Abstract
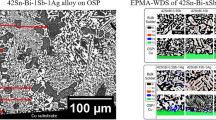
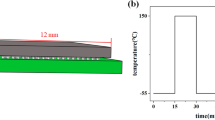
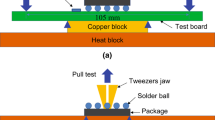
Pb-free solder alloys based on the Sn-Ag-Cu (SAC) ternary eutectic have promise for widespread adoption across assembly conditions and operating environments, but enhanced microstructural control is needed. Micro-alloying with elements such as Zn was demonstrated for promoting a preferred solidification path and joint microstructure earlier in simple (Cu/Cu) solder joints studies for different cooling rates. This beneficial behavior now has been verified in reworked ball grid array (BGA) joints, using dissimilar SAC305 (Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu, wt.%) solder paste. After industrial assembly, BGA components joined with Sn-3.5Ag-0.74Cu-0.21Zn solder were tested in thermal cycling (−55°C/+125°C) along with baseline SAC305 BGA joints beyond 3000 cycles with continuous failure monitoring. Weibull analysis of the results demonstrated that BGA components joined with SAC + Zn/SAC305 have less joint integrity than SAC305 joints, but their lifetime is sufficient for severe applications in consumer, defense, and avionics electronic product field environments. Failure analysis of the BGA joints revealed that cracking did not deviate from the typical top area (BGA component side) of each joint, in spite of different Ag3Sn blade content. Thus, SAC + Zn solder has not shown any advantage over SAC305 solder in these thermal cycling trials, but other characteristics of SAC + Zn solder may make it more attractive for use across the full range of harsh conditions of avionics or defense applications.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K.N. Tu, A.M. Gusak, and M. Li, J. Appl. Phys. 93, 1335 (2003).
S.K. Kang, P.A. Lauro, D.-Y. Shih, D.W. Henderson, and K.J. Puttlitz, IBM J. Res. Dev. 49, 607 (2005).
C. Andersson, Z. Lai, J. Liu, H. Jiang, and Y. Yu, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 394, 20 (2005).
I.E. Anderson, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 18, 55 (2007).
K.-W. Moon, W.J. Boettinger, U.R. Kattner, F.S. Biancaniello, and C.A. Handwerker, J. Electron. Mater. 29, 1122 (2000).
D. Swenson, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 18, 39 (2007).
I.E. Anderson, J.W. Walleser, J.L. Harringa, F. Laabs, and A. Kracher, J. Electron. Mater. 38, 2770 (2009).
I.E. Anderson, J.K. Walleser, and J.L. Harringa, JOM 59, 38 (2007).
W. Liu and N.-C. Lee, JOM 59, 26 (2007).
W. Liu, P. Bachorik, and N-C. Lee, in Proceedings of 58th Electronic Components and Technology Conference (2008), p. 627.
D.D. Hillman and R. Wilcoxon, in SMTAI Conference Proceedings (2006).
Materials Preparation Center, Ames Laboratory, US DOE Basic Energy Sciences, Ames, IA, USA. Available from: www.mpc.ameslab.gov.
A.U. Telang and T.R. Bieler, JOM 57, 44 (2005).
I.E. Anderson and J.L. Harringa, J. Electron. Mater. 35, 1 (2006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anderson, I.E., Boesenberg, A., Harringa, J. et al. Comparison of Extensive Thermal Cycling Effects on Microstructure Development in Micro-alloyed Sn-Ag-Cu Solder Joints. J. Electron. Mater. 41, 390–397 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-011-1763-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-011-1763-1