Abstract
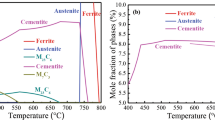
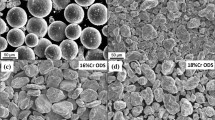
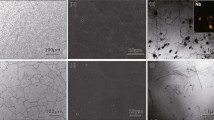
Niobium-containing ferritic stainless steels are finding new applications in automotive exhaust components because of their oxidation resistance, thermal fatigue resistance, and high-temperature strength. The mechanical behavior of Nb-containing ferritic steels at service temperatures of 973 K (700 °C) and higher results from the convolution of dynamic microstructural changes including precipitation, precipitate coarsening, strain hardening, recovery, and recrystallization. The relative contributions of these competing processes have yet to be clarified. In this study, the high-temperature flow strength of an 18Cr-2Mo-0.5Nb ferritic stainless steel (SUS 444) was correlated with microstructure under different strain and initial precipitate distributions to clarify the relative role of the strengthening and softening processes. High-temperature tensile tests at 1023 K (750 °C) of un-aged (initial microstructure is precipitate-free) and pre-aged (initial microstructure contains precipitates) samples were carried out and transmission electron microscopy was used to assess dislocation distributions and precipitate morphology. The difference in the stress–strain curves between un-aged and pre-aged samples was drastic; the yield strength of the un-aged sample was twice that of the pre-aged sample, and the un-aged sample exhibits a noticeable yield drop. Transmission electron microscopy revealed a Laves phase nucleated and grew during the high-temperature tensile test in the un-aged sample and the majority of the precipitates in the pre-aged sample were the same Laves phase. Furthermore, a strain effect on precipitate growth was recognized in un-aged and pre-aged conditions by comparing grip (no strain) and gage (strained) sections of tensile samples. The dominant strengthening contribution in un-aged samples is initially the precipitate shearing mechanism and it changes to Orowan strengthening beyond the ultimate tensile strength, whereas the dominant contribution in the pre-aged samples appears to be Orowan strengthening throughout the stress–strain curve.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Nakamura, K. Miyakusu and Y. Uematsu: Current advances in materials and processes - the Iron and Steel Institute of Japan, 1991, vol. 4, pp. 1788-91.
K. Ohmura, N. Fujita, M. Kikuchi, T. Tsuzaki and I. Hiroshige: Current advances in materials and processes - the Iron and Steel Institute of Japan, 1991, vol. 4, pp. 1796-99.
N. Fujita, K. Ohmura, M. Kikuchi, T. Suzuki, S. Funaki and I. Hiroshige: Scripta Mater., 1996, vol. 35, pp. 705-10.
N. Fujita, K. Ohmura and A. Yamamoto: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2003, vol. 351, pp. 272-81.
N. Nabiran, S. Klein, S. Weber, and W. Theisen: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2015, vol. 46A, pp. 102-14.
A. Miyazaki, K. Takao and O. Furukimi: ISIJ International, 2002, vol. 42, pp. 916-20.
N. Fujita and M. Kikuchi: Tetsu-to-Hagané, 2003, vol. 89, pp. 510-17.
D. G. Morris, M. A. Munoz-Morris and C. Baudin: Acta Mater. 2004, vol. 52, pp. 2827-36.
G. M. Sim, J. C. Ahn, S. C. Hong, K. J. Lee and K. S. Lee: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2005, vol. 396, pp. 159-65.
Y. Uematsu, M. Akita, M. Nakajima and K. Tokaji: Int. J. Fatigue, 2008, vol. 30, pp. 642-48.
T. Yamagishi, M. Akita, M. Nakajima, Y. Uematsu and K. Tokaji: Procedia Engineering, 2010, vol. 2, pp. 275-81.
S. J. Ko and Y-J. Kim (2012) Mater. Sci. Eng. A 534:7-12.
Y-T. Chiu and C-K. Lin: J. Power Sources, 2012, vol. 219, pp. 112-19.
Z. Y. Liu, F. Gao, L. Z. Jiang and G. D. Wang: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2010, vol. 527, pp. 3800-6.
Y-T. Chiu, C-K. Lin and J-C. Wu: J. Power Sources, 2011, vol. 196, pp. 2005-12.
Y-T. Chiu and C-K. Lin: J. Power Sources, 2012, vol. 198, pp. 149-57.
S. V. Mehtonen, L. P. Karjalainen and D. A. Porter: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2013, vol. 571, pp. 1-12.
M. Kato: Introduction to the theory of dislocations, pp. 139-144, Shokabo, Tokyo, 1999.
T. Sawatani, S. Minamino and H. Morikawa: Trans. ISIJ, 1982, vol. 22, pp. 172-80.
F. J. Humphreys and M. Hatherly: Recrystallization and Related Annealing Phenomena Second Edition, pp. 451-467, Elsevier, UK, 2004.
R. Horiuchi and H. Yoshinaga: Trans. JIM, 1965, vol. 6, pp. 131-38.
H. Nakashima, K. Iwasaki, S. Goto and H. Yoshinaga: Marer. Trans. JIM, 1990, vol. 31, pp. 35-45.
W. C. Oliver and W. D. Nix: Acta Metall., 1982, vol. 30, pp. 1335-47.
I. M. Lifshitz and V. V. Slyozov: J. Phys. Chem. Solids, 1961, vol. 19, pp. 35-50.
C. Wagner: Z. Electrochem., 1961, vol. 65, pp. 581-91.
E.A. Brandes, and G.B. Brook: Smithells Metals Reference Book, 7th edn., Butterworth – Heinernann, Read Educational and Professional Publishing, UK, 1998, pp. 13-19–13-20.
R. S. W. Shewfelt and L. M. Brown: Phil. Mag. 1974, vol. 30, pp. 1135-45.
R. S. W. Shewfelt and L. M. Brown: Phil. Mag. 1977, vol. 35, pp. 945-62.
G.F. Vander Voot: Metallography, Principles and Practice, McGraw Hill, NY, 1984.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the Nanoscale Characterization and Fabrication Laboratory of the Institute for Critical Technology and Applied Science (NCFL-ICTAS) at Virginia Tech for the use of its facilities. K.I. thanks Professor Hideharu Nakashima in Kyushu University for fruitful discussions. K.I. was partly supported by Strategic Young Researcher Overseas Visits Program (JSPS #R2408, Japan).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted January 9, 2014.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ikeda, Ki., Yamoah, N.K.G., Reynolds, W.T. et al. Effect of Laves Phase on High-Temperature Deformation and Microstructure Evolution in an 18Cr-2Mo-0.5Nb Ferritic Stainless Steel. Metall Mater Trans A 46, 3460–3469 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-015-2936-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-015-2936-y