functional MRI and neurogenetics. Journal of Neurotrauma, 23(10), 1450–1467.
McAllister, K. A., Usrey, W. M., Noctor, S. C., & Rayport, S. (Eds.). (2010). Fundamentals of cellular neurobiology. Essentials of Neuropsychiatry and Behavioral Neuroscience. Washington: American Psychiatric Publishing, Inc.
McAuley, G., Schrag, M., et al. (2010). Quantification of punctate iron sources using magnetic resonance phase. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 63(1), 106–115.
McCrea, M., Prichep, L., et al. (2010). Acute effects and recovery after sport-related concussion: a neurocognitive and quantitative brain electrical activity study. The Journal of Head Trauma Rehabilitation, 25(4), 283–292.
McIntosh, A. S., & McCrory, P. (2005). Preventing head and neck injury. British Journal of Sports Medicine, 39(6), 314–318.
McKee, A. C., Cantu, R. C., et al. (2009). Chronic traumatic encephalopathy in athletes: progressive tauopathy after repetitive head injury. Journal of Neuropathology and Experimental Neurology, 68(7), 709–735.
McKee, A. C., Gavett, B. E., Stern, R. A., Nowinski, C. J., Cantu, R. C., Kowall, N. W., Perl, D. P., Hedley-Whyte, E. T., Price, B., Sullivan, P. M., Lee, H.-S., Kubilus, C. A., Daneshvar, D. H., Wulff, M., & Budson, A. E. (2010). TDP-43 proteinopathy and motor neuron disease in chronic traumatic encephalopathy. Journal of Neuropathology and Experimental Neurology, 69(9), 918–929.
Meaney, D. F., & Smith, D. H. (2011). Biomechanics of concussion. Clinics in Sports Medicine, 30(1), 19–31. vii.
Medaglia, J. D., Chiou, K. S., et al. (2011). The less BOLD, the Wiser: support for the latent resource hypothesis after traumatic brain injury. Human Brain Mapping.
Merkley, T. L., Bigler, E. D., et al. (2008). Diffuse changes in cortical thickness in pediatric moderate-to-severe traumatic brain injury. Journal of Neurotrauma, 25(11), 1343–1345.
Messe, A., Caplain, S., et al. (2010). Diffusion tensor imaging and white matter lesions at the subacute stage in mild traumatic brain injury with persistent neurobehavioral impairment. Human Brain Mapping.
Metting, Z., Rodiger, L. A., et al. (2007). Structural and functional neuroimaging in mild-to-moderate head injury. Lancet Neurology, 6(8), 699–710.
Metting, Z., Rodiger, L. A., et al. (2009). Perfusion computed tomography in the acute phase of mild head injury: regional dysfunction and prognostic value. Annals of Neurology, 66(6), 809–816.
Miles, L., Grossman, R. I., et al. (2008). Short-term DTI predictors of cognitive dysfunction in mild traumatic brain injury. Brain Injury, 22(2), 115–122.
Mohammed Sulaiman, A., Denman, N., et al. (2011). Stereology and ultrastructure of chronic phase axonal and cell soma pathology in stretch-injured central nerve fibers. Journal of Neurotrauma, 28(3), 383–400.
Monnerie, H., Tang-Schomer, M. D., et al. (2010). Dendritic alterations after dynamic axonal stretch injury in vitro. Experimental Neurology, 224(2), 415–423.
Morganti-Kossmann, M. C., Satgunaseelan, L., et al. (2007). Modulation of immune response by head injury. Injury, 38(12), 1392–1400.
Morganti-Kossmann, M. C., Yan, E., et al. (2010). Animal models of traumatic brain injury: is there an optimal model to reproduce human brain injury in the laboratory? Injury, 41(Suppl 1), S10–S13.
Morino, T., Ogata, T., et al. (2003). Delayed neuronal damage related to microglia proliferation after mild spinal cord compression injury. Neurosciences Research, 46(3), 309–318.
Nilsson, B., & Nordstrom, C. H. (1977). Rate of cerebral energy consumption in concussive head injury in the rat. Journal of Neurosurgery, 47(2), 274–281.
Nilsson, P., Hillered, L., et al. (1993). Regional changes in interstitial K+ and Ca2+ levels following cortical compression contusion trauma in rats. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism: Official Journal of the International Society of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism, 13(2), 183–192.
Niogi, S. N., & Mukherjee, P. (2010). Diffusion tensor imaging of mild traumatic brain injury. The Journal of Head Trauma Rehabilitation, 25(4), 241–255.
Niogi, S. N., Mukherjee, P., et al. (2008). Structural dissociation of attentional control and memory in adults with and without mild traumatic brain injury. Brain, 131(Pt 12), 3209–3221.
Oppenheimer, D. R. (1968). Microscopic lesions in the brain following head injury. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 31(4), 299–306.
Ottens, A. K., Kobeissy, F. H., et al. (2006). Neuroproteomics in neurotrauma. Mass Spectrometry Reviews, 25(3), 380–408.
Pardini, J. E., Pardini, D. A., et al. (2010). Postconcussive symptoms are associated with compensatory cortical recruitment during a working memory task. Neurosurgery, 67(4), 1020–1027. discussion 1027–1028.
Parizel, P. M., Ozsarlak, et al. (1998). Imaging findings in diffuse axonal injury after closed head trauma. European Radiology, 8(6), 960–965.
Park, E., Bell, J. D., et al. (2009). An analysis of regional microvascular loss and recovery following two grades of fluid percussion trauma: a role for hypoxia-inducible factors in traumatic brain injury. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism, 29(3), 575–584.
Pasco, A., Ter Minassian, A., et al. (2006). Dynamics of cerebral edema and the apparent diffusion coefficient of water changes in patients with severe traumatic brain injury. A prospective MRI study. European Radiology, 16(7), 1501–1508.
Peerless, S. J., & Rewcastle, N. B. (1967). Shear injuries of the brain. Canadian Medical Association Journal, 96(10), 577–582.
Peskind, E. R., Petrie, E. C., et al. (2011). Cerebrocerebellar hypometabolism associated with repetitive blast exposure mild traumatic brain injury in 12 Iraq war Veterans with persistent post-concussive symptoms. NeuroImage, 54(Suppl 1), S76–S82.
Pettus, E. H., & Povlishock, J. T. (1996). Characterization of a distinct set of intra-axonal ultrastructural changes associated with traumatically induced alteration in axolemmal permeability. Brain Research, 722(1–2), 1–11.
Ponsford, J., Cameron, P., et al. (2011). Long-term outcomes after uncomplicated mild traumatic brain injury: a comparison with trauma controls. Journal of Neurotrauma, 28(6), 937–946.
Povlishock, J. T. (1993). Pathobiology of traumatically induced axonal injury in animals and man. Annals of Emergency Medicine, 22(6), 980–986.
Povlishock, J. T., & Pettus, E. H. (1996). Traumatically induced axonal damage: evidence for enduring changes in axolemmal permeability with associated cytoskeletal change. Acta Neurochirurgica. Supplement, 66, 81–86.
Povlishock, J. T., Becker, D. P., et al. (1983). Axonal change in minor head injury. Journal of Neuropathology and Experimental Neurology, 42(3), 225–242.
Prabhu, S. P. (2011). The role of neuroimaging in sport-related concussion. Clinics in Sports Medicine, 30(1), 103–114. ix.
Ramlackhansingh, A. F., Brooks, D. J., et al. (2011). Inflammation after trauma: microglial activation and traumatic brain injury. Annals of Neurology.
Rink, A., Fung, K. M., et al. (1995). Evidence of apoptotic cell death after experimental traumatic brain injury in the rat. The American Journal of Pathology, 147(6), 1575–1583.
Ropper, A. H., & Gorson, K. C. (2007). Clinical practice. Concussion. The New England Journal of Medicine, 356(2), 166–172.
Ruttan, L., Martin, K., et al. (2008). Long-term cognitive outcome in moderate to severe traumatic brain injury: a meta-analysis examining timed and untimed tests at 1 and 4.5 or more years after injury. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, 89(12 Suppl), S69–S76.
Saatman, K. E., Abai, B., et al. (2003). Traumatic axonal injury results in biphasic calpain activation and retrograde transport impairment in mice. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism: Official Journal of the International Society of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism, 23(1), 34–42.
Sabet, A. A., Christoforou, E., et al. (2008). Deformation of the human brain induced by mild angular head acceleration. Journal of Biomechanics, 41(2), 307–315.
Scheid, R., Preul, C., et al. (2003). Diffuse axonal injury associated with chronic traumatic brain injury: evidence from T2*-weighted gradient-echo imaging at 3T. AJNR. American Journal of Neuroradiology, 24(6), 1049–1056.
Scheid, R., Walther, K., et al. (2006). Cognitive sequelae of diffuse axonal injury. Archives of Neurology, 63(3), 418–424.
Sigmund, G. A., Tong, K. A., et al. (2007). Multimodality comparison of neuroimaging in pediatric traumatic brain injury. Pediatric Neurology, 36(4), 217–226.
Singleton, R. H., Zhu, J., et al. (2002). Traumatically induced axotomy adjacent to the soma does not result in acute neuronal death. The Journal of Neuroscience: The Official Journal of the Society for Neuroscience, 22(3), 791–802.
Slobounov, S. M., Zhang, K., et al. (2010). Functional abnormalities in normally appearing athletes following mild traumatic brain injury: a functional MRI study. Experimental Brain Research, 202(2), 341–354.
Slobounov, S. M., Gay, M., et al. (2011). Alteration of brain functional network at rest and in response to YMCA physical stress test in concussed athletes: RsFMRI study. NeuroImage, 55(4), 1716–1727.
Smits, M., Hunink, M. G., et al. (2008). Outcome after complicated minor head injury. AJNR. American Journal of Neuroradiology, 29(3), 506–513.
Smits, M., Dippel, D. W., et al. (2010). Minor head injury: CT-based strategies for management–a cost-effectiveness analysis. Radiology, 254(2), 532–540.
Smits, M., Houston, G. C., et al. (2010b). Microstructural brain injury in post-concussion syndrome after minor head injury. Neuroradiology.
Spain, A., Daumas, S., et al. (2010). Mild fluid percussion injury in mice produces evolving selective axonal pathology and cognitive deficits relevant to human brain injury. Journal of Neurotrauma, 27(8), 1429–1438.
Staal, J. A., Dickson, T. C., et al. (2010). Initial calcium release from intracellular stores followed by calcium dysregulation is linked to secondary axotomy following transient axonal stretch injury. Journal of Neurochemistry, 112(5), 1147–1155.
Stevens, R. D., Pustavoitau, A., et al. (2008). Brain imaging in intensive care medicine. Seminars in Neurology, 28(5), 631–644.
Strich, S. J. (1956). Diffuse degeneration of the cerebral white matter in severe dementia following head injury. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 19(3), 163–185.
Strong, A. J., & Dardis, R. (2005). Depolarisation phenomena in traumatic and ischaemic brain injury. Advances and Technical Standards in Neurosurgery, 30, 3–49.
Sulaiman, A. M., Denman, N., et al. (2011). Stereology and ultrastructure of chronic phase axonal and cell soma pathology in stretch-injured central nerve fibers. Journal of Neurotrauma, 28(3), 383–400.
Suskauer, S. J., & Huisman, T. A. (2009). Neuroimaging in pediatric traumatic brain injury: current and future predictors of functional outcome. Developmental Disabilities Research Reviews, 15(2), 117–123.
Talavage, T. M., Nauman, E., et al. (2010). Functionally-detected cognitive impairment in high school football players without clinically-diagnosed concussion. Journal of Neurotrauma. in press
Tang, L., Ge, Y., et al. (2011). Thalamic resting-state functional networks: disruption in patients with mild traumatic brain injury. Radiology.
Tang-Schomer, M. D., Patel, A. R., et al. (2010). Mechanical breaking of microtubules in axons during dynamic stretch injury underlies delayed elasticity, microtubule disassembly, and axon degeneration. The FASEB Journal, 24(5), 1401–1410.
Tavazzi, B., Signoretti, S., et al. (2005). Cerebral oxidative stress and depression of energy metabolism correlate with severity of diffuse brain injury in rats. Neurosurgery, 56(3), 582–589.
Tomei, G., Spagnoli, D., et al. (1990). Morphology and neurophysiology of focal axonal injury experimentally induced in the guinea pig optic nerve. Acta Neuropathologica, 80(5), 506–513.
Tong, K. A., Ashwal, S., et al. (2008). Susceptibility-weighted MR imaging: a review of clinical applications in children. AJNR. American Journal of Neuroradiology, 29(1), 9–17.
Topal, N. B., Hakyemez, B., et al. (2008). MR imaging in the detection of diffuse axonal injury with mild traumatic brain injury. Neurological Research, 30(9), 974–978.
Tournier, J. D., Mori, S., et al. (2011). Diffusion tensor imaging and beyond. Magnetic resonance in medicine : official journal of the Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine / Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.
Turner, G. R., & Levine, B. (2008). Augmented neural activity during executive control processing following diffuse axonal injury. Neurology, 71(11), 812–818.
Vagnozzi, R., Signoretti, S., et al. (2010). Assessment of metabolic brain damage and recovery following mild traumatic brain injury: a multicentre, proton magnetic resonance spectroscopic study in concussed patients. Brain, 133(11), 3232–3242.
Vajtr, D., Benada, O., et al. (2009). Correlation of ultrastructural changes of endothelial cells and astrocytes occurring during blood brain barrier damage after traumatic brain injury with biochemical markers of BBB leakage and inflammatory response. Physiological Research / Academia Scientiarum Bohemoslovaca, 58(2), 263–268.
van de Looij, Y., Mauconduit, F., et al. (2011). Diffusion tensor imaging of diffuse axonal injury in a rat brain trauma model. NMR in Biomedicine.
Viano, D. C., Hamberger, A., et al. (2009). Concussion in professional football: animal model of brain injury–part 15. Neurosurgery, 64(6), 1162–1173. discussion 1173.
Wager-Smith, K., & Markou, A. (2010). Depression: a repair response to stress-induced neuronal microdamage that can grade into a chronic neuroinflammatory condition? Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews.
Wang, J. Y., Bakhadirov, K., et al. (2008). Diffusion tensor tractography of traumatic diffuse axonal injury. Archives of Neurology, 65(5), 619–626.
Wang, J. A., Lin, W., et al. (2009). Membrane trauma and Na+ leak from Nav1.6 channels. American Journal of Physiology. Cell Physiology, 297(4), C823–C834.
Wang, J., Hamm, R. J., et al. (2011). Traumatic axonal injury in the optic nerve: evidence for axonal swelling, disconnection, dieback, and reorganization. Journal of Neurotrauma, 28(7), 1185–1198.
Warner, M. A., Youn, T. S., et al. (2010). Regionally selective atrophy after traumatic axonal injury. Archives of Neurology, 67(11), 1336–1344.
Weight, D. G. (1998). Minor head trauma. The Psychiatric Clinics of North America, 21(3), 609–624.
Werner, C., & Engelhard, K. (2007). Pathophysiology of traumatic brain injury. British Journal of Anaesthesia, 99(1), 4–9.
Westerhausen, R., Moosmann, M., et al. (2010). Identification of attention and cognitive control networks in a parametric auditory fMRI study. Neuropsychologia, 48(7), 2075–2081.
Whitney, N. P., Eidem, T. M., et al. (2009). Inflammation mediates varying effects in neurogenesis: relevance to the pathogenesis of brain injury and neurodegenerative disorders. Journal of Neurochemistry, 108(6), 1343–1359.
Wilde, E. A., Bigler, E. D., et al. (2006). Post-traumatic amnesia predicts long-term cerebral atrophy in traumatic brain injury. Brain Injury, 20(7), 695–699.
Wilde, E. A., Newsome, M. R., et al. (2011). Brain imaging correlates of verbal working memory in children following traumatic brain injury. International journal of psychophysiology, 82(1), 86–96.
Williams, D. H., Levin, H. S., et al. (1990). Mild head injury classification. Neurosurgery, 27(3), 422–428.
Wu, T. C., Wilde, E. A., et al. (2010). Longitudinal changes in the corpus callosum following pediatric traumatic brain injury. Developmental Neuroscience.
Xie, M., Tobin, J. E., et al. (2010). Rostrocaudal analysis of corpus callosum demyelination and axon damage across disease stages refines diffusion tensor imaging correlations with pathological features. Journal of Neuropathology and Experimental Neurology, 69(7), 704–716.
Yallampalli, R., Wilde, E. A., Bigler, E. D., McCauley, S. R., Hanten, G., Troyanskaya, M., Hunter, J. V., et al. (2011). Acute white matter differences in the fornix following mild traumatic brain injury using diffusion tensor imaging. Journal of Neuroimaging. doi:10.1111/j.1552-6569.2010.00537.x.
Yeo, R. A., Phillips, J. P., et al. (2006). Magnetic resonance spectroscopy detects brain injury and predicts cognitive functioning in children with brain injuries. Journal of Neurotrauma, 23(10), 1427–1435.
Yeo, R., Gasparovic, C., et al. (2010). A longitudinal proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy study of mild traumatic brain injury. Journal of Neurotrauma.
Yoshino, A., Hovda, D. A., et al. (1991). Dynamic changes in local cerebral glucose utilization following cerebral conclusion in rats: evidence of a hyper- and subsequent hypometabolic state. Brain Research, 561(1), 106–119.
Zhang, L., Yang, K. H., et al. (2001). Biomechanics of neurotrauma. Neurological Research, 23(2–3), 144–156.
Zhu, T., Hu, R., et al. (2011). Quantification of accuracy and precision of multi-center DTI measurements: a diffusion phantom and human brain study. NeuroImage, 56(3), 1398–1411.
Ziebell, J. M., & Morganti-Kossmann, M. C. (2010). Involvement of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines in the pathophysiology of traumatic brain injury. Neurotherapeutics, 7(1), 22–30.
Zohar, O., Rubovitch, V., et al. (2011). Behavioral consequences of minimal traumatic brain injury in mice. Acta Neurobiologiae Experimentalis, 71(1), 36–45.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bigler, E.D., Maxwell, W.L. Neuropathology of mild traumatic brain injury: relationship to neuroimaging findings. Brain Imaging and Behavior 6, 108–136 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-011-9145-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-011-9145-0