Abstract
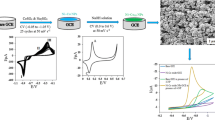
This study describes, the synthesis of cobalt oxide nanostructures using ascorbic acid as a growth directing agent by the hydrothermal method. Ascorbic acid is used for the first time for the synthesis of cobalt oxide nanostructures and a unique morphology is prepared in the present study. The cobalt oxide nanostructures were characterized by scanning electron microcopy, x-ray diffraction, and x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy techniques. These analytical techniques demonstrated well defined morphology, good crystalline quality, and high purity of as prepared cobalt oxide nanostructures. The glassy carbon electrode was modified with cobalt oxide nanostructures for the development of a sensitive and selective electrochemical hydrazine sensor. The developed hydrazine sensor exhibits a linear range of 2–24 μM. The sensitivity and limit of detection of presented hydrazine sensors are 12,734 μA/mM/cm2 and 0.1 μM respectively. The developed hydrazine sensor is highly selective, stable, and reproducible. The proposed sensor is successfully applied for the detection of hydrazine from different water samples. The present study provides the development of an alternative tool for the reliable monitoring of hydrazine from environmental and biological samples.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Umar, S.K. Kansal, and S.K. Mehta, Sens. Actuators B Chem. 188, 372 (2013).
M. Mazloum-Ardakani, A. Khoshroo, and L. Hosseinzadeh, Sens. Actuators B Chem. 214, 132 (2015).
Y. He, J. Zheng, and S. Dong, Analyst 137, 4841 (2012).
B. Haghighi, H. Hamidi, and S. Bozorgzadeh, Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 398, 1411 (2010).
Q. Sheng, Y. He, and J. Zheng, Microchim. Acta 177, 479 (2012).
S. Kocak and B. Aslışen, Sens. Actuators B Chem. 196, 610 (2014).
H.J. Zhang, J.S. Huang, H.Q. Hou, and T.Y. You, Electroanalysis 21, 1869 (2009).
L. Zheng and J.F. Song, Talanta 79, 319 (2009).
A. Salimi, L. Miranzadeh, and R. Hallaj, Talanta 75, 147 (2008).
G.Z. Hu, Z.P. Zhou, Y. Guo, H.Q. Hou, and S.J. Shao, Electrochem. Commun. 12, 422 (2010).
Q.F. Yi and W.Q. Yu, J. Electroanal. Chem. 633, 159 (2009).
J.B. Zheng, Q.L. Sheng, L. Li, and Y. Shen, J. Electroanal. Chem. 611, 155 (2007).
K.I. Ozoemena and T. Nyokong, Talanta 67, 162 (2005).
A.S. Adekunle and K.I. Ozoemena, J. Electroanal. Chem. 645, 41–49 (2010).
P.R. Solanki, A. Kaushik, V.V. Agrawal, and B.D. Malhotra, NPG Asia Mater. 3, 17 (2011).
X. Wang, X.Y. Chen, L.S. Gao, H.G. Zheng, Z. Zhang, and Y.T. Qian, J. Phys. Chem. B 108, 16401 (2004).
J. Feng and H.C. Zeng, Chem. Mater. 15, 2829 (2003).
G.K. Kouassi, J. Irudayaraj, and G. McCarty, J. Nanobiotechnol. 3, 1 (2005).
S.P. Singh, S.K. Arya, P. Pandey, B.D. Malhotra, S. Saha, K. Sreenivas, and V. Gupta, Appl. Phys. Lett. 91, 063901 (2007).
A. Salimi, R. Hallaj, and S. Soltanian, Electroanalysis 21, 2693 (2009).
A.A. Ansari, A. Kaushik, P.R. Solanki, and B.D. Malhotra, Electroanalysis 21, 965 (2009).
A. Kumar, R. Malhotra, B.D. Malhotra, and S.K. Grover, Anal. Chim. Acta 414, 43 (2000).
Z.H. Ibupoto, K. Khun, X. Liu, and M. Willander, Mater. Sci. Eng. C 33, 3889 (2013).
A. Earnshaw and N. Greenwood, Chemistry of the Elements, 2nd ed. (Butterworth Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 1997).
Y. Yu, C.H. Chen, J.L. Shui, and S. Xie, Chem. Int. Ed. 44, 7085 (2005).
Y.G. Li, B. Tan, and Y.Y. Wu, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 128, 14258 (2006).
T. Maruyama and S. Arai, J. Electrochem. Soc. 143, 1383 (1996).
L. Yan, X.M. Zhang, T. Ren, H.P. Zhang, X.L. Wang, and J.S. Suo, Chem. Commun. 8, 860 (2002).
J. Wollenstein, M. Burgmair, G. Plescher, T. Sulima, J. Hildenbrand, and H. Bottner, Sens. Actuators B Chem. 93, 442 (2003).
X. Yao, X. Xin, Y. Zhang, J. Wang, Z. Liu, and X. Xu, J. Alloys Compd. 521, 95 (2012).
T. He, D.R. Chen, X.L. Jiao, and Y.L. Wang, Adv. Mater. 18, 1078 (2006).
G. Feng, L. Chunzhong, H. Yanjie, and Z. Ling, J. Cryst. Growth 304, 369 (2007).
P. Dutta, M.S. Seehra, S. Thota, and J. Kumar, J. Phys. Condens. Matter 20, 015218 (2008).
W.-M. Zhang, M. Chen, and Y.-Q. Jiang, Int. Nano Lett. 3, 1 (2013).
G. Wang, X. Shen, J. Horvat, B. Wang, H. Liu, D. Wexler, and J. Yao, J. Phys. Chem. C 113, 4357 (2009).
A. Umar, M.M. Rahman, and Y.B. Hahn, J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 9, 4686 (2009).
Y. Ni, J. Zhu, L. Zhang, and J. Hong, CrystEngComm 12, 2213 (2010).
J. Liu, Y. Li, J. Jiang, and X. Huang, Dalton Trans. 39, 8693 (2010).
A. Umar, M.M. Rahman, S.H. Kim, Y.B. Hahn, Chem. Commun. 2, 166 (2008).
B. Fang, C.H. Zhang, W. Zhang, and G.F. Wang, Electrochim. Acta 55, 178 (2009).
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge and cordially thank the financial assistance provided by Scientific Research Institute at King Saud University for funding through their Research Group Project No. RGP-VPP-236.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tahira, A., Nafady, A., Baloach, Q. et al. Ascorbic Acid Assisted Synthesis of Cobalt Oxide Nanostructures, Their Electrochemical Sensing Application for the Sensitive Determination of Hydrazine. J. Electron. Mater. 45, 3695–3701 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-016-4547-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-016-4547-9