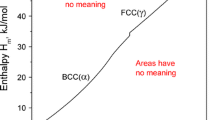
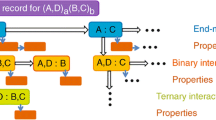
Abstract
The connection between CALPHAD models and Phase-Field models is discussed against the background of minimization of the total Gibbs energy of a system. Both methods are based on separation of a multiphase system into individual contributions of the bulk phases, which are described by appropriate models in composition, temperature, and pressure. While the CALPHAD method uses a global minimization of the total Gibbs energy, the Phase-Field method introduces local interactions, interfaces, and diffusion and allows for non-equilibrium situations. Thus, the Phase-Field method is much more general by its concept, however, it can profit a lot if realistic thermodynamic descriptions, as provided by the CALPHAD method, are incorporated. The present paper discusses details of a direct coupling between the Multiphase-Field method and the CALPHAD method. Examples are presented from solidification of technical Mg and Ni base alloys and some problems arising from common practice concerning thermodynamic descriptions in order-disorder systems.





Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
1In an atomistic picture \({\upeta _{\upalpha \upbeta}}\) will be different pairs of phases, however, when used in a Phase-Field calculation on a microscopic scale, this would only be justified for numerical stability reasons.
References
W. A. Oates, H. Wenzel, and T. Mohri, Putting More Physics into Calphad Solution Models, CalPhad-computer Coupling of Phase Diagrams and Thermochemistry, 1996, 20, p 37-45
B.P. Burton, N. Dupin, S.G. Fries, G. Grimvall, A.F. Guillermet, P. Miodownik, W.A. Oates, and V. Vinogred, Using ab initio calculations in the CALPHAD environment, Z. Mettallk (2007) 92:514-525
Elder K. R., Grant M., Modeling Elastic and Plastic Deformations in Nonequilibrium Processing using Phase-Field Crystals. Phys. Rev. E (2004) 70, 051605-1-051605-18
Goldenfeld N., Athreya B. P., Dantzig J. A., Renormalization Group Approach to Multiscale Simulation of Polycrystalline Materials using the Phase-Field Crystal Model. Phys. Rev. E (2005) 72:020601-1-020601-4
Tijssens M. G. A., James G. D, Towards an Improved Continuum Theory for Phase Transformations. Mat. Sci. Eng. A (2004) 378:453-458
G. Caginalp, P. Fife, Phase-Field Methods for Interfacial Boundaries. Phys. Rev. B (1986) 33:7792-7794
Wheeler A. A., Boettinger W. J., McFadden G. B., Phase-Field Model for Isothermal Phase Transitions in Binary Alloys. Phys. Rev. A (1992) 45 7424-7439
Kim S. G., Kim W. T., Suzuki T. Phase-field Model for Binary Alloys. Phys. Rev. E (1999) 60, 7186-7197
U. Grafe, B. Böttger, J. Tiaden, and S. G. Fries, Coupling of Multicomponent Thermodynamic Databases to a Phase-Field Model: Application to Solidification and Solid State Transformations of Superalloys, Scripta Mat., 2000, 42, p 1179-1186
Cha P. -R., Yeon D. -H., Yoon J. -K., A Phase-Field Model for Isothermal Solidification of Multicomponent Alloys. Acta Mat. (2001), 49, 3295-3307
Zhu J. Z., Liu Z. K., Vaithyanathan V., Chen L.Q, Linking Phase-Field Model to CALPHAD: Application to Precipitate Shape Evolution in Ni-base Alloys. Acta Mat. (2002), 46, 401-406
Kobayashi H., Ode M., Kim S. G., Kim W. T., Suzuki T., Phase-Field Model for Solidification of Ternary Alloys Coupled with Thermodynamic Database. Scripta Mat. (2003), 48, 689-694
Qin R. S., Wallach E. R., A Phase-Field Model Coupled with a Thermodynamic Database. Acta Mat., 51, (2003), 6199-6210
Li D. Y., Choudhury S., Liu Z. K., Chen L. -Q., Effect of External Mechanical Constraints on the Phase Diagram of Epitaxial PbZr1−xTixO3 Thin Films – Thermodynamic Calculations and Phase-Field Simulations. Appl. Phys. Lett. (2003) , 83, 1608-1610
Wu K., Chang Y. A., Wang Y., Simulating Interdiffusion Microstructures in Ni-Al-Cr Diffusion Couples: A Phase-Field Approach Coupled with Calphad Database. Scripta Mat. (2004), 50, 1145-1150
Eiken J., Böttger B., Steinbach I., Multi Phase-Field Approach for Alloy Solidification. Rev. E (2006), 73, 066122-1-066122-9
Steinbach I., Pezzolla F., Nestler B., Seeelberg M., Prieler R., Schmitz G. J., Rezende J. L. L, A Phase-Field Concept for Multiphase Systems. Physica D (1996), 94, 135-147
Tiaden J., Nestler B., Diepers H. J, Steinbach I. The Multiphase-Field Model with an Integrated Concept for Modeling Solute Diffusion. Physica D (1998), 115, 73-86
Steinbach I., Pezzolla F., A Generalized Field Method for Multiphase Transformations using Interface Fields. Physica D (1999), 134, 385-393
Perepezko J. H., Wilde G., Alloy Metastability During Nucleation-Controlled Reactions. Ber. Bunsenges. Phys. Chem. (1998), 102, 1074-1082
Fries S. G., Sundman B., Development of Multicomponent Thermodynamic Databases for Use in Process Modelling and Simulations. J. Phys. Chem. Sol. 66, (2005) 226-230
Schmid-Fetzer R., Janz A., Gröbner J., Ohno M., Aspects of Quality Assurance in a Thermodynamic Mg Alloy Database. Anv. Eng. Mater. (2005), 7, 1142-1149
C. E. Campbel, W. J. Boettinger, and U. R. Kattner, Development of Diffusion Mobility Database for Ni-Base Super alloys, Acta Mat., (2002) 50:775-792
Warnken N., Ma D., Mathes M., Steinbach I., Investigation of Eutectic Island Formation in SX Superalloys. Mat. Sci. Eng. A (2005), 413-414, 267-271
Ohno M., Schmid-Fetzer R., Thermodynamic Assessment of Mg-Al-Mn Phase Equilibria, Focusing on Mg-rich Alloys. Z. Metallk. (2005) , 96, 857-869
Böttger B., Eiken J., Ohno M., Klaus G., Fehlbier M., Schmid-Fetzer R., Steinbach I., Bührig-Polazcek A., Controlling Microstructure in Magnesium Alloys: A Combined Thermodynamic, Experimental and Simulation Approach. Adv. Eng. Mat. (2006), 8(4), 241-247
G. Klaus and A. Bührig-Polazcek, Unpublished research at Foundry Institute Aachen, 2005
Acknowledgments
We like to thank Dr. N. Dupin for providing information for the Ni database and the German research foundation (DFG) for financial support under the integrated project SPP1168 and the collaborative research center SFB370.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Steinbach, I., Böttger, B., Eiken, J. et al. CALPHAD and Phase-Field Modeling: A Successful Liaison. J Phs Eqil and Diff 28, 101–106 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11669-006-9009-2
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11669-006-9009-2