Abstract
Objective
To assess the efficacy and safety of Moluodan (摩罗丹) in treating dysplasia in chronic atrophic gastritis (CAG) patients.
Methods
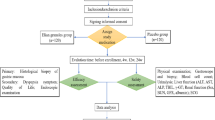
This was a multi-centered, double-blind, randomized controlled trial. The total of 196 subjects were assigned to receive either Moluodan or folic acid in a 2:1 ratio by blocked randomization. Mucosa marking targeting biopsy (MTB) was used to insure the accuracy and consistency between baseline and after 6-month treatment. Primary outcomes were histological score, response rate of pathological lesions and dysplasia disappearance rate. Secondary endpoints included gastroscopic findings, clinical symptom and patient reported outcome (PRO) instrument.
Results
Dysplasia score decreased in Moluodan group (P =0.002), significance was found between groups (P =0.045). Dysplasia disappearance rates were 24.6% and 15.2% in Moluodan and folic acid groups respectively, no significant differences were found (P =0.127). The response rate of atrophy and intestinal metaplasia were 34.6% and 23.0% in Moluodan group, 24.3% and 13.6% in folic acid group. Moluodan could improve erythema (P =0.044), and bile reflux (P =0.059), no significance between groups. Moluodan was better than folic acid in improving epigastric pain, epigastric suffocation, belching and decreased appetite (P <0.05), with symptom disappearance rates of 37% to 83%.
Conclusions
Moluodan improved dysplasia score in histopathology, and erythema and bile reflux score in endoscopy, and superior to folic acid in improving epigastric pain, epigastric suffocation, belching and decreased appetite. [ChiCTR-TRC-00000169]
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lewin KJ. Nomenclature problems of gastrointestinal epithelial neoplasia. Am J Surg Pathol 1998;22:1043–1047.
de Vries AC, van Grieken NC, Looman CW, Casparie MK, de Vries E, Meijer GA, et al. Gastric cancer risk in patients with premalignant gastric lesions: a nationwide cohort study in the Netherlands. Gastroenterology 2008;134:945–952.
Lauwers GY, Riddell RH. Gastric epithelial dysplasia. Gut 1999;45:784–790.
Correa P. Clinical implications of recent developments in gastric cancer pathology and epidemiology. Semin Oncol 1985;12:2–10.
Ming SC. Cellular and molecular pathology of gastric carcinoma and precursor lesions: a critical review. Gastric Cancer 1998;1:31–50.
Wu B. The outcome of low-grade gastric intraepithelial neoplasia and the comparative study between endoscopic therapy and surgical resection for high-grade gastric intraepithelial neoplasia and early gastric cancer [dissertation]. Beijing: Chinese PLA Postgraduate Medical School; 2011.
Dixon MF. Gastrointestinal epithelial neoplasia: Vienna revisited. Gut 2002;51:130–131.
Li EF, Mei JQ, Su TC, Miu YX. Regulating function of Moluodan on the gastric electrogram of chronic gastric diseases. Chin Tradit Patent Med (Chin) 1992;14:24–25.
Jin ZH, Kang Y, Jiao JJ, Ma DL, Zhang CL. A experimental study on the effect of Moluodan on secretion function in mice with chronic gastritis. Tianjin Med (Chin) 1990;3:179–180.
Jiao JJ, Ma DL, Kang Y, Jin ZH, Zhang CL. The pathological changes of experimental mice with chronic gastritis treated by Moluodan. Tianjin Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 1990;3:38–39.
Yu Z, Wang G, Chen GY, Chang J, Zhang Y, Zhang RM. Muoluodan concentrated pill in treatment of chronic atrophic gastritis (the stomach-yin of deficiency and stagnated blood of stomach meridian): a prospective, randomized, controlled trial. West China Med J (Chin) 2007;22:287–289.
Guo XJ. The curative effect observation on 200 cases of intetinal metaplasia of atrophic gastritis treated with Moluo Pills. J Beijing Univ Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 1997;17:33–35.
Si JM, Sun LM, Fan YJ, Wang LJ. Trial of a novel endoscopic tattooing biopsy forceps on animal model. World J Gastroenterol 2005;11:1859–1861.
Digestive Disease Branch of Chinese Medical Association. Consensus on chronic gastritis in China (Shanghai 2006). Chin J Gastroenterol (Chin) 2007;27:45–49.
Schlemper RJ, Riddell RH, Kato Y, Borchard F, Cooper HS, Dawsey SM, et al. The Vienna classification of gastrointestinal epithelial neoplasia. Gut 2000;47:251–255.
Wang F. Weifuchun for the treatment of 40 cases with chronic atrophic gastritis. Fujian Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2003;34:31.
Wu HM. Clinical research on Weifuchun for the treatment of chronic atrophic gastritis. Chin Med Factory Mine (Chin) 2000;13:215–216.
Zhu SS, Joel Mason, Shi Y, Hu YB, Li RR, Wang M, et al. The interventional effect of folic acid on the development of gastric and other gastrointestinal cancers—clinical trial and follow-up for seven years. Chin J Gastrocnterol (Chin) 2002;7:73–78.
Xiao SD, Meng XJ, Shi Y, Hu YB, Zhu SS, Wang CW. Interventional study of high dose folic acid in gastric carcinogenesis in beagles. Gut 2002;50:61–64.
Zhu SS, Hu YB, Shi Y, Fang JY, Gu WQ, Jiang SJ, et al. Reversion of the precancerous lesions of gastric cancer with some vitamins: a preliminary clinical observasion. Chin J Gastroenterol (Chin) 1996;1:70–74.
Chinese Medical Association of Digestive Endoscopy. Endoscopic classification and trial standards on treatment of chronic gastritis. Chin J Dig Endosc (Chin) 2004;21:77–78.
Dixon MF, Genta RM, Yardley JH, Correa P. Classification and grading of gastritis. The updated Sydney system. International Workshop on the histopathology of gastritis, Houston 1994. Am J Surg Pathol 1996;20:1161–1181.
Correa P, Fontham ET, Bravo JC, Bravo LE, Ruiz B, Zarama G, et al. Chemoprevention of gastric dysplasia: randomized trial of antioxidant supplements and anti-Helicobacter pylori therapy. J Natl Cancer Inst 2000;92:1881–1888.
Tang XD, Wang P, Liu BY, Zi MJ. Development and analysis of patient reported outcome instrument for chronic gastrointestinal disease. J Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2009;50:27–29.
Wang P, Tang XD, Liu BY, Zi MJ. Development of a patientreported outcome instrument for chronic gastrointestinal diseases: item selection. J Chin Intergr Med (Chin) 2012;10:1092–1098.
Sun LM, Si JM, Chen SJ, Liu WL, Zhao L, Wang LJ. The establishment and clinical applicance of technique of mucosa marking targeting biopsy. Heptogastroenterology 2009;56:59–62.
Schistosomes, liver flukes and Helicobacter pylori. IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risk to Humans. World Health Organization. IARC Monogr Eval Carcinog Risks Hum 1997;61:177.
Hu YP, Cui L, Yang JJ, Liu T, Wang XF, Liu FG. Diagnosis and clinical significance of gastric tunica mucosa epithelial reactive hyperplasia and dysplasia. Clin Misdiagnosis Mistherapy (Chin) 2012; 25:65–68.
Dong B, Xie YQ, Chen K, Wang T, Tang W, You WC, et al. Differences in biological features of gastric dysplasia, indefinite dysplasia, reactive hyperplasia and discriminant analysis of these lesions. World J Gastroenterol 2005;11:3595–600.
Li P, Zhang ST. Criteria of endoscopic diagnosis of chronic gastritis and Its appraisal. Chin J Clin Gastroenterol (Chin) 2006;18:136–138.
Yang XY, Wu YL, Zhu YH, Tang ZP, Zhu SL, Feng L, et al. Gastric mucosal low-grade intraepithelial neoplasia treated with Weifuchun combined with folic acid and its outcome. J Intern Med Concepts Pract (Chin) 2013;8:24–28.
Yuan WQ, Wang L, Wang XH. Research progress on clinical pathology of gastric intraepithelial neoplasia. Chin J Coal Industry Med (Chin) 2004;7:490–491.
Xu CP, Liu WW. Follow-up study on chronic gastritis, intestinal metaplasia and dysplasia. Chin J Dig (Chin) 1984:10.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the 11th Five-Year Plan from Ministry of Sciences and Technology of China (No. 2006BAI04A08)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, Xd., Zhou, Ly., Zhang, St. et al. Randomized double-blind clinical trial of Moluodan (摩罗丹) for the treatment of chronic atrophic gastritis with dysplasia. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 22, 9–18 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-015-2114-5
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-015-2114-5