Abstract
Objectives
To observe the regulation of Chinese herbal medicine, Modifified Qing’e Pill (加味青娥丸, MQEP), on the expression of adiponectin, bone morphogenetic protein 2 (BMP2), osteoprotegerin (OPG) and other potentially relevant risk factors in patients with nontraumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head (ONFH).
Methods
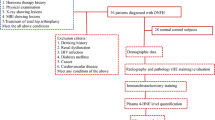
A total of 96 patients with nontraumatic ONFH were unequal randomly divided into treatment group (60 cases) and control group (36 cases). The treatment group were treated with MQEP while the control group were treated with simulated pills. Both groups were given caltrate D. Six months were taken as a treatment course. Patients were followed up every 2 months. The levels of plasma adiponectin, BMP2, OPG, von Willebrand factor (vWF), von Willebrand factor cleaving protease (vWF-cp), plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 (PAI-1), tissue plasminogen activator (tPA), C-reactive protein (CRP), blood rheology, bone mineral density (BMD) of the femoral head and Harris Hip Score were measured before and after treatment.
Results
After 6 months of treatment, compared with the control group, patients in the treatment group had signifificantly higher adiponectin and BMP2 levels (P<0.01 and P=0.013, respectively), lower vWF, PAI-1 and CRP levels (P=0.019, P<0.01 and P<0.01, respectively), and lower blood rheology parameters. BMD of the femoral neck, triangle area and Harris Hip Score in the treatment group were signifificantly higher than those in the control group. Moreover, plasma adiponectin showed a positive association with BMP2 (r=0.231, P=0.003) and a negative association with PAI-1 (r=–0.159, P<0.05).
Conclusion
MQEP may play a protective role against nontraumatic ONFH by increasing the expression of adiponectin, regulating bone metabolism and improving the hypercoagulation state, which may provide an experimental base for its clinical effects.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mont MA, Jones LC, Hungerford DS. Nontraumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head: ten years later. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2006;88: 1117–1132.
Tingart M, Beckmann J, Opolka A, Matsuura M, Wiech O, Grifka J, et al. Influence of factors regulating bone formation and remodeling on bone quality in osteonecrosis of the femoralhead. Calcif Tissue Int 2008;82: 300–308.
Kamiva N, Shafer S, Oxendine I, Mortlock DP, Chandler RL, Oxburgh L, et al. Acute BMP2 upregulation following induction of ischemic osteonecrosis in immature femoral head. Bone 2013;53: 239–247.
ARCO. Committee on terminology and classification. ARCO News 1992;4: 41–46.
Nozaki Y, Kumagai K, Miyata N, Niwa M. Pravastatin reduces steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head in SHRSP rats. Acta Orthop 2012;83: 87–92.
Lykissas MG, Gelalis ID, Kostas-Agnantis IP, Vozonelos G, Korompilias AV. The role of hypercoagulability in the development of osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Orthop Rev (Pavia) 2012;4: 73–78.
Miyanishi K, Yamamoto T, Irisa T, Yamashita A, Jingushi S, Noguchi Y, et al. Bone marrow fat cell enlargement and a rise in intraosseous pressure in steroid-treated rabbits with osteonecrosis. Bone 2002;30: 185–190.
Calder JD, Buttery L, Revell PA, Pearse M, Polak JM. Apoptosis—a significant cause of bone cell death in osteonecrosis of the femoral head. J Bone Joint Surg Br 2004;86: 1209–1213
Youm YS, Lee SY, Lee SH. Apoptosis in the osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Clin Orthop Surg 2010;2: 250–255.
Assouline-Dayan Y, Chang C, Greenspan A, Shoenfeld Y, Gershwin ME. Pathogenesis and natural history of osteonecrosis. Semin Arthrit Rheum 2002;32: 94–124.
Kadowaki T, Yamauchi T, Kubota N, Hara K, Ueki K, Tobe K. Adiponectin and adiponectin receptors in insulin resistance, diabetes, and the metabolic syndrome. J Clin Invest 2006;116: 1784–1792.
Tamang HK, Timilsina U, Singh KP, Shrestha S, Pandey B, Basnet S, et al. Assessment of adiponectin level in obese and lean Nepalese population and its possible correlation with lipidprofile: a cross-sectional study. Indian J Endocrinol Metab 2013;17: 349–354.
Williams GA, Wang Y, Callon KE, Watson M, Lin JM, Lam JB, et al. In vitro and in vivo effects of adiponectin on bone. Endocrinology 2009;150: 3603–3610.
Berner HS, Lyngstadaas SP, Spahr A, Monjo M, Thommesen L, Drevon CA, et al. Adipo-nectin and its receptors are expressed in bone-forming cells. Bone 2004;35: 842–849.
Shinoda Y, Yamaguchi M, Ogata N, Akune T, Kubota N, Yamauchi T, et al. Regulation of bone formation by adiponectin through autocrine/paracrine and endocrine pathways. J Cell Biochem 2006;99: 196–208.
Lee HW, Kim SY, Kim AY, Lee EJ, Choi JY, Kim JB. Adiponectin stimulates osteoblast differentiation through induction of COX2 in mesenchymal progenitor cells. Stem Cells 2009;27: 2254–2262.
Luo XH, Guo LJ, Yuan LQ, Xie H, Zhou HD, Wu XP, et al. Adiponectin stimulates human osteoblasts proliferation and differentiation via the MAPK signaling pathway. Exp Cell Res 2005;309: 99–109.
Oshima K, Nampei A, Matsuda M, Iwaki M, Fukuhara A, Hashimoto J, et al. Adipo-nectin increases bone mass by suppressing osteoclast and activating osteoblast. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2005;331: 520–526.
Shehzad A, Iqbal W, Shehzad O, Lee YS. Adiponectin: regulation of its production and its role in human diseases. Hormones (Athens) 2012;11: 8–20.
Ehling A, Schäffler A, Herfarth H, Tarner IH, Anders S, Distler O, et al. The potential of adiponectin in driving arthritis. J Immunol 2006;176: 4468–4478.
Mather KJ, Goldberg RB. clinical use of adiponectin as a marker of metabolic dysregulation. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 2014;28: 107–117.
Shuai B, Shen L, Yang YP, Xie J, Shou ZX, Wei B. Low plasma adiponectin as a potential biomarker for osteonecrosis of the femoral head. J Rheumatol 2010;37: 2151–2155.
Huang CY, Lee CY, Chen MY, Tsai HC, Hsu HC, Tang CH. Adiponectin increases BMP-2 expression in osteoblasts via AdipoR receptor signaling pathway. J Cell Physiol 2010;224: 475–483.
Kamiya N, Shafer S, Oxendine I, Mortlock DP, Chandler RL, Oxburgh L, et al. Acute BMP2 upregulation following induction of ischemic osteonecrosis in immature femoral head. Bone 2013;53: 239–247.
Malizos KN, Karantanas AH, Varitimidis SE, Dailiana ZH, Bargiotas K, Maris T. Osteo necrosis of the femoral head: etiology, imaging and treatment. Eur J Radiol 2007;63: 16–28.
Molino D, de Santo NG, Marotta R, Anastasio P, Mosavat M, de Lucia D. Plasma levels of plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1, factor I, prothrombin activation fragment 1+2, anticardiolipin, and antiprothrombin antibodies are risk factors for thrombosis in hemodialysis patients. Semin Nephrol 2004;24: 495–501.
Zalavras C, Dailiana Z, Elisaf M, Bairaktari E, Vlachogiannopoulos P, Katsaraki A, et al. Potential aetiological factors concerning the development of osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Eur J Clin Invest 2000;30: 215–221.
Chauhan AK, Motto DG, Lamb CB, Bergmeier W, Dockal M, Plaimauer B, et al. Systemic antithrombotic effects of ADAMTS13. J Exp Med 2006;203: 767–776.
Jansson JH, Nilsson TK, Johnson O. von Willebrand factor in plasma: a novel risk factor for recurrent myocardial infarction and death. Br Heart J 1991;66: 351–355.
Jansson JH, Johansson B, Boman K, Nilsson TK. Hypofibrinolysis in patients with hyper-tension and elevated cholesterol. J Intern Med 1991;229: 309–316.
Li JH, Wu YL, Ye JH, Ning YG, Yu HY, Peng ZJ, et al. Effects of blood-activating and stasis-removing drugs combined with VEGF gene transfer on angiogenesis inischemic necrosis of the femoral head. J Tradit Chin Med 2009;29: 216–219.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81273907)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Cg., Shen, L., Yang, YP. et al. Effects of Modified Qing’e Pill (加味青娥丸) on expression of adiponectin, bone morphogenetic protein 2 and coagulation-related factors in patients with nontraumatic osteonecrosis of femoral head. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 23, 183–189 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-016-2407-3
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-016-2407-3