Abstract
In this study, friction stir processing (FSP) was applied to the GTAW (TIG)-welded AZ91C cast alloy to refine the microstructure and optimize the mechanical properties of the weld zone. Microstructural investigation of the samples was performed by optical microscopy and the phases in the microstructure were determined by x-ray diffraction (XRD). The microstructural evaluations showed that FSP destroys the coarse dendritic microstructure. Furthermore, it dissolves the secondary hard and brittle β-Mg17Al12 phase existing at grain boundaries of the TIG weld zone. The closure and decrease in amount of porosities along with the elimination of the cracks in the microstructure were observed. These changes were followed by a significant grain refinement to an average value of 11 µm. The results showed that the hardness values increased to the mean ones, respectively, for as-cast (63 Hv), TIG weld zone (67 Hv), and stir zone (79 Hv). The yield and ultimate strength were significantly enhanced after FSP. The fractography evaluations, by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), indicated to a transition from brittle to ductile fracture surface after applying FSP to the TIG weld zone.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Sameer Kumar, C. Tara Sasanka, K. Ravindra, and K.N.S. Suman, Magnesium and Its Alloys in Automotive Applications: A Review, Am. J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2015, 4, p 12–30
J. Wegrzyn, M. Mazur, A. Szymanski, and B. Balcerowska, Development of a Filler for Welding Magnesium Alloy GA8, Weld. Int., 1987, 2, p 146–150
Z.J. Lu, W.J. Evans, J.D. Parker, and S. Birley, Simulation of Microstructure and Liquation Cracking in 7017 Aluminium Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1996, 220, p 1–7
J. Sheng, G.Q. You, S.Y. Long, and F.S. Pan, Abnormal Macropore Formation During Double-Sided Gas Tungsten Arc Welding Of Magnesium AZ91D Alloy, Mater. Charact., 2008, 59, p 1059–1065
A. Razal Rose, K. Manisekar, V. Balasubramanian, and S. Rajakumar, Prediction and Optimization of Pulsed Current Tungsten Inert Gas Welding Parameters to Attain Maximum Tensile Strength in AZ61A Magnesium Alloy, Mater. Des., 2012, 37, p 334–348
G. Padmanaban and V. Balasubramania, Optimization of Pulsed Current Gas Tungsten Arc Welding Process Parameters to Attain Maximum Tensile Strength in AZ31B Magnesium Alloy, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China, 2011, 21, p 467–476
C. Xu, G. Sheng, H. Wang, and X. Yuan, Reinforcement of Mg/Ti Joints Using Ultrasonic Assisted Tungsten Inert Gas Welding–Brazing Technology, Sci. Technol. Weld. Join., 2014, 19, p 703–707
M. Marya and G.R. Edwards, Chloride Contributions in Flux Assisted GTA Welding of Magnesium Alloys, Weld. J., 2002, 81, p 292-s–298-s
W. Zhou, T.Z. Long, and C.K. Mark, Hot Cracking in Tungsten Inert Gas Welding of Magnesium Alloy AZ91D, Mater. Sci. Technol., 2007, 23, p 1294–1299
W. Tiejun and L. Zhiwen, A Continuum Damage Model for Weld Heat Affected Zone Under Low Cycle Fatigue Loading, Eng. Fract. Mech., 1990, 37, p 825–829
F.Y. Zheng, Y.J. Wu, L.M. Peng, X.W. Li, P.H. Fu, and W.J. Ding, Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of Friction Stir Processed Mg-2.0Nd-0.3Zn-1.0Zr Magnesium Alloy, J. Magnes. Alloys, 2013, 1, p 122–127
E. Cerri and P. Leo, Effect of Friction Stir Processing on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of a HPDC Magnesium Alloy, Mater. Sci. Forum, 2014, 783–786, p 1735–1740
F. Chai, D.T. Zhang, and Y.Y. Li, Effect of rotation speeds on microstructures and tensile properties of submerged friction stir processed AZ31 magnesium alloy, Mater. Res. Innov., 2014, 18, p S4-152–S4-156
American Welding Society, Welding Handbook, 7th ed., vol. 4, AWS, Miami, FL, 1989
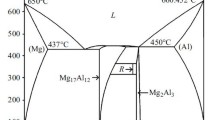
A.K. Dahle, Y.C. Lee, M.D. Nave, P.L. Schaffer, and D.H. St John, Development of the As-Cast Microstructure in Magnesium-Aluminium Alloys, J. Light Met., 2001, 1, p 61–72
D.X. Sun, D.Q. Sun, X.Y. Gu, and Z.Z. Xuan, Hot Cracking of Metal Inert Gas Arc Welded Magnesium Alloy AZ91D, ISIJ Int., 2009, 49, p 270–274
I.J. Polmear, Light Alloys: Metallurgy of the Light Metals, 2nd ed., Chapman and Hall, London, 1989, ISBN 0-340-49175-2
ASM Handbook Committee, Alloy Phase Diagrams, ASM International, Materials Park, OH, 1992
Sindo Kou and Welding Metallurgy, 2, Wiley, New York, 1987
Q. Han, E.A. Kenik, S.R. Agnew, and S. Viswanathan, Solidification Behavior of Commercial Magnesium Alloys, Magnesium Technology 2001, J.N. Hryn, Ed., The Minerals, Metals and Materials Society (TMS), Warrendale, PA, 2001.
G.C. Sih, Multiscale Fatigue Crack Initiation and Propagation of Engineering Materials, Structural Integrity and Microstructural Worthiness: Solid Mathematics and Its Applications, vol. 152, Springer, New York, 2008.
M.D. Nave, A.K. Dahle, and D.H. St. John, Magnesium Technology 2000, H.I. Kaplan, J.N. Hryn, and B.B. Clow, Ed., The Minerals, Metals and Materials Society (TMS), Warrendale, PA, 2000
J.D.I. Shearouse and B.A. Mikucki, The Origin of Microporosity in Magnesium Alloy AZ91, SAE Trans. J. Mater. Manuf., 1994, 103, p 542–552
M. Hilpert and L. Wagner, Surface Treatment IV, C.A. Brebbiaand and J.M. Kenny, Ed., WIT Press, 1999, p 331
W.C. Zheng, S. Li, B. Tang, and D.B. Zeng, Microstructure and Properties of Mg-Al Binary Alloys, China Foundry, 2006, 3, p 270–274
M.M. Avedesian, Magnesium and Magnesium Alloys, ASM International, Materials Park, OH, 1999
Alaknanda, R.S. Anand, and P. Kumar, Flaw Detection in Radiographic Weld Images Using Morphological Approach, NDT & E Int. 39, p 29–33
V. Jain, R.S. Mishra, and A.K. Gupta, Gouthama, Study of β-Precipitates and Their Effect on the Directional Yield Asymmetry of Friction Stir Processed and Aged AZ91C Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2013, 560, p 500–509
A.H. Feng, B.L. Xiao, Z.Y. Ma, and R.S. Chen, Effect of Friction Stir Processing Procedures on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Mg-Al-Zn Casting, Effect of Friction Stir Processing Procedures on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Mg-Al-Zn Casting, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2009, 40, p 2447–2456
N. Afrin, D.L. Chen, X. Cao, and M. Jahazi, Strain Hardening Behavior of a Friction Stir Welded Magnesium Alloy, Scr. Mater., 2007, 57, p 1004–1007
ASM Speciality Handbook, Magnesium and Magnesium Alloys, ASM International, Materials Park, OH, 1999, p 1–314
W. Wen, W. Kuaishe, G. Qiang, and W. Nan, Effect of Friction Stir Processing on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Cast AZ31 Magnesium Alloy, Rare Met. Mater. Eng., 2012, 41, p 1522–1526
X.B. Liu, R.S. Chen, and E.H. Han, Effects of Ageing Treatment on Microstructures and Properties of Mg-Gd-Y-Zr Alloys With and Without Zn Additions, J. Alloys Compd., 2008, 465, p 232–238
W. Blum, P. Zhang, B. Watzinger, B.V. Grossmann, and H.G. Haldenwanger, Comparative Study of Creep of the Die-Cast Mg-Alloys AZ91, AS21, AS41, AM60 and AE42, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2001, 319–321, p 735–740
A. Fallahi, A. Ataee, and F. Biglari, Effects of Crystal Orientation on Stress Distribution Near the Triple Junction in a Tricrystal γ-TiAl, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2010, 527, p 4576–4581
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hassani, B., Karimzadeh, F., Enayati, M.H. et al. Effect of Friction Stir Processing on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of AZ91C Magnesium Cast Alloy Weld Zone. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 25, 2776–2785 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-016-2129-x
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-016-2129-x