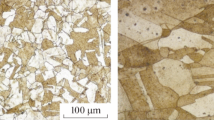
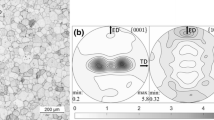
Abstract
The evolution of crystallographic texture in polycrystalline copper and nickel has been studied. The deformation texture evolution in these two materials over seven orders of magnitude of strain rate from 3 × 10−4 to ~2.0 × 10+3 s−1 show little dependence on the stacking fault energy (SFE) and the amount of deformation. Higher strain rate deformation in nickel leads to weaker \( \left\langle {101} \right\rangle \) texture because of extensive microband formation and grain fragmentation. This behavior, in turn, causes less plastic spin and hence retards texture evolution. Copper maintains the stable end \( \left\langle {101} \right\rangle \) component over large strain rates (from 3 × 10−4 to 10+2 s−1) because of its higher strain-hardening rate that resists formation of deformation heterogeneities. At higher strain rates of the order of 2 × 10+3 s−1, the adiabatic temperature rise assists in continuous dynamic recrystallization that leads to an increase in the volume fraction of the \( \left\langle {101} \right\rangle \) component. Thus, strain-hardening behavior plays a significant role in the texture evolution of face-centered cubic materials. In addition, factors governing the onset of restoration mechanisms like purity and melting point govern texture evolution at high strain rates. SFE may play a secondary role by governing the propensity of cross slip that in turn helps in the activation of restoration processes.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
U.F. Kocks, C.N. Tome, and H.R. Wenk: Texture and Anisotropy, Cambridge University Press, London, UK, 1998.
S. Speziale, I. Lonardelli, L.Miyagi, J. Pehl, C.E. Tommaseo, and H.-R. Wenk: J. Phys. Cond. Matter, 2006, vol. 18, pp. S1007–20.
B. Plunkett, O. Cazacu, and R.A. Lebensohn: J. Phys. IV Proc., 2006, vol. 134, pp. 81–86.
M.A. Meyers: Dynamic Behaviour of Materials, Wiley, New York, NY, 1994.
R.J. Asaro and A. Needleman: Acta Metall., 1985, vol. 33, pp. 923–53.
S.R. Kalidindi, C.A. Bronkhorst, and L. Anand: J. Mech. Phys. Solids, 1992, vol. 40, pp. 537–69.
T. Leffers: Scripta Metall., 1968, vol. 2, pp. 447–52.
T. Leffers and O.B. Pederson: Scripta Mater., 2002, vol. 46, pp. 741–46.
U.F. Kocks and H. Mecking: Prog. Mater. Sci., 2003, vol. 48, pp. 171–273.
G.R. Canova, C. Fressengeas, A. Molinari, and U.F. Kocks: Acta Metall., 1988, vol. 36, pp. 1961–70.
J.W. Hutchinson: Proc. R. Soc., 1976, vol. A348, pp. 101–27.
A. Bhattacharyya, D. Rittel, and G. Ravichandran: Scripta Mater., 2005, vol. 52, pp. 657–61.
A. Bhattacharyya, D. Rittel, and G. Ravichandran: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2006, vol. 37A, pp. 1137–45.
A.T. English and G.Y. Chin: Acta Metall., 1965, vol. 13, pp. 1013–16.
M.G. Stout, J.S. Kallend, U.F. Kocks, M.A. Przystupa, and A.D. Rollett: Proc. Eighth Conf. on Texture of Materials, 1988, vol. 5.9, pp. 479–84.
J. Hirsch and K. Lucke: Acta Metall., 1988, vol. 36, no. 76–1-3, pp. 2863–2927.
D.A. Hughes, R. Lebensohn, H.R. Wenk, and A. Kumar: Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A, 2000, vol. 456, pp. 921–53.
S. Suwas, R.K. Ray, J.J. Fundenberger, T. Grosdidien, and W. Skrotzki: Solid State Phenom., 2005, vol. 105, pp. 345–50.
R.K. Ray: Acta Metall. Mater., 1995, vol. 43, pp. 3861–72.
ASM International: High Strain Rate Compression Testing, Mechanical Testing, vol 8, ASM Handbook, ASM International, Materials Park, OH, 1985, pp. 190–207.
T. Ungár, J. Gubicza, G. Ribárik, and A. Borbély: J. Appl. Cryst., 2001, vol. 34, pp. 298–310.
G. Ribárik, T. Ungár, and J. Gubicza: J. Appl. Cryst., 2001, vol. 34, pp. 669–76.
F. Montheillet and J. Le Coze: Phys. Stat. Sol. A, 2002, vol. 189, pp. 51–58.
W. Skrotzki, N. Scheerbaum, C. Oertel, R.A. Massion, S. Suwas, and L.S. Toth: Acta Mater., 2007, vol. 55, pp. 2013–24.
M.A. Meyers, V. Nesterenko, J. LaSalvia, and Q. Xue: Mater. Sci. Engg. A, 2001, vol. 317, pp. 204–25.
M.A. Meyers, Y. Xu, Q. Xue, M. Perez-Prado, and T. McNelly: Acta Mat., 2003, vol. 51, pp. 1307–25.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the X-ray equipment support from the national facility (DST-IRPHA) at I.I.T. Bombay. Thanks are due to Professor I. Samajdar for providing this facility. The authors are also thankful to Dr. D.-I. Kim (KIST, Seoul) and to Professor K.H. Oh (SNU, Seoul) for providing the REDS software. The authors thank Mr. S. Sasidhara for help in carrying out the compression tests using DARTEC. The authors thank DST for the microscopy facility at the Institute of Nano Science Initiative in Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore. The authors are grateful to Professors G. Ravichandran and R.K. Ray for discussion on various aspects of the present study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted August 12, 2009
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gurao, N.P., Kapoor, R. & Suwas, S. Effect of Strain Rate on Evolution of the Deformation Microstructure and Texture in Polycrystalline Copper and Nickel. Metall Mater Trans A 41, 2794–2804 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-010-0360-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-010-0360-x