Abstract
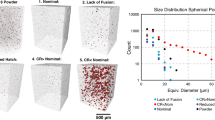
Additive manufacturing (AM) brings disruptive changes to the ways parts, and products are designed, fabricated, tested, qualified, inspected, marketed, and sold. These changes introduce novel technical challenges and concerns arising from the maturity and diversity of today’s AM processes, feedstock materials, and process parameter interactions. AM bears a resemblance with laser and electron beam welding in the so-called conduction mode, which involves a multitude of dynamic physical events between the projected feedstock and a moving heat source that eventually influence AM part properties. For this paper, an air vent was selected for its thin-walled, hollow, and variable cross section, and limited size. The studied air vents, randomly selected from a qualification batch, were fabricated out of 316L stainless steel using a 4 kW fiber laser powder-fed AM system, referred to as construction laser additive direct (CLAD). These were systematically characterized by microhardness indentation, visual examination, optical and scanning electron microscopy, and electron-back-scattering diffraction in order to determine AM part suitability for service and also broadly discuss metallurgical phenomena. The paper then briefly expands the discussion to include additional engineering alloys and further analyze relationships between AM process parameters and AM part properties, consistently utilizing past experience with the same powder-fed CLAD 3D printer, the well-established science and technology of welding and joining, and recent publications on additive manufacturing.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. Atzeni, A. Salmi, Int J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2012, vol 62, pp. 1147.
S. H. Huang, P. Liu, A. Mokasdar, L. Hou, Int J Adv Manuf Technol., 2012, vol. 67,pp. 1191.
G. N. Levy, R. Schindel, J. P. Kruth, CIRP Annals – Manuf. Technol., 2003, vol. 52, pp. 589.
O. Ivanova, C. Williams, T. Campbell, Rapid Prototyping Journal, 2013, vol. 19, pp. 353.
J. Ruan and S. Jianzhong: in Solid Freeform Fabrication Symposium, Austin, TX, 2006, pp. 233.
P. Mognol, P. Muller, and J.Y. Hascoët: in Conference on Advanced Research in Virtual and Rapid Prototyping, Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Advanced Research in Virtual and Rapid Prototyping, Leiria, Portugal, 2011, 28 September–1 October, pp. 473.
L. Thivillon, P. Bertrand, B. Laget, I. Smurov, J. of Nuclear Mater., 2009, Vol. 385, pp. 236.
Wohlers Report 2012: Additive Manufacturing and 3D Printing State of the Industry Annual Worldwide Progress Report, Wohlers Associates Inc., Fort Collins, Colorado.
P. Mercelis, J. P. Kruth, Rapid Prototyping Journal, 2006, vol.12, pp. 254.
A.S. Wu, D.W. Brown, M. Kumar, G.F. Gallegos, W.E. King, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2014, vol. 45A, pp 6260.
D. Hu and R. Kovacevic, Int. J. Machine Tools Manuf., 2003, vol. 4, pp. 51.
A.J. Pinkerton, L. Li, J. of Manuf. Sci. Eng., 2004, vol. 126, pp. 33.
A.J. Pinkerton and L. Li: J. Phys. D, 1885, vol. 37.
M. S. F. De Lima, S. Sankaré, Mater. & Design, 2014, vol. 55, pp. 526.
R. Li, Y. Shi, Z. Wang, L. Wang, J. Li. J. Wei, Applied Surface Science, 2010, vol. 256, pp. 4350.
K. Zhang, S. Wang, W. Liu, X. Shang, Mater. & Design, 2014, vol. 55, pp. 104.
T. Amine, J.W. Newkirk, F. Liou, Case Studies in Thermal Engineering, 2014, vol 3 pp. 21.
D. Majumdar, A. Pinkerton, Z. Liu, I. Manna, L. Li, Applied Surface Science, 2005, vol. 247, pp. 373.
P.G.E Jerrard, L. Hao, and K.E. Evans: Proc. IMechE Part B, 2009, vol. 223(B11), pp. 1409–16.
S.A. Lin, J.T. Lee, W.T. Tsai, Microstructural aspects and oxidation behaviour of laser surface cladded silicon-containing stainless steels, Scripta Mater., 1998, vol. 38, pp. 559.
J.W. Elmer, S.M. Allen, T.W. Eager, Metall. Trans. A, 1989, vol. 20, pp. 2117.
D. Gu, Y. Shen, Mater. & Design, 2009, Vol. 30, pp. 2903.
K. C. Mills, B. J. Keene, International Materials Reviews, 1990, vol. 35, pp. 185.
D.L. Olson and G.R. Edwards: Philos. Trans. R Soc. B 04/1998.
S.A David, J.M. Vitek, International Materials Reviews, 1989, vol. 34, pp. 213.
J.A. Brooks and J.C. Lippold: in ASM Handbook: Welding, Brazing and Soldering, 1994, pp. 15.
S.A. David, S.S. Babu, J.M. Vitek, J of Materials, 2003, vol. 55, pp. 14.
W. Kurz, C. Bezençon, M. Gäumann, Sci. and Technol. of Advanced Mater., 2001 vol. 2, pp.185.
S. Katayama and A. Matsunawa: Solidification Microstructures in Laser Welded Stainless Steels, Proc. ICALEO, 1984, pp. 60.
R.S. Amano, S. Marek, B.F. Schultz, P.K. Rohtagi, J. of Manuf. Sci. and Eng., 2014, vol. 136, pp. 1.
E. Yasa, J. Deckers and J.P. Kruth: Proceedings of The International Conference on Advanced Research in Virtual and Rapid Prototyping, Leiria, Portugal, 6–10 October 2009, pp. 207–14.
D. J. Kotecki, T.A. Sievert, WRC-1992 Constitution Diagram for Stainless Steel Weld Metal: A Modification of the WRC 1998 Diagram, Welding Journal, 1992, vol. 71, pp. 171.
T. Takalo, N. Suutala, T. Moisio, Metall. Trans. A, 1979, vol. 10, pp. 1173.
G. Pacary, M. Moline, and J.C. Lippold: A Diagram for Predicting the Weld-Solidification-Cracking Susceptibility of Pulsed-Laser Welds in Austenitic Stainless Steels, Edison Welding Institute, 1990.
J.C Lippold, Solification Behavior and Cracking Susceptibility of Pulsed Laser Welds in Austentic Stainless Steels, Welding Journal, 1994, vol. 73, pp. 129s-139s.
A. Simchi, Metall. and Mater. Trans. B, 2004, vol. 35, pp. 937.
L.A. Krol Dobrzanski, L. Reimann, I. Czaja, Archives of Mater. Sci. and Eng., 2013, vol. 60, pp.87.
G. Strano, L. Hao, R.M. Everson, K.E. Evans, J. Mater. Processing Technol., 2013, vol. 213, pp. 589.
C. Kamath, B. El-Dasher, G.F. Gallegos, W.E. King, A. Sisto, Int. J.of Advanced Manuf. Technol., 2014, vol.74 pp. 65.
K. Yihong, S.B. Tor, and N.H Loh: Comparison of Two Metallic Additive Manufacturing Technologies: Selective Laser Melting, Electron Beam Melting, Progresses in Additive Manufacturing, C.C Kai, Y.W. Yee, T.M. Jen, and L. Erjia, eds., ISBN 978-981-09-0446-3, p. 231, Singapore.
M. Marya, L.G. Hector, R. Verma, W. Tong, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2005, 418 (1), 341-356.
W. Tong, H. Tao, N. Zhang, X. Jiang, M. Marya, Jr, L.G. Hector, and X.Q Gayden, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2005, vol. 36A, pp. 2651.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted August 29, 2014.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marya, M., Singh, V., Marya, S. et al. Microstructural Development and Technical Challenges in Laser Additive Manufacturing: Case Study with a 316L Industrial Part. Metall Mater Trans B 46, 1654–1665 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-015-0310-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-015-0310-5