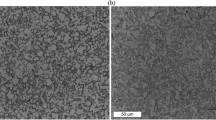
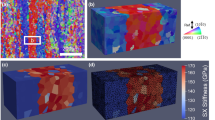
Abstract
The dwell effects of Ti624x (x = 2 to 6) alloys, including dwell fatigue life debit, fracture mode and strain accumulation, were characterized and compared. With increasing Mo content, the dwell fatigue life debit decreases quickly, and dwell fatigue fracture exhibits a transition from subsurface to surface initiation. Accompanying these changes, the accumulated strain decreases, and the pattern of secondary cracks loses morphological features typical of dwell cracks. These variations in the fatigue behavior of Ti624x were attributed on the fundamental level to the dual effects of Mo: It decreases the β transus of titanium and, as a slow diffuser, reduces the rate of phase transformation from β to α. A higher Mo content encourages nucleation of multiple variants of α laths and promotes the transition from aligned colonies to basketweave microstructure during cooling after β forging. As a result both the grain size and microtexture intensity of α grains in the two-phase processed and heat treated microstructure are reduced. Smaller grain size of the alloys with higher Mo content produces smaller slip band spacing and reduces accumulated strain during dwell fatigue, thus reducing propensity for crack initiation. Microtexture was shown to be the direct cause of dwell sensitivity, and their relationship was described with the aid of a two-region redistribution model based on a previous two-element redistribution model proposed by Bache.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Banerjee and J. C. Williams: Acta Mater., 2013, vol. 61, pp. 844-79.
J. C. Williams and E. A. Starke: Acta Mater., 2003, vol. 51, pp. 5775-99.
G. Lütjering and J.C. Williams: Titanium. Springer Verlag, Berlin, 2007.
Z. Song and D. W. Hoeppner: Int. J. Fatigue, 1989, vol. 11, pp. 85-90.
M. R. Bache: Int. J. Fatigue, 2003, vol. 25, pp. 1079-87.
Transportation Safety Board of Canada: Uncontained Engine Failure, Report No. A97F0059, 1997.
M. R. Bache, M. Cope, H. M. Davies, W. J. Evans, and G. Harrison: Int. J. Fatigue, 1997, vol. 19, pp. s83-s88.
M. L. Thomsen and D. W. Hoeppner: Int. J. Fatigue, 1998, vol. 20, pp. 309-17.
M. Kassner, Y. Kosaka, and J. Hall: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1999, vol. 30, pp. 2383-89.
V. Sinha, J. E. Spowart, M. J. Mills, and J. C. Williams: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2006, vol. 37, pp. 1507–18.
A. L. Pilchak and J. C. Williams: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2011, vol. 42A, pp. 1000-27.
W.J. Evans: Proc. Third Int. Confer. Creep Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct., Institute of Materials, 1987, pp. 603–13.
S.H. Spence, W.J. Evans, and M. Cope: Proc. 9th Int. Conf. Fract., B.L. Karihaloo, Y.W. Mai, M.I. Ripley, and R.O. Ritchie, eds., Pergamon Press Ltd, Sydney, 1997, pp. 1571–78.
M. R. Bache: Int. J. Fatigue, 1999, vol. 21, pp. S105-S11.
V. Sinha, M. J. Mills, and J. C. Williams: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2004, vol. 35A, pp. 3141-48.
N. Gey, P. Bocher, E. Uta, L. Germain, and M. Humbert: Acta Mater., 2012, vol. 60, pp. 2647-55.
R. Whittaker, K. Fox, and A. Walker: Mater. Sci. Technol., 2010, vol. 26, pp. 676-84.
L. Germain, N. Gey, M. Humbert, P. Vo, M. Jahazi, and P. Bocher: Acta Mater., 2008, vol. 56, pp. 4298-308.
L. Germain, N. Gey, M. Humbert, P. Bocher, and M. Jahazi: Acta Mater., 2005, vol. 53, pp. 3535-43.
Thomas R. Bieler and S. L. Semiatin: Int. J. Plast., 2002, vol. 18, pp. 1165-89.
E. E. Sackett, L. Germain, and M. R. Bache: Int. J. Fatigue, 2007, vol. 29, pp. 2015-21.
S. Ghosh and P. Chakraborty: Int. J. Fatigue, 2013, vol. 48, pp. 231-46.
M. Anahid, M. K. Samal, and S. Ghosh: J. Mech. Phys. Solids, 2011, vol. 59, pp. 2157-76.
F. P. E. Dunne and D. Rugg: Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct., 2008, vol. 31, pp. 949-58.
K. Kirane and S. Ghosh: Int. J. Fatigue, 2008, vol. 30, pp. 2127-39.
F. P. E. Dunne, D. Rugg, and A. Walker: Int. J. Plast., 2007, vol. 23, pp. 1061-83.
A. N. Stroh: Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A, 1954, vol. 223, pp. 404–14.
N. Gey, P. Bocher, E. Uta, M. Humbert, and J. Gilgert: Proc. 12th World Confer. Titan., L. Zhou, H. Chang, Y.F. Lu, and D.S. Xu, eds., Science Press, Beijing, 2011, pp. 879–82.
E. Uta, N. Gey, P. Bocher, M. Humbert, and J. Gilgert: J. Microsc., 2009, vol. 233, pp. 451-59.
A.P. Woodfield, M.D. Gorman, R.R. Corderman, J.A. Sutliff, and B. Yamrom: in Titanium’ 95: Sci. Technol., P.A. Blenkinsop, W.J. Evans, and H.M. Flower, eds., Institute of Materials, Birmingham, 1995, pp. 1116–23.
M.R. Bache, C. Pleydell-Pearce, R. Ding, and I.P. Jones: Proc. 12th World Conf. Titan., L. Zhou, H. Chang, Y.F. Lu, and D.S. Xu, eds., Science Press, Beijing, 2011, pp. 1152–55.
F. Bridier, P. Villechaise, and J. Mendez: Acta Mater., 2008, vol. 56, pp. 3951-62.
S. I. Rokhlin, J. Y. Kim, B. Xie, V. A. Yakovlev, and B. Zoofan: Proc. 29th Ann. Rev. Progr. Quant. Nondestr. Eval., D.O. Thompson and D.E. Chimenti, eds., American Institute of Physics, Melville, 2002, vol. 20, pp. 1371–78.
S. I. Rokhlin, J. Y. Kim, B. Xie, and B. Zoofan: NDT & E Int., 2007, vol. 40, pp. 462-70.
T. Neeraj and M. J. Mills: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2001, vol. 319, pp. 415-19.
T. Neeraj, D. H. Hou, G. S. Daehn, and M. J. Mills: Acta Mater., 2000, vol. 48, pp. 1225-38.
J. C. Williams, R. G. Baggerly, and N. E. Paton: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2002, vol. 33, pp. 837-50.
M. J. Blackburn and J. C. Williams: ASM Trans. Q., 1969, vol. 62, pp. 398-409.
M. Zhang, F. Bridier, P. Villechaise, J. Mendez, and D. L. McDowell: Acta Mater., 2010, vol. 58, pp. 1087-96.
L. Xiao and Y. Umakoshi: J. Mater. Sci. Lett., 2002, vol. 21, pp. 517-19.
L. Xiao and Y. Umakoshi: Philos. Mag. A, 2002, vol. 82, pp. 2379-96.
I. Bantounas, D. Dye, and T. C. Lindley: Acta Mater., 2009, vol. 57, pp. 3584-95.
A.L. Pilchak, M.C. Brandes, R.E.A. Williams, and J.C. Williams: Proc. 12th World Conf. Titan., L. Zhou, H. Chang, Y.F. Lu, and D.S. Xu, eds., Science Press, Beijing, 2011, pp. 993–97.
I. Bantounas, T. C. Lindley, D. Rugg, and D. Dye: Acta Mater., 2007, vol. 55, pp. 5655-65.
F. Bridier, P. Villechaise, and J. Mendez: Acta Mater., 2005, vol. 53, pp. 555-67.
F. P. E. Dunne, A. Walker, and D. Rugg: Proc. R. Soc. A, 2007, vol. 463, pp. 1467-89.
S. B. Biner and J. R. Morris: Philos. Mag., 2003, vol. 83, pp. 3677-90.
C. Déprés, C. F. Robertson, and M. C. Fivel: Philos. Mag., 2004, vol. 84, pp. 2257-75.
D. R. Mitchell and T. J. Tucker: Weld. J., 1969, vol. 48, pp. S23-S33.
T. Ahmed and H. J. Rack: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1998, vol. 243, pp. 206-11.
Acknowledgments
The support of this work by the National Science Foundation of China through Grant 51171195 is gratefully acknowledged. We thank Dr. Dongsheng Xu for his constructive discussion throughout this work and appreciate the help of Dr. Jun Tan, Mr. Miao Song and Mr. Jinglong Wen from Shenyang National Laboratory for Materials Science for their help with EBSD analysis, TEM and fatigue tests, respectively.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted May 13, 2014.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qiu, J., Ma, Y., Lei, J. et al. A Comparative Study on Dwell Fatigue of Ti-6Al-2Sn-4Zr-xMo (x = 2 to 6) Alloys on a Microstructure-Normalized Basis. Metall Mater Trans A 45, 6075–6087 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-014-2541-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-014-2541-5