Abstract
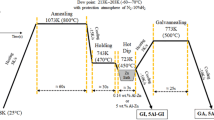
Alloying elements, such as Mn, Mo, Si, and Cr, are commonly used to enhance the strength of advanced high-strength steels. Those elements also play an important role in the hot-dip galvanizing (GI) and galvannealing (GA) process. In this study, two kinds of CMnSiCr dual-phase steels were galvanized and galvannealed using a hot-dip simulator to investigate the effect of the alloying elements on the microstructure of the GI and GA coatings. The results showed that the dual-phase steels had good galvanizability because no bare spots were observed and the Fe-Zn phases were readily formed at the interface. However, the alloying reaction during the GA process was significantly hindered. XPS analysis showed that external oxidation occurred under an extremely low dew point [213 K to 203 K (−60 °C to −70 °C)] atmosphere during the annealing prior to hot dipping. However, most of the oxides were reduced during the GI process. After the GI process, the Al was present as solid solutes in the Fe-Zn phase, suggesting that the Fe-Zn phase was formed from the transformation of the Fe-Al inhibition alloy. Meanwhile, the solubility of Si in the ζ phase was extremely low. With continued GA reaction, the ζ phase transformed into the δ phase, which contained approximately 1.0 at.pct Si. The Si also diffused into the Zn layer during the GA reaction. Hence, the ζ phase did not homogeneously nucleate at the steel substrate/Zn coating interface, but was found at the area away from the interface. Therefore, the Fe-Zn phases on the CMnSiCr dual-phase steels were relatively non-uniform compared to those on interstitial-free steel.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. Mintz: Int. Mater. Rev., 2001, vol. 46, pp. 169-97.
H. Bablik, F. Gotzl, R. Kukaczka: Werkst. U. Korro., 1951, vol. 2, pp. 163–65.
M. Urednieck, J.S. Kirkaldy: Z. Metallkd., 1973, vol. 64, pp. 899-910.
M. Blumenau, M. Norden, F. Friedel, K. Peters: Surf. Coat. Tech., 2011, vol. 205, pp. 3319-27.
E.M. Bellhouse, A.I.M. Mertens, J.R. McDermid: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2007, vol. 463, pp. 147-56.
I. Hertveldt, S. Claessens, and B.C. De Cooman: Mater. Sci. Tech., 2001, vol. 17, pp. 1500–07.
I. Hertveldt, S. Claessens, and B.C. De Cooman: Mater. Sci. Tech., 2001, vol. 17, pp. 1508–15.
P. Drillet, Z. Zermout, D. Bouleau, and J. M. Mataigne: 5th Int. Conf. on Zinc and Zinc Alloy Coated Steel Sheet, 2001, Belgium, pp. 195.
J. Mahieu, B.C. De Cooman, J. Maki, and S. Claessens: Iron Steelmaker, 2002, vol. 29, pp. 29–37.
R. Khnodker, A. Mertens, J.R. McDermid: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2007, vol. 463, pp. 157-65.
P. Drillet, Z. Zermout, D. Bouleau, J. Mataigne, and S. Claessens: 6th Int. Conf. on Zinc and Zinc Alloy Coated Steel Sheet, Chicago, 2004, pp. 1123.
J. Foct, G. Reumont, G. Dupont, P. Perrot: J. Phys., 1993, vol. 3, pp. 961-6.
R.W. Sandelin: Wire and Wire Products, 1940, vol. 15, pp. 655.
J. Foct, P. Perrot, G. Reumont: Scr. Metall. Mater., 1993, vol. 28, pp. 1195-1200.
M.S. Kozdras, P. Niessen: Metallography, 1989, vol. 22, pp. 253-67.
N.Y. Tang: J. Phase Equilib. Diff., 2008, vol. 29, pp. 337-44.
C.E. Jordan, A.R. Marder: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1997, vol. 28A, pp. 2683-94.
C.S. Lin, M. Meshii, C.C. Cheng: ISIJ Int., 1995, vol. 35, pp. 503-11.
S. Dionne: JOM-US, 2006, vol. 58, pp. 32-40.
J.R. Kilpatrick: Prakt. Metallogr.-Pr. M., 1991, vol. 28, pp. 649-58.
C.S. Lin, M. Meshii: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1994, vol. 25B, pp. 721-30.
Y.F. Gong, H.S. Kim, and B.C. De Cooman: ISIJ Int., 2009, vol. 49, pp. 557–63.
Y.F. Gong, H.S. Kim, and B.C. De Cooman: ISIJ Int., 2008, vol. 48, pp. 1745–51.
H. Liu, Y. He, S. Swaminathan, M. Rohwerder, L. Li: Surf. Coat. Tech., 2011, vol. 206, pp. 1237-43.
E.M. Bellhouse, J.R. McDermid: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2008, vol. 491, pp. 39-46.
A.S. Khanna: Introduction to High Temperature Oxidation and Corrosion, Materials Park, ASM International, USA, 2002, pp. 2-7.
H. Bake: ASM Handbook: Alloy Phase Diagrams, vol. 3, ASM International, Ohio, 1992, pp. 2–276.
B. Schuhmacher, T. Heller, M. Steinhorst, and W. Warnecke: 7th Int. Conf. on Zinc and Zinc Alloy Coated Steel Sheet, 2007, Osaka, p. 397.
M. Fujine: 7th Int. Conf. on Zinc and Zinc Alloy Coated Steel Sheet, 2007, Osaka, p. 374.
J. Maki, J. Mahieu, B.C. De Cooman, and S. Claessens: Mater. Sci. Tech., 2003, vol. 19, pp. 125–31.
J. Mahieu, S. Claessens, and B.C. De Cooman: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2001, vol. 32A, pp. 2905–08.
J. Mahieu, S. Claessens, B.C. De Cooman, and F. Goodwin: 6th Int. Conf. on Zinc and Zinc Alloy Coated Steel Sheet, 2004, Chicago, pp. 529.
A.R.P. Ghuman and J.I. Glodstein: Metall. Trans. A, 1971, pp. 2903–14.
A.R. Borzillo, W.C. Hahn: Trans. ASM, 1969, vol. 62, pp. 729-39.
J. Inagaki, Y. Sakurai, A. Nishimoto: Tetsu. Hagane., 1993, vol. 79, pp. 1273–77.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by China Steel Corporation, Kaohsiung, Taiwan. The authors would like to thank J. S. Lin of China Steel Corporation for his help on the preparation of galvanized and galvannealed steels using the hot-dip simulator of China Steel Corporation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted November 4, 2012.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, KC., Chu, PW., Lin, CS. et al. Galvanizing and Galvannealing Behavior of CMnSiCr Dual-Phase Steels. Metall Mater Trans A 44, 2690–2698 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-013-1612-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-013-1612-3