Abstract
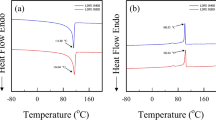
Viscosity is one of the most important properties of mold flux and affects the process of continuous casting significantly. In order to describe the variation of viscosity of mold flux accurately in a wide range of temperature occurring in the casting mold, a non-Arrhenius Vogel–Fulcher–Tammann (VFT) model was adopted in this study. The results showed that the adjusted coefficient of determination (Adj. R 2) of non-Arrhenius VFT Model ranges from 0.92 to 0.96, which suggests this model could be well adapted to predict the relationship between viscosity and temperature of mold flux. The temperature at which viscosity becomes infinite, T VFT, increased with the addition of Cr2O3 and improvement of basicity, while it decreased with the addition of B2O3, as it was determined by both the degree of polymerization of the melt structure and crystallization behavior of the melt. Also, the pseudo-activation energy, E VFT, of Samples 1 to 5 was 60.1 ± 3.6, 94.7 ± 14.9, 101.7 ± 19.0, 38.0 ± 4.8, and 32.4 ± 4.0 kJ/mol, respectively; it increased with the addition of Cr2O3 and B2O3, but deceased with the increase of basicity.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Kajitani, Y. Kato, K. Harada, K. Saito, K. Harashima, and W. Yamada: ISIJ Int., 2008, vol. 48, pp.1215-1224.
E. Takeuchi and J.K. Brimacombe: Metall. Trans. B, 1984, vol. 15, pp.493-509.
Y. Chung, A. W. Cramb: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2000, vol. 31, pp.957-71.
B. Thomas and J. Sengupta: JOM, 2006, vol. 58, pp. 16–18.
H. Harmuth and G. Xia: ISIJ Int., 2015, vol. 55, pp. 775-80.
A. Kondratiev, E. Jak, and P. C. Hayes: JOM, 2002, vol. 54, pp.41-45.
L. Zhou, W. Wang, and K. Zhou: ISIJ Int., 2015, vol. 55, pp. 1961-1924.
G. Kim and IL Sohn: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2013, vol. 45, pp. 86-95.
X. Qi, G. Wen, P. Tang: J. Iron Steel Res. Int., 2010, vol. 17, pp. 6-10.
Z. Zhang, G. Wen, P. Tang, and S. Sridhar: ISIJ Int., 2008, vol. 48, pp.739-46.
E. Benavidez, L. Santini, M. Valentini, and E. Brandaleze: 11th International Congress on Metallurgy & Materials SAM/CONAMET 2011, 2012, vol. 1, pp. 389–96.
T. Iida, H. Sakai, Y. Kita, and K. Shigeno: ISIJ Int., 2000, vol. 40, pp.S110-S114.
K.C. Mills and S. Sridhar: Ironmak Steelmak., 1999, vol. 26, pp.262-268.
H.S. Ray and S. Pal: Ironmak Steelmak., 2004, vol. 31, pp.125-130.
D. H. Vogel: Physikalische Zeitschrift, 1921, vol. 22, pp.645-646.
G. S. Fulcher: J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 1925, vol. 8, pp. 339-355.
G. Tammann and W. Hesse: Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem, 1926, vol. 156, pp.245-257.
D. Giordano and D. B. Dingwell: Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 2003, vol. 208, pp.337-349.
D. Giordano, J. K. Russell, and D. B. Dingwell: Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 2008, vol. 271, pp.123-134.
C. A. Angell: J. Phys. Chem. Solids, 1988, vol. 49, pp.863-871.
H. Lu and W. Huang: Smart Mater. Struct. 2013, vol. 22, pp.1-8.
B. Mokhtarani, A. Sharifi, H. R. Mortaheb, M. Mirzaei, M. Mafi, and F. Sadeghian: J. Chem. Thermodyn., 2009, vol. 41, pp.323-329.
L. Zhou, W. Wang, B. Lu, and G. Wen: Met. Mater. Int., 2015, vol.21, pp.126-133.
L. Zhou, W. Wang, F. Ma, J. Li, J. Wei, H. Matsuur, and F. Tsukihashi.: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2012, vol. 43, pp.354-362.
H. Tweer, J. H. Simmons, and P. B. Macedo: J. Chem. Phys., 1971, vol. 54, pp.1952-1959.
L. Zhou and W. Wang: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2016, vol. 47, pp.1548-1552.
C. Xu, W. Wang, L. Zhou, S. Xie, and C. Zhang: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2015, vol. 46, pp.882-892.
V. De. Eisenhüttenleute: Slag Atlas, 2th Edition, Verlag Stahleisen GmbH, Dusseldorf ,1995, pp. 119.
L. Zhou, W. Wang, J. Wei, K. Zhou: ISIJ Int., 2015, vol. 55, pp. 821-829.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Science Foundation of China (51504294, 51322405), and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2016T90760) is also great acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted May 23, 2016.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, L., Wang, W. Study of the Viscosity of Mold Flux Based on the Vogel–Fulcher–Tammann (VFT) Model. Metall Mater Trans B 48, 220–226 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-016-0835-2
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-016-0835-2