Abstract
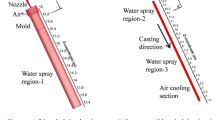
During the centrifugal continuous casting process, unreasonable casting parameters can cause violent level fluctuation, serious gas entrainment, and formation of frozen shell pieces at the meniscus. Thus, in the current study, a three-dimensional multiphase turbulent model was established to study the transport phenomena during centrifugal continuous casting process. The effects of nozzle position, casting and rotational speed on the flow pattern, centrifugal force acting on the molten steel, level fluctuation, gas entrainment, shear stress on mold wall, and motion of inclusions during centrifugal continuous casting process were investigated. Volume of Fluid model was used to simulate the molten steel-air two-phase. The level fluctuation and the gas entrainment during casting were calculated by user-developed subroutines. The trajectory of inclusions in the rotating system was calculated using the Lagrangian approach. The results show that during centrifugal continuous casting, a large amount of gas was entrained into the molten steel, and broken into bubbles of various sizes. The greater the distance to the mold wall, the smaller the centrifugal force. Rotation speed had the most important influence on the centrifugal force distribution at the side region. Angular moving angle of the nozzle with 8° and keeping the rotation speed with 60 revolutions per minute can somehow stabilize the level fluctuation. The increase of angular angle of nozzle from 8 to 18 deg and rotation speed from 40 to 80 revolutions per minute favored to decrease the total volume of entrained bubbles, while the increase of distance of nozzle moving left and casting speed had reverse effects. The trajectories of inclusions in the mold were irregular, and then rotated along the strand length. After penetrating a certain distance, the inclusions gradually moved to the center of billet and gathered there. More work, such as the heat transfer, the solidification, and the inclusions entrapment during centrifugal continuous casting, will be performed.





























Similar content being viewed by others
References
[1] B.D. Khakhalin, A.N. Smolyakov: Metallurgist, 1957, vol. 1, pp. 176-178.
[2] L.S. Konstantinov, B.D. Khokhalin, A.N. Smoliakov: Metallurgist, 1958, vol. 2, pp. 495-497.
[3] I.O. Tsypin, N.S. Pavlenko, V.A. Rusalkin: Met. Sci. Heat Treat, 1968, vol. 10, pp. 745-746.
[4] G. Martinez, M. Garnier, F. Durand: Appl. Sci. Res, 1987, vol. 44, pp. 225-239.
C.B. Stravs, J.N. Jager: Apparatus for forming pipe or other articles in continuous lengths, the United States, 1904, p. 777561.
G.R. Leghorn: Continuous centrifugal casting of tube using liquid mold, the United States, 1971, p. 3616842.
W.H. Milispaugh: Centrifugal casting method, the United States, 1931, p. 1828335.
[8] J. Anagnostopoulos, G. Bergeles: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1999, vol. 30B, p. 1095-1105.
[9] A. Theodorakakos, G. Bergeles: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1998, vol. 29B, p. 1321-1327.
J. Aoki, B.G. Thomas, J. Peter, K. D. Peaslee: Proc. AISTech 2004 Conf., 2004, pp. 1045–56.
[11] L. Zhang: Modell. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng, 2000, vol. 8: pp. 463.
[12] Y. Xie, S. Orsten, F. Oeters: ISIJ Int., 1992, vol. 32, pp. 66-75.
[13] J.E. Lait, J.K. Brimacombe, F.Weinberg: Ironmaking Steelmaking, 1974, vol. 1, pp. 90-97.
[14] C.W. Hirt, B.D. Nichols: J. Comput. Phys., 1981, vol. 39, pp. 201-225.
[15] B.G. Thomas, X. Huang, R.C. Sussman: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1994, vol. 25B, pp. 527-547.
[16] Y. Ho, W. Hwang: ISIJ Int., 1996, vol. 36, pp. 1030-1035.
[17] G.A. Panaras, A. Theodorakakos, G. Bergeles: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1998, vol. 29B, pp. 1117-1126.
[18] L. Tan, H. Shen, B. Liu, X. Liu, R. Xu, Y. Li: Acta Metall. Sin., 2003, vol. 39, pp. 435-438.
[19] L. Zhang, Y. Wang, X. Zuo: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2008, vol. 39B, pp. 534-550.
[20] R. Chaudhary, G. Lee, B.G. Thomas, S. Kim: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2008, vol. 39B, pp. 870-884.
[21] Y. Wang, L. Zhang: ISIJ Int., 2010, vol. 50, pp. 1777-1782.
[22] Y. Wang, L. Zhang: ISIJ Int., 2010, vol. 50, pp. 1783-1791.
[23] I.C. Ramos, J.J. Barreto, S.G. Hernandez: ISIJ Int., 2013, vol. 53, pp. 802-808.
[24] B.G. Thomas, L. Zhang: ISIJ Int., 2001, vol. 41, pp. 1181-1193.
[25] R. Mirandal, M.A. Barron, J. Barreto, L. Hoyos, J. Gonzalez: ISIJ Int., 2005, vol. 45, pp. 1626-1635.
[26] Y. Wang, L. Zhang: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2011, vol. 42B, pp. 1319-1351.
R. Liu, B.G. Thomas, B. Forman, H. Yin: Proc. AISTech 2012 Conf., 2012, pp. 1317–27.
[28] H.A. Gutierrez, G.B. Cardiel, J.J. Barreto, S.G. Hernandez: ISIJ Int., 2014, vol. 54, pp. 1304-1313.
[29] L. Zhang, B.G. Thomas: ISIJ Int., 2003, vol. 43, pp. 271-291.
[30] S. Asai, J. Szekely: Ironmaking Steelmaking, 1975, vol. 2, pp. 205-213.
[31] Q. Yuan, B.G. Thomas, S.P. Vanka: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2004, vol. 35B, pp. 703-714.
[32] D. Mazumdar, R.I.L. Guthrie: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1994, vol. 25B, pp. 308-312.
[33] A. Alexiadis, P. Gardin, J.F. Domgin: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2004, vol. 35B, pp. 949-956.
[34] Q. Wang, L. Zhang, S. Sridhar, W. Yang, Y. Wang, S. Yang: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2016, vol. 47B, pp. 1594-1612.
[34] Q. Wang, L. Zhang: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2016, vol. 47B, pp. 1933-1949.
R. Liu, B.G. Thomas, L. Kalra, T. Bhattacharya, A. Dasgupta: Proc. AISTech 2013 Conf., 2013, pp. 1351–64.
[37] B.E. Launder, D.B. Spalding: Comput. Method Appl. M., 1974, vol. 3, pp. 269-289.
[38] B.G. Thomas, Q. Yuan, S. Sivaramakrishnan, T. Shi, S.P. Vanka, M.B. Assar: ISIJ Int., 2001, vol. 41, pp. 1262-1271.
[39] B.E. Launder, D.B. Spalding: Mathematical Models of Turbulence. New York: Academic Press, 1972.
[40] Y. Ho, C. Chen, W. Hwang: ISIJ Int., 1994, vol. 34, pp. 255-264.
[41] X. Song, S. Cheng, Z. Cheng: ISIJ Int., 2012, vol. 52, pp. 1824-1831.
[42] E. Loth: Progress in Energy and Combustion Science, 2000, vol. 26, pp. 161-223.
[43] L. Zhang: Steel Res. Int., 2006, vol. 77, pp. 158-169.
[44] C. Pfeiler, M. Wu, A. Ludwig: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2005, vol. 413-414, pp. 115-120.
[45] J.U. Brackbill, D.B. Kothe, C. Zemach: J. Comput. Phys., 1992, vol. 100, pp. 335-354.
[46] P. Liovic, J. Liow, M. Rudman: ISIJ Int., 2001, vol. 41, pp. 225-233.
ANSYS FLUENT 14.0. Canonsburg, PA: ANSYS, Inc, 2011.
[48] Y. Miki, B.G. Thomas: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1999, vol. 30B, pp. 639-654.
[49] P.G. Mukunda, S.R. A, S.S. Rao: Met. Mater. Int., 2010, vol. 16, pp. 137-143.
[50] J. Bohacekn, A. Kharicha, A. Ludwig, M. Wu: ISIJ Int., 2014, vol. 54, pp. 266-274.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for support from the National Science Foundation China (Grant No. 51274034, Grant No. 51404019, Grant No. 51504020), Beijing Key Laboratory of Green Recycling and Extraction of Metals (GREM), the Laboratory of Green Process Metallurgy and Modeling (GPM2) and the High Quality Steel Consortium (HQSC) at the School of Metallurgical and Ecological Engineering at University of Science and Technology Beijing (USTB), China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted December 2, 2015.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Q., Zhang, L. & Sridhar, S. Modeling on Fluid Flow and Inclusion Motion in Centrifugal Continuous Casting Strands. Metall Mater Trans B 47, 2623–2642 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-016-0701-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-016-0701-2